This pipeline uses various statistical tests to identify miRs whose expression levels correlated to selected clinical features.
Testing the association between 420 genes and 11 clinical features across 521 samples, statistically thresholded by Q value < 0.05, 9 clinical features related to at least one genes.
-
7 genes correlated to 'AGE'.
-
HSA-MIR-432 , HSA-MIR-153-2 , HSA-MIR-141 , HSA-MIR-26A-1 , HSA-MIR-410 , ...
-
35 genes correlated to 'PRIMARY.SITE.OF.DISEASE'.
-
HSA-MIR-10B , HSA-MIR-1201 , HSA-MIR-30C-2 , HSA-MIR-1259 , HSA-MIR-20A , ...
-
1 gene correlated to 'GENDER'.
-
HSA-MIR-651
-
45 genes correlated to 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'.
-
HSA-MIR-10B , HSA-MIR-92A-1 , HSA-MIR-1201 , HSA-MIR-20A , HSA-MIR-30C-2 , ...
-
4 genes correlated to 'PATHOLOGY.T'.
-
HSA-MIR-144 , HSA-MIR-206 , HSA-MIR-502 , HSA-MIR-501
-
2 genes correlated to 'PATHOLOGY.N'.
-
HSA-MIR-146A , HSA-MIR-625
-
31 genes correlated to 'PATHOLOGICSPREAD(M)'.
-
HSA-LET-7F-2 , HSA-MIR-106A , HSA-MIR-628 , HSA-MIR-142 , HSA-MIR-616 , ...
-
2 genes correlated to 'TUMOR.STAGE'.
-
HSA-MIR-146A , HSA-MIR-625
-
41 genes correlated to 'NEOADJUVANT.THERAPY'.
-
HSA-MIR-106A , HSA-MIR-103-2 , HSA-MIR-26A-1 , HSA-LET-7F-2 , HSA-MIR-331 , ...
-
No genes correlated to 'Time to Death', and 'RADIATIONS.RADIATION.REGIMENINDICATION'.
Complete statistical result table is provided in Supplement Table 1
Table 1. Get Full Table This table shows the clinical features, statistical methods used, and the number of genes that are significantly associated with each clinical feature at Q value < 0.05.
| Clinical feature | Statistical test | Significant genes | Associated with | Associated with | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to Death | Cox regression test | N=0 | ||||
| AGE | Spearman correlation test | N=7 | older | N=5 | younger | N=2 |
| PRIMARY SITE OF DISEASE | t test | N=35 | rectum | N=29 | colon | N=6 |
| GENDER | t test | N=1 | male | N=0 | female | N=1 |
| HISTOLOGICAL TYPE | ANOVA test | N=45 | ||||
| PATHOLOGY T | Spearman correlation test | N=4 | higher pT | N=0 | lower pT | N=4 |
| PATHOLOGY N | Spearman correlation test | N=2 | higher pN | N=0 | lower pN | N=2 |
| PATHOLOGICSPREAD(M) | ANOVA test | N=31 | ||||
| TUMOR STAGE | Spearman correlation test | N=2 | higher stage | N=0 | lower stage | N=2 |
| RADIATIONS RADIATION REGIMENINDICATION | t test | N=0 | ||||
| NEOADJUVANT THERAPY | t test | N=41 | yes | N=32 | no | N=9 |
Table S1. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'Time to Death'
| Time to Death | Duration (Months) | 0.1-135.5 (median=8) |
| censored | N = 327 | |
| death | N = 59 | |
| Significant markers | N = 0 |
Table S2. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'AGE'
| AGE | Mean (SD) | 66.82 (13) |
| Significant markers | N = 7 | |
| pos. correlated | 5 | |
| neg. correlated | 2 |
Table S3. Get Full Table List of 7 genes significantly correlated to 'AGE' by Spearman correlation test
| SpearmanCorr | corrP | Q | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-MIR-432 | -0.2249 | 2.511e-07 | 0.000105 |
| HSA-MIR-153-2 | 0.2109 | 1.19e-06 | 0.000499 |
| HSA-MIR-141 | 0.2021 | 3.318e-06 | 0.00139 |
| HSA-MIR-26A-1 | 0.1904 | 1.216e-05 | 0.00507 |
| HSA-MIR-410 | -0.1756 | 6.142e-05 | 0.0256 |
| HSA-MIR-616 | 0.1743 | 7.021e-05 | 0.0291 |
| HSA-MIR-33B | 0.1706 | 9.244e-05 | 0.0383 |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of HSA-MIR-432 to 'AGE'. P value = 2.51e-07 with Spearman correlation analysis. The straight line presents the best linear regression.
