(primary solid tumor cohort)
This pipeline computes the correlation between significantly recurrent gene mutations and selected clinical features.
Testing the association between mutation status of 52 genes and 4 clinical features across 507 patients, one significant finding detected with Q value < 0.25.
-
MAP3K1 mutation correlated to 'AGE'.
Table 1. Get Full Table Overview of the association between mutation status of 52 genes and 4 clinical features. Shown in the table are P values (Q values). Thresholded by Q value < 0.25, one significant finding detected.
|
Clinical Features |
Time to Death |
AGE | GENDER |
RADIATIONS RADIATION REGIMENINDICATION |
||
| nMutated (%) | nWild-Type | logrank test | t-test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | |
| MAP3K1 | 38 (7%) | 469 |
0.916 (1.00) |
0.000845 (0.176) |
1 (1.00) |
0.346 (1.00) |
| CDH1 | 33 (7%) | 474 |
0.909 (1.00) |
0.0619 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.84 (1.00) |
| TP53 | 184 (36%) | 323 |
0.966 (1.00) |
0.186 (1.00) |
0.0914 (1.00) |
0.47 (1.00) |
| MAP2K4 | 20 (4%) | 487 |
0.0878 (1.00) |
0.134 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.611 (1.00) |
| PIK3CA | 178 (35%) | 329 |
0.455 (1.00) |
0.0485 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| GATA3 | 54 (11%) | 453 |
0.812 (1.00) |
0.00918 (1.00) |
0.493 (1.00) |
0.147 (1.00) |
| RUNX1 | 18 (4%) | 489 |
0.236 (1.00) |
0.481 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.422 (1.00) |
| PTEN | 17 (3%) | 490 |
0.896 (1.00) |
0.579 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| MLL3 | 36 (7%) | 471 |
0.473 (1.00) |
0.0145 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.563 (1.00) |
| TBX3 | 13 (3%) | 494 |
0.235 (1.00) |
0.0275 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| PIK3R1 | 14 (3%) | 493 |
0.213 (1.00) |
0.88 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| CBFB | 8 (2%) | 499 |
0.632 (1.00) |
0.367 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| AKT1 | 12 (2%) | 495 |
0.223 (1.00) |
0.548 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.194 (1.00) |
| TBL1XR1 | 8 (2%) | 499 |
0.811 (1.00) |
0.0425 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.69 (1.00) |
| CTCF | 13 (3%) | 494 |
0.149 (1.00) |
0.365 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| NCOR1 | 17 (3%) | 490 |
0.624 (1.00) |
0.53 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.58 (1.00) |
| FOXA1 | 8 (2%) | 499 |
0.0014 (0.29) |
0.0133 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| AFF2 | 13 (3%) | 494 |
0.887 (1.00) |
0.0186 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.357 (1.00) |
| VASN | 6 (1%) | 501 |
0.13 (1.00) |
0.858 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.668 (1.00) |
| ZFP36L1 | 7 (1%) | 500 |
0.951 (1.00) |
0.0859 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.198 (1.00) |
| RB1 | 9 (2%) | 498 |
0.69 (1.00) |
0.305 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.455 (1.00) |
| C1ORF65 | 7 (1%) | 500 |
0.254 (1.00) |
0.656 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.0935 (1.00) |
| CDKN1B | 5 (1%) | 502 |
0.469 (1.00) |
0.982 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| GPS2 | 6 (1%) | 501 |
0.242 (1.00) |
0.986 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.668 (1.00) |
| NEK5 | 8 (2%) | 499 |
0.672 (1.00) |
0.106 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.456 (1.00) |
| MYB | 8 (2%) | 499 |
0.219 (1.00) |
0.255 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.224 (1.00) |
| OR5I1 | 5 (1%) | 502 |
0.686 (1.00) |
0.213 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.13 (1.00) |
| KRAS | 4 (1%) | 503 |
0.532 (1.00) |
0.209 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.579 (1.00) |
| UBC | 7 (1%) | 500 |
0.292 (1.00) |
0.548 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| DCAF4L2 | 7 (1%) | 500 |
0.595 (1.00) |
