This pipeline computes the correlation between cancer subtypes identified by different molecular patterns and selected clinical features.
Testing the association between subtypes identified by 4 different clustering approaches and 4 clinical features across 16 patients, no significant finding detected with P value < 0.05.
-
CNMF clustering analysis on array-based mRNA expression data identified 2 subtypes that do not correlate to any clinical features.
-
Consensus hierarchical clustering analysis on array-based mRNA expression data identified 3 subtypes that do not correlate to any clinical features.
-
CNMF clustering analysis on sequencing-based miR expression data identified 2 subtypes that do not correlate to any clinical features.
-
Consensus hierarchical clustering analysis on sequencing-based miR expression data identified 2 subtypes that do not correlate to any clinical features.
Table 1. Get Full Table Overview of the association between subtypes identified by 4 different clustering approaches and 4 clinical features. Shown in the table are P values from statistical tests. Thresholded by P value < 0.05, no significant finding detected.
|
Clinical Features |
Time to Death |
AGE | GENDER |
PATHOLOGY T |
| Statistical Tests | logrank test | t-test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test |
| mRNA CNMF subtypes | 0.666 | 0.182 | 0.585 | 0.0601 |
| mRNA cHierClus subtypes | 0.0699 | 0.948 | 1 | 0.131 |
| MIRseq CNMF subtypes | 0.197 | 0.374 | 0.0885 | 0.0601 |