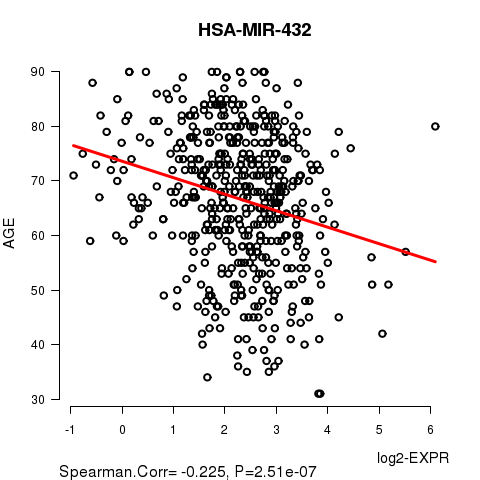
Table S4. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'PRIMARY.SITE.OF.DISEASE'
| PRIMARY.SITE.OF.DISEASE | Labels | N |
| COLON | 377 | |
| RECTUM | 140 | |
| Significant markers | N = 35 | |
| Higher in RECTUM | 29 | |
| Higher in COLON | 6 |
Table S5. Get Full Table List of top 10 genes differentially expressed by 'PRIMARY.SITE.OF.DISEASE'
| T(pos if higher in 'RECTUM') | ttestP | Q | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-MIR-10B | -9.25 | 1.427e-17 | 6e-15 | 0.7571 |
| HSA-MIR-1201 | 8.31 | 3.75e-15 | 1.57e-12 | 0.7157 |
| HSA-MIR-30C-2 | 7.78 | 1.331e-13 | 5.56e-11 | 0.6956 |
| HSA-MIR-1259 | 7.6 | 3.24e-13 | 1.35e-10 | 0.6798 |
| HSA-MIR-20A | 6.73 | 9.408e-11 | 3.91e-08 | 0.6793 |
| HSA-MIR-1977 | 6.45 | 4.377e-10 | 1.82e-07 | 0.6582 |
| HSA-MIR-425 | 6.46 | 5.171e-10 | 2.14e-07 | 0.6754 |
| HSA-MIR-191 | 6.03 | 4.834e-09 | 2e-06 | 0.6589 |
| HSA-MIR-224 | 5.98 | 6.626e-09 | 2.73e-06 | 0.6517 |
| HSA-LET-7G | 5.86 | 1.513e-08 | 6.22e-06 | 0.6572 |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of HSA-MIR-10B to 'PRIMARY.SITE.OF.DISEASE'. P value = 1.43e-17 with T-test analysis.