0.625 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| HLA-DRB1 | 4 (1%) | 503 |
0.551 (1.00) |
0.616 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.579 (1.00) |
| SF3B1 | 10 (2%) | 497 |
0.386 (1.00) |
0.378 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| SYCE1L | 4 (1%) | 503 |
0.278 (1.00) |
0.717 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| AVPI1 | 4 (1%) | 503 |
0.672 (1.00) |
0.5 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| ATP10B | 12 (2%) | 495 |
0.686 (1.00) |
0.5 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| PIWIL1 | 8 (2%) | 499 |
0.189 (1.00) |
0.718 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| CCT6B | 6 (1%) | 501 |
0.167 (1.00) |
0.565 (1.00) |
0.0693 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| PPEF1 | 7 (1%) | 500 |
0.7 (1.00) |
0.533 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.68 (1.00) |
| C12ORF36 | 4 (1%) | 503 |
0.357 (1.00) |
0.157 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| SHD | 6 (1%) | 501 |
0.334 (1.00) |
0.603 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| CBLB | 9 (2%) | 498 |
0.367 (1.00) |
0.556 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| ZNF268 | 4 (1%) | 503 |
0.638 (1.00) |
0.726 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.303 (1.00) |
| HIST1H2BC | 4 (1%) | 503 |
0.556 (1.00) |
0.657 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| C8ORF31 | 4 (1%) | 503 |
0.6 (1.00) |
0.803 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.303 (1.00) |
| FAM47C | 10 (2%) | 497 |
0.248 (1.00) |
0.103 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.735 (1.00) |
| DALRD3 | 6 (1%) | 501 |
0.613 (1.00) |
0.0641 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.353 (1.00) |
| ITPKB | 8 (2%) | 499 |
0.381 (1.00) |
0.0126 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.456 (1.00) |
| C4ORF40 | 4 (1%) | 503 |
0.33 (1.00) |
0.486 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.579 (1.00) |
| CD5L | 5 (1%) | 502 |
0.895 (1.00) |
0.846 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.33 (1.00) |
| ATN1 | 8 (2%) | 499 |
0.235 (1.00) |
0.72 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.456 (1.00) |
| KCNT2 | 9 (2%) | 498 |
0.717 (1.00) |
0.251 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.455 (1.00) |
| ATP1A4 | 9 (2%) | 498 |
0.059 (1.00) |
0.482 (1.00) |
0.102 (1.00) |
0.123 (1.00) |
P value = 0.000845 (t-test), Q value = 0.18
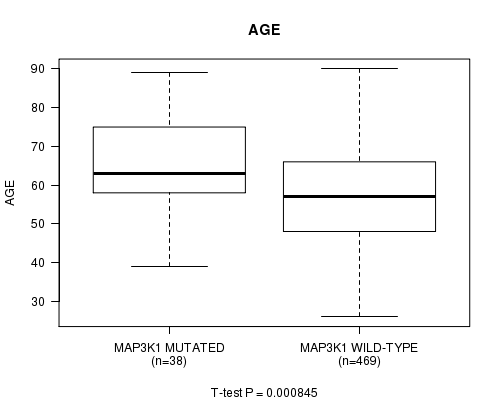
Table S1. Gene #6: 'MAP3K1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 507 | 57.8 (13.1) |
| MAP3K1 MUTATED | 38 | 64.7 (12.3) |
| MAP3K1 WILD-TYPE | 469 | 57.2 (13.1) |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image Gene #6: 'MAP3K1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
-
Mutation data file = BRCA-TP.mutsig.cluster.txt
-
Clinical data file = BRCA-TP.clin.merged.picked.txt
-
Number of patients = 507
-
Number of significantly mutated genes = 52
-
Number of selected clinical features = 4
-
Exclude genes that fewer than K tumors have mutations, K = 3
For survival clinical features, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of tumors with and without gene mutations were plotted and the statistical significance P values were estimated by logrank test (Bland and Altman 2004) using the 'survdiff' function in R
For continuous numerical clinical features, two-tailed Student's t test with unequal variance (Lehmann and Romano 2005) was applied to compare the clinical values between tumors with and without gene mutations using 't.test' function in R
For binary or multi-class clinical features (nominal or ordinal), two-tailed Fisher's exact tests (Fisher 1922) were used to estimate the P values using the 'fisher.test' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.
This is an experimental feature. The full results of the analysis summarized in this report can be downloaded from the TCGA Data Coordination Center.