| MIRseq cHierClus subtypes | 0.0833 | 0.647 | 0.245 | 0.308 |
Table S1. Get Full Table Description of clustering approach #1: 'mRNA CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 7 | 9 |
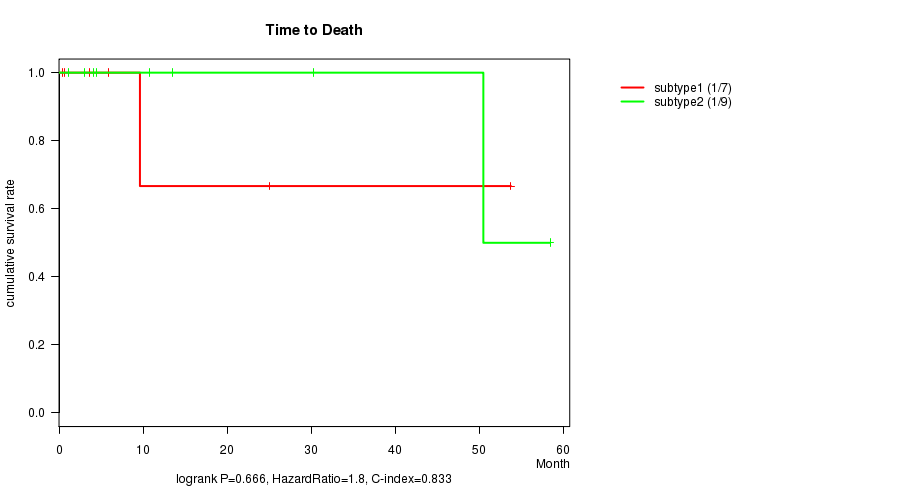
P value = 0.666 (logrank test)
Table S2. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 16 | 2 | 0.5 - 58.5 (7.8) |
| subtype1 | 7 | 1 | 0.5 - 53.8 (5.9) |
| subtype2 | 9 | 1 | 1.1 - 58.5 (10.8) |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
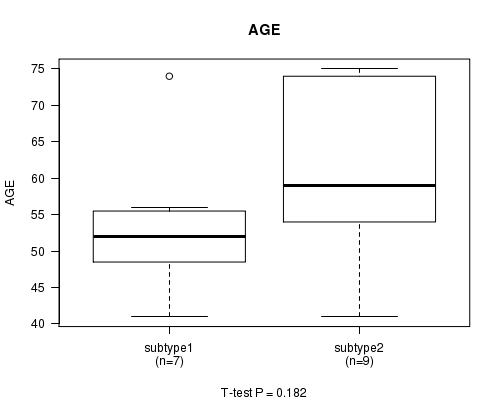
P value = 0.182 (t-test)
Table S3. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 16 | 57.9 (11.5) |
| subtype1 | 7 | 53.6 (10.3) |
| subtype2 | 9 | 61.3 (11.7) |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
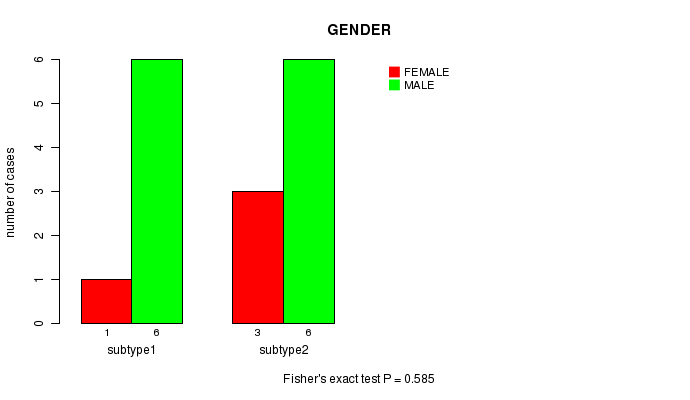
P value = 0.585 (Fisher's exact test)
Table S4. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 12 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 6 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 6 | 3 |
Figure S3. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'GENDER'
P value = 0.0601 (Fisher's exact test)
Table S5. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T'
| nPatients | T1 | T2+T3 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 6 |
| subtype2 | 6 | 3 |
Figure S4. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T'
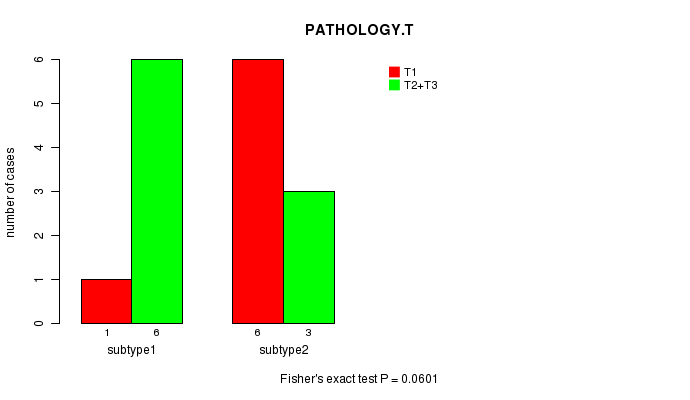
Table S6. Get Full Table Description of clustering approach #2: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 4 | 7 | 5 |
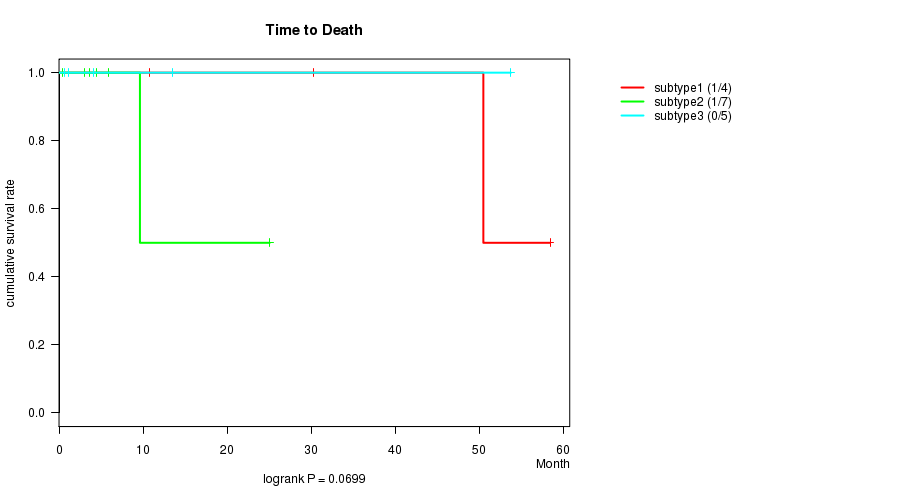