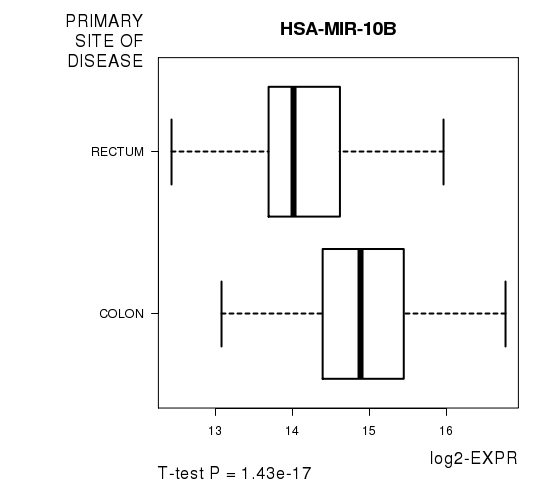
Table S6. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'GENDER'
| GENDER | Labels | N |
| FEMALE | 249 | |
| MALE | 272 | |
| Significant markers | N = 1 | |
| Higher in MALE | 0 | |
| Higher in FEMALE | 1 |
Table S7. Get Full Table List of one gene differentially expressed by 'GENDER'
| T(pos if higher in 'MALE') | ttestP | Q | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-MIR-651 | -3.99 | 7.466e-05 | 0.0314 | 0.6032 |
Figure S3. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of HSA-MIR-651 to 'GENDER'. P value = 7.47e-05 with T-test analysis.
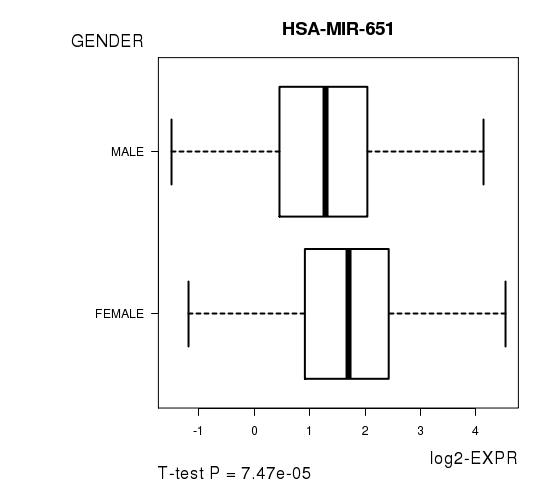
Table S8. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE | Labels | N |
| COLON ADENOCARCINOMA | 327 | |
| COLON MUCINOUS ADENOCARCINOMA | 48 | |
| RECTAL ADENOCARCINOMA | 127 | |
| RECTAL MUCINOUS ADENOCARCINOMA | 10 | |
| Significant markers | N = 45 |
Table S9. Get Full Table List of top 10 genes differentially expressed by 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| ANOVA_P | Q | |
|---|---|---|
| HSA-MIR-10B | 1.408e-18 | 5.91e-16 |
| HSA-MIR-92A-1 | 1.435e-12 | 6.01e-10 |
| HSA-MIR-1201 | 3.035e-12 | 1.27e-09 |
| HSA-MIR-20A | 4.542e-12 | 1.89e-09 |
| HSA-MIR-30C-2 | 2.873e-11 | 1.2e-08 |
| HSA-MIR-1259 | 3.785e-10 | 1.57e-07 |
| HSA-MIR-224 | 6.751e-10 | 2.79e-07 |
| HSA-MIR-181D | 1.014e-09 | 4.19e-07 |
| HSA-LET-7G | 1.215e-09 | 5.01e-07 |
| HSA-MIR-425 | 1.609e-09 | 6.61e-07 |
Figure S4. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of HSA-MIR-10B to 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'. P value = 1.41e-18 with ANOVA analysis.
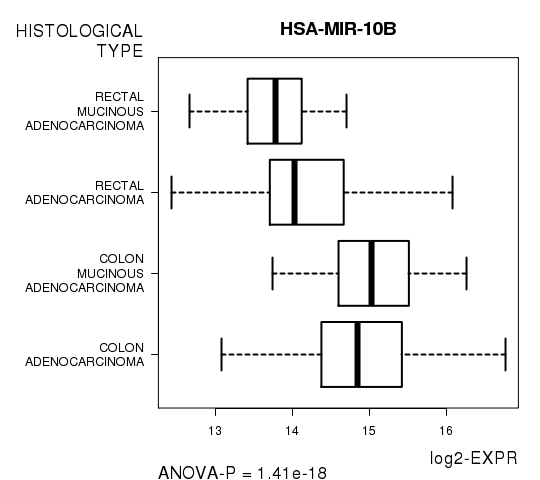
Table S10. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'PATHOLOGY.T'
| PATHOLOGY.T | Mean (SD) | 2.84 (0.63) |
| N | ||
| T0 | 1 | |
| T1 | 18 | |
| T2 | 90 | |
| T3 | 361 | |
| T4 | 47 | |
| Significant markers | N = 4 | |
| pos. correlated | 0 | |
| neg. correlated | 4 |
Table S11. Get Full Table List of 4 genes significantly correlated to 'PATHOLOGY.T' by Spearman correlation test
| SpearmanCorr | corrP | Q | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-MIR-144 | -0.1775 | 4.933e-05 | 0.0207 |
| HSA-MIR-206 | -0.2221 | 7.771e-05 | 0.0326 |
| HSA-MIR-502 | -0.1697 | 0.0001053 | 0.044 |
| HSA-MIR-501 | -0.1692 | 0.0001104 | 0.046 |
Figure S5. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of HSA-MIR-144 to 'PATHOLOGY.T'. P value = 4.93e-05 with Spearman correlation analysis.
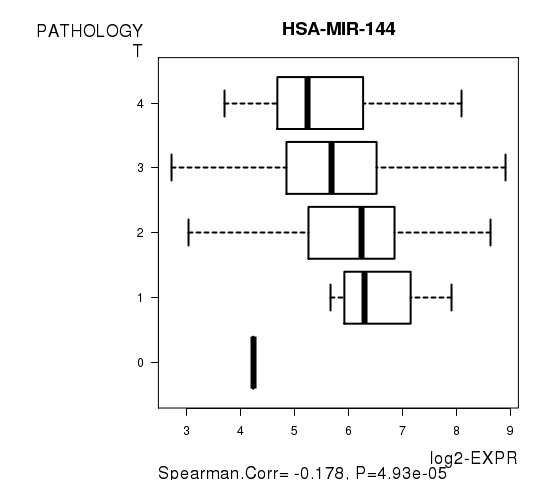
Table S12. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'PATHOLOGY.N'
| PATHOLOGY.N | Mean (SD) | 0.61 (0.78) |
| N | ||
| N0 | 296 | |
| N1 | 127 | |
| N2 | 94 | |
| Significant markers | N = 2 | |
| pos. correlated | 0 | |
| neg. correlated | 2 |
Table S13. Get Full Table List of 2 genes significantly correlated to 'PATHOLOGY.N' by Spearman correlation test
| SpearmanCorr | corrP | Q | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-MIR-146A | -0.1814 | 3.327e-05 | 0.014 |
| HSA-MIR-625 | -0.1777 | 4.832e-05 | 0.0202 |
Figure S6. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of HSA-MIR-146A to 'PATHOLOGY.N'. P value = 3.33e-05 with Spearman correlation analysis.