P value = 0.0699 (logrank test)
Table S7. Clustering Approach #2: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 16 | 2 | 0.5 - 58.5 (7.8) |
| subtype1 | 4 | 1 | 10.8 - 58.5 (40.4) |
| subtype2 | 7 | 1 | 0.5 - 25.1 (4.4) |
| subtype3 | 5 | 0 | 0.7 - 53.8 (4.1) |
Figure S5. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
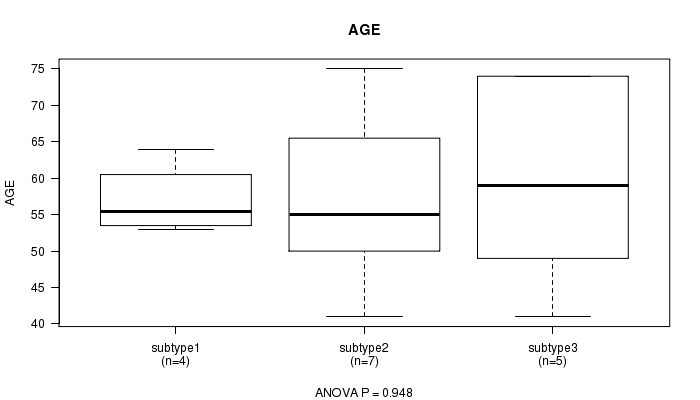
P value = 0.948 (ANOVA)
Table S8. Clustering Approach #2: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 16 | 57.9 (11.5) |
| subtype1 | 4 | 57.0 (5.0) |
| subtype2 | 7 | 57.4 (13.0) |
| subtype3 | 5 | 59.4 (14.8) |
Figure S6. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
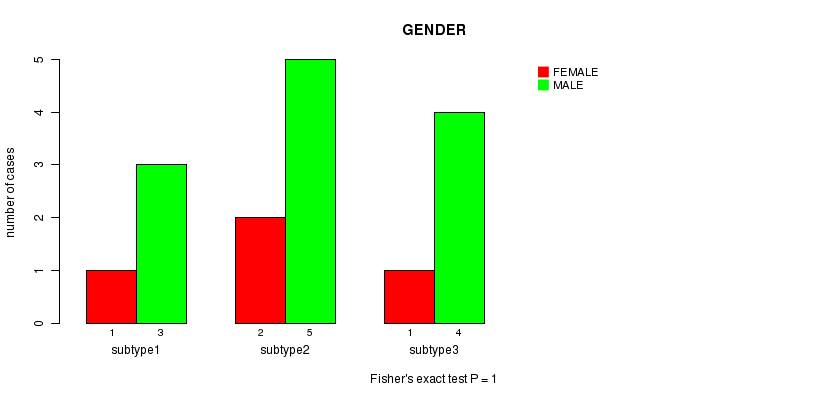
P value = 1 (Fisher's exact test)
Table S9. Clustering Approach #2: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 12 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 5 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 4 | 1 |
Figure S7. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'GENDER'
P value = 0.131 (Fisher's exact test)
Table S10. Clustering Approach #2: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T'
| nPatients | T1 | T2+T3 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 6 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 2 |
Figure S8. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T'
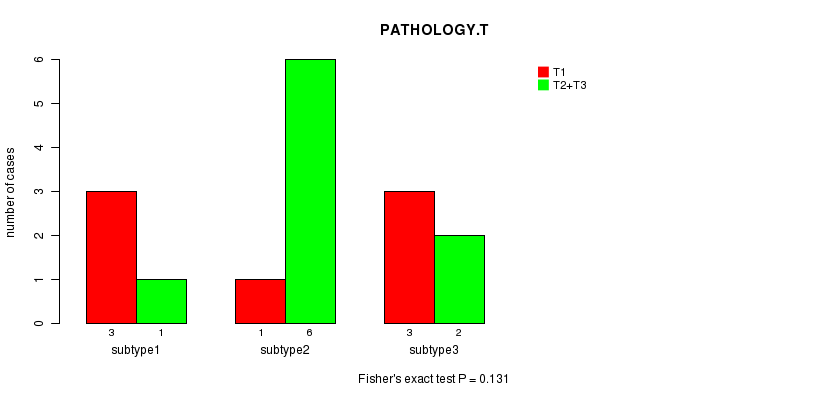
Table S11. Get Full Table Description of clustering approach #3: 'MIRseq CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 7 | 9 |