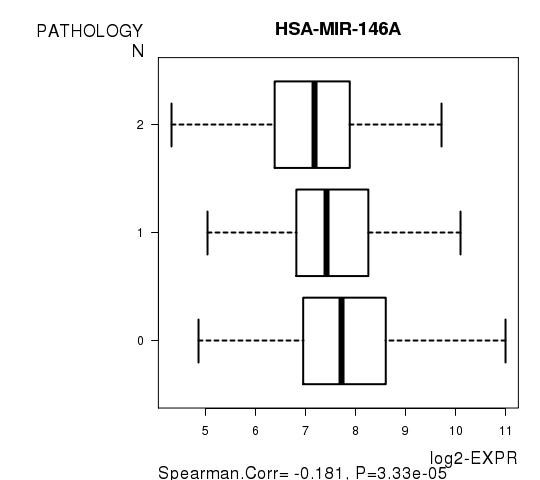
Table S14. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'PATHOLOGICSPREAD(M)'
| PATHOLOGICSPREAD(M) | Labels | N |
| M0 | 393 | |
| M1 | 67 | |
| M1A | 9 | |
| M1B | 1 | |
| MX | 42 | |
| Significant markers | N = 31 |
Table S15. Get Full Table List of top 10 genes differentially expressed by 'PATHOLOGICSPREAD(M)'
| ANOVA_P | Q | |
|---|---|---|
| HSA-LET-7F-2 | 2.56e-08 | 1.08e-05 |
| HSA-MIR-106A | 4.642e-08 | 1.95e-05 |
| HSA-MIR-628 | 9.245e-08 | 3.86e-05 |
| HSA-MIR-142 | 4.735e-07 | 0.000197 |
| HSA-MIR-616 | 1.158e-06 | 0.000482 |
| HSA-MIR-199A-2 | 1.516e-06 | 0.000629 |
| HSA-MIR-1271 | 1.535e-06 | 0.000636 |
| HSA-MIR-199B | 1.564e-06 | 0.000646 |
| HSA-MIR-140 | 2.194e-06 | 0.000904 |
| HSA-MIR-199A-1 | 2.266e-06 | 0.000931 |
Figure S7. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of HSA-LET-7F-2 to 'PATHOLOGICSPREAD(M)'. P value = 2.56e-08 with ANOVA analysis.
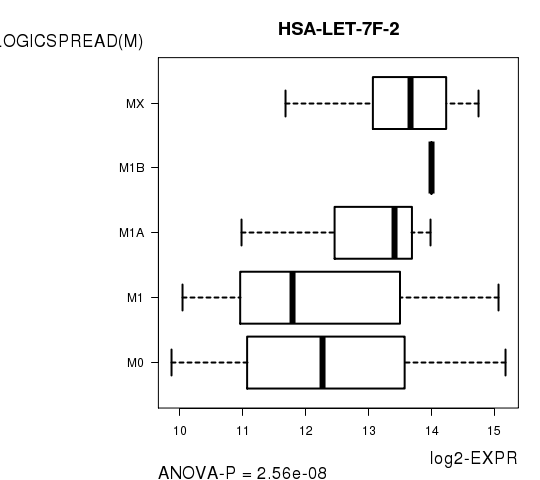
Table S16. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'TUMOR.STAGE'
| TUMOR.STAGE | Mean (SD) | 2.42 (0.95) |
| N | ||
| Stage 1 | 90 | |
| Stage 2 | 188 | |
| Stage 3 | 149 | |
| Stage 4 | 75 | |
| Significant markers | N = 2 | |
| pos. correlated | 0 | |
| neg. correlated | 2 |
Table S17. Get Full Table List of 2 genes significantly correlated to 'TUMOR.STAGE' by Spearman correlation test
| SpearmanCorr | corrP | Q | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-MIR-146A | -0.2106 | 1.934e-06 | 0.000812 |
| HSA-MIR-625 | -0.2004 | 6.05e-06 | 0.00253 |
Figure S8. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of HSA-MIR-146A to 'TUMOR.STAGE'. P value = 1.93e-06 with Spearman correlation analysis.
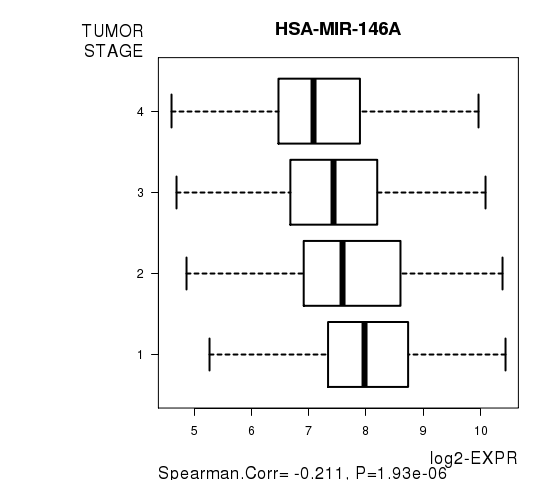
No gene related to 'RADIATIONS.RADIATION.REGIMENINDICATION'.