P value = 0.197 (logrank test)
Table S12. Clustering Approach #3: 'MIRseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 16 | 2 | 0.5 - 58.5 (7.8) |
| subtype1 | 7 | 1 | 0.7 - 30.3 (5.9) |
| subtype2 | 9 | 1 | 0.5 - 58.5 (10.8) |
Figure S9. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'MIRseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
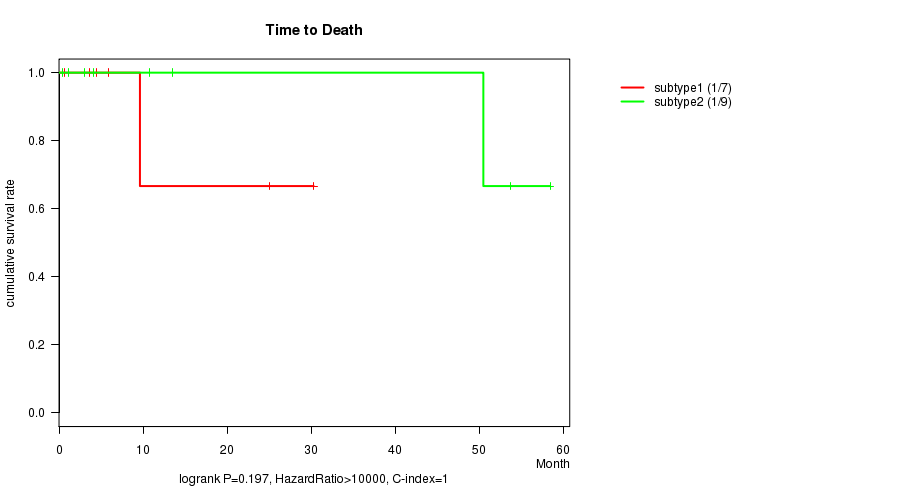
P value = 0.374 (t-test)
Table S13. Clustering Approach #3: 'MIRseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 16 | 57.9 (11.5) |
| subtype1 | 7 | 55.0 (10.4) |
| subtype2 | 9 | 60.2 (12.4) |
Figure S10. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'MIRseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
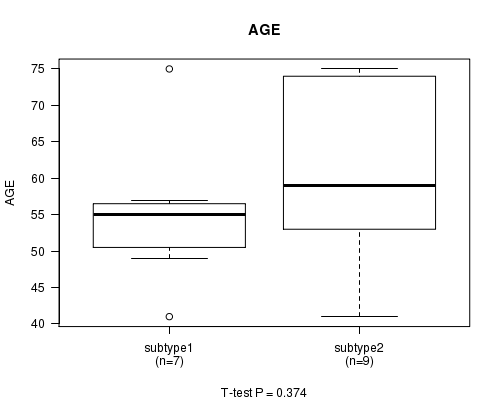
P value = 0.0885 (Fisher's exact test)
Table S14. Clustering Approach #3: 'MIRseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 12 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 7 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 5 | 4 |
Figure S11. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'MIRseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'GENDER'
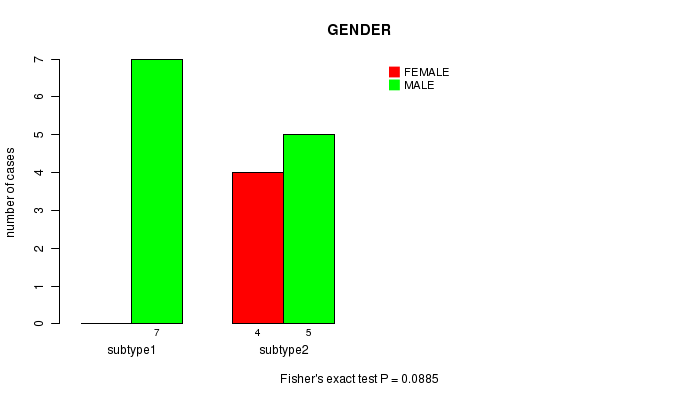
P value = 0.0601 (Fisher's exact test)
Table S15. Clustering Approach #3: 'MIRseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T'
| nPatients | T1 | T2+T3 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 6 |
| subtype2 | 6 | 3 |
Figure S12. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'MIRseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T'
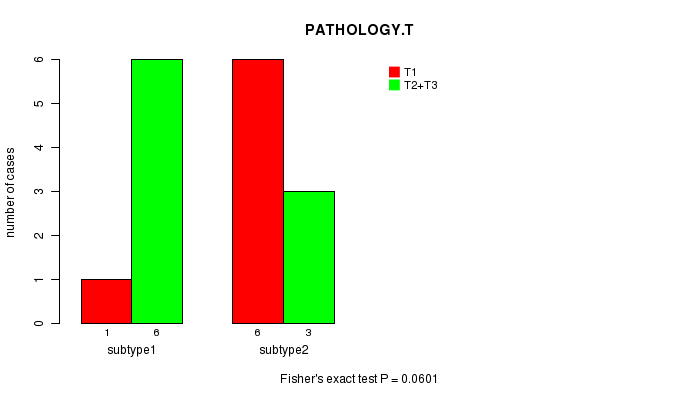
Table S16. Get Full Table Description of clustering approach #4: 'MIRseq cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 5 | 11 |
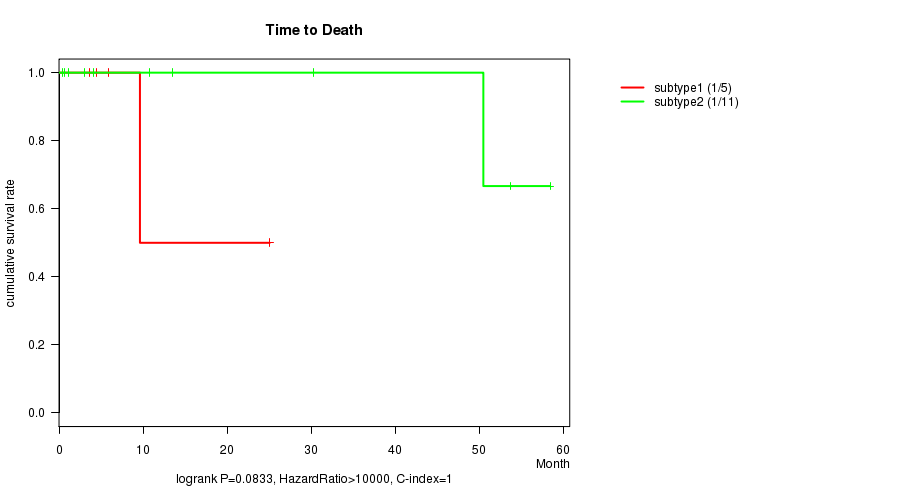
P value = 0.0833 (logrank test)
Table S17. Clustering Approach #4: 'MIRseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 16 | 2 | 0.5 - 58.5 (7.8) |
| subtype1 | 5 | 1 | 3.6 - 25.1 (5.9) |
| subtype2 | 11 | 1 | 0.5 - 58.5 (10.8) |
Figure S13. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'MIRseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
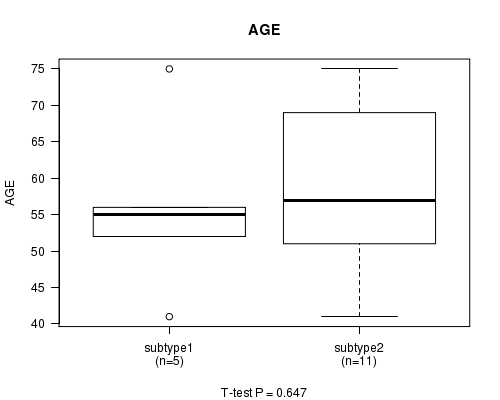
P value = 0.647 (t-test)
Table S18. Clustering Approach #4: 'MIRseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 16 | 57.9 (11.5) |
| subtype1 | 5 | 55.8 (12.3) |
| subtype2 | 11 | 58.9 (11.6) |
Figure S14. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'MIRseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
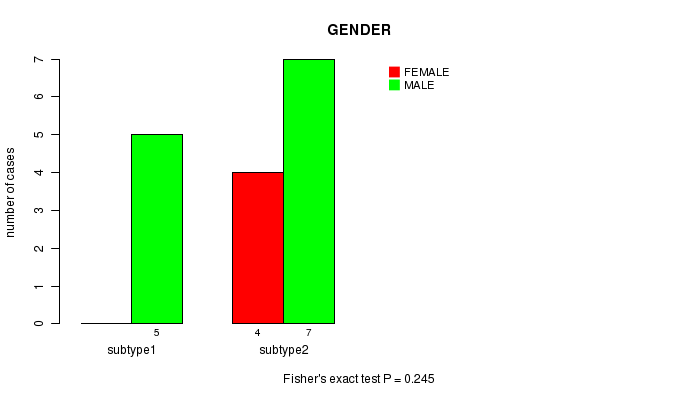
P value = 0.245 (Fisher's exact test)
Table S19. Clustering Approach #4: 'MIRseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 12 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 7 | 4 |
Figure S15. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'MIRseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'GENDER'
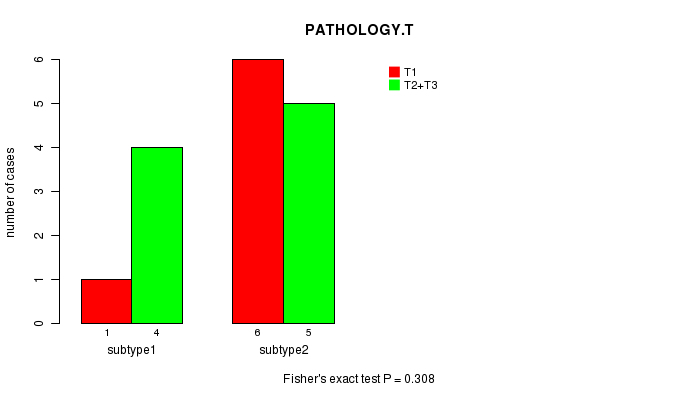
P value = 0.308 (Fisher's exact test)
Table S20. Clustering Approach #4: 'MIRseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T'
| nPatients | T1 | T2+T3 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 6 | 5 |
Figure S16. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'MIRseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T'
-
Cluster data file = KIRP.mergedcluster.txt
-
Clinical data file = KIRP.clin.merged.picked.txt
-
Number of patients = 16
-
Number of clustering approaches = 4
-
Number of selected clinical features = 4
-
Exclude small clusters that include fewer than K patients, K = 3
consensus non-negative matrix factorization clustering approach (Brunet et al. 2004)
Resampling-based clustering method (Monti et al. 2003)
For survival clinical features, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of tumors with and without gene mutations were plotted and the statistical significance P values were estimated by logrank test (Bland and Altman 2004) using the 'survdiff' function in R
For continuous numerical clinical features, two-tailed Student's t test with unequal variance (Lehmann and Romano 2005) was applied to compare the clinical values between two tumor subtypes using 't.test' function in R
For binary clinical features, two-tailed Fisher's exact tests (Fisher 1922) were used to estimate the P values using the 'fisher.test' function in R
For continuous numerical clinical features, one-way analysis of variance (Howell 2002) was applied to compare the clinical values between tumor subtypes using 'anova' function in R
This is an experimental feature. Location of data archives could not be determined.