Table S18. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'RADIATIONS.RADIATION.REGIMENINDICATION'
| RADIATIONS.RADIATION.REGIMENINDICATION | Labels | N |
| NO | 8 | |
| YES | 513 | |
| Significant markers | N = 0 |
Table S19. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'NEOADJUVANT.THERAPY'
| NEOADJUVANT.THERAPY | Labels | N |
| NO | 71 | |
| YES | 450 | |
| Significant markers | N = 41 | |
| Higher in YES | 32 | |
| Higher in NO | 9 |
Table S20. Get Full Table List of top 10 genes differentially expressed by 'NEOADJUVANT.THERAPY'
| T(pos if higher in 'YES') | ttestP | Q | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-MIR-106A | 7.08 | 1.012e-10 | 4.25e-08 | 0.699 |
| HSA-MIR-103-2 | 6.58 | 1.506e-09 | 6.31e-07 | 0.7083 |
| HSA-MIR-26A-1 | 6.36 | 5.445e-09 | 2.28e-06 | 0.7011 |
| HSA-LET-7F-2 | -6.06 | 1.962e-08 | 8.18e-06 | 0.6702 |
| HSA-MIR-331 | 5.91 | 3.805e-08 | 1.58e-05 | 0.685 |
| HSA-MIR-1826 | 5.95 | 3.95e-08 | 1.64e-05 | 0.7086 |
| HSA-MIR-23A | 5.43 | 3.616e-07 | 0.00015 | 0.6815 |
| HSA-MIR-23B | 5.26 | 7.385e-07 | 0.000305 | 0.6632 |
| HSA-MIR-7-1 | 5.2 | 9.846e-07 | 0.000406 | 0.6741 |
| HSA-LET-7D | 5.19 | 1.01e-06 | 0.000415 | 0.6584 |
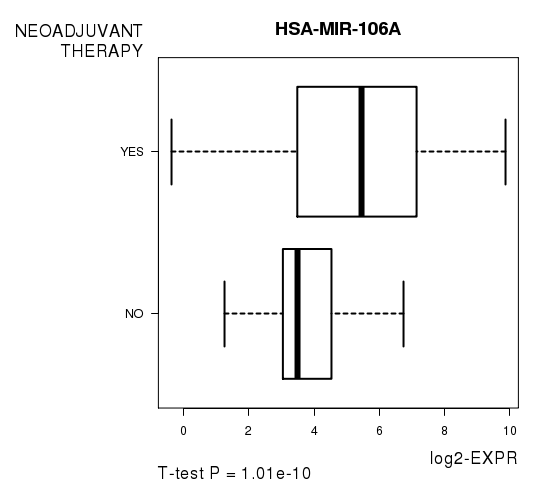
Figure S9. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of HSA-MIR-106A to 'NEOADJUVANT.THERAPY'. P value = 1.01e-10 with T-test analysis.
-
Expresson data file = COADREAD.miRseq_RPKM_log2.txt
-
Clinical data file = COADREAD.clin.merged.picked.txt
-
Number of patients = 521
-
Number of genes = 420
-
Number of clinical features = 11
For survival clinical features, Wald's test in univariate Cox regression analysis with proportional hazards model (Andersen and Gill 1982) was used to estimate the P values using the 'coxph' function in R. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were plot using the four quartile subgroups of patients based on expression levels
For continuous numerical clinical features, Spearman's rank correlation coefficients (Spearman 1904) and two-tailed P values were estimated using 'cor.test' function in R
For two-class clinical features, two-tailed Student's t test with unequal variance (Lehmann and Romano 2005) was applied to compare the log2-expression levels between the two clinical classes using 't.test' function in R
For multi-class clinical features (ordinal or nominal), one-way analysis of variance (Howell 2002) was applied to compare the log2-expression levels between different clinical classes using 'anova' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.
This is an experimental feature. The full results of the analysis summarized in this report can be downloaded from the TCGA Data Coordination Center.