This pipeline computes the correlation between significantly recurrent gene mutations and selected clinical features.
Testing the association between mutation status of 28 genes and 8 clinical features across 293 patients, 2 significant findings detected with Q value < 0.25.
-
BAP1 mutation correlated to 'TUMOR.STAGE'.
-
TP53 mutation correlated to 'Time to Death'.
Table 1. Get Full Table Overview of the association between mutation status of 28 genes and 8 clinical features. Shown in the table are P values (Q values). Thresholded by Q value < 0.25, 2 significant findings detected.
|
Clinical Features |
Time to Death |
AGE | GENDER |
KARNOFSKY PERFORMANCE SCORE |
PATHOLOGY T |
PATHOLOGY N |
PATHOLOGICSPREAD(M) |
TUMOR STAGE |
||
| nMutated (%) | nWild-Type | logrank test | t-test | Fisher's exact test | t-test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | |
| BAP1 | 27 (9%) | 266 |
0.0136 (1.00) |
0.742 (1.00) |
0.00238 (0.461) |
0.00295 (0.568) |
0.627 (1.00) |
0.00411 (0.789) |
0.000388 (0.0764) |
|
| TP53 | 6 (2%) | 287 |
0.000354 (0.07) |
0.259 (1.00) |
0.188 (1.00) |
0.0158 (1.00) |
0.271 (1.00) |
0.579 (1.00) |
0.0249 (1.00) |
|
| VHL | 138 (47%) | 155 |
0.668 (1.00) |
0.0301 (1.00) |
0.269 (1.00) |
0.359 (1.00) |
0.0815 (1.00) |
0.756 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.169 (1.00) |
| SV2C | 3 (1%) | 290 |
0.731 (1.00) |
0.0205 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| PBRM1 | 107 (37%) | 186 |
0.533 (1.00) |
0.813 (1.00) |
0.204 (1.00) |
0.429 (1.00) |
0.823 (1.00) |
0.751 (1.00) |
0.593 (1.00) |
0.872 (1.00) |
| SETD2 | 34 (12%) | 259 |
0.762 (1.00) |
0.0994 (1.00) |
0.181 (1.00) |
0.137 (1.00) |
0.61 (1.00) |
0.101 (1.00) |
0.0865 (1.00) |
|
| KDM5C | 18 (6%) | 275 |
0.0803 (1.00) |
0.206 (1.00) |
0.00486 (0.928) |
0.622 (1.00) |
0.516 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.856 (1.00) |
|
| MTOR | 24 (8%) | 269 |
0.123 (1.00) |
0.203 (1.00) |
0.119 (1.00) |
0.298 (1.00) |
0.0602 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.346 (1.00) |
|
| PTEN | 9 (3%) | 284 |
0.769 (1.00) |
0.219 (1.00) |
0.503 (1.00) |
0.347 (1.00) |
0.0286 (1.00) |
0.613 (1.00) |
0.0971 (1.00) |
|
| EBPL | 6 (2%) | 287 |
0.48 (1.00) |
0.527 (1.00) |
0.00161 (0.316) |
0.117 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.0646 (1.00) |
|
| PIK3CA | 10 (3%) | 283 |
0.253 (1.00) |
0.808 (1.00) |
0.743 (1.00) |
0.342 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.336 (1.00) |
|
| TSPAN19 | 4 (1%) | 289 |
0.319 (1.00) |
0.467 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.458 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.437 (1.00) |
0.223 (1.00) |
|
| NBPF10 | 19 (6%) | 274 |
0.173 (1.00) |
0.305 (1.00) |
0.133 (1.00) |
0.147 (1.00) |
0.113 (1.00) |
0.0274 (1.00) |
0.115 (1.00) |
|
| TOR1A | 3 (1%) | 290 |
0.0532 (1.00) |
0.704 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.0753 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| MUC4 | 41 (14%) | 252 |
0.454 (1.00) |
0.247 (1.00) |
0.597 (1.00) |
0.00706 (1.00) |
0.217 (1.00) |
0.0431 (1.00) |
0.0021 (0.409) |
|
| UQCRFS1 | 3 (1%) | 290 |
0.321 (1.00) |
0.518 (1.00) |
0.278 (1.00) |
0.0452 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.0554 (1.00) |
|
| WDR52 | 9 (3%) | 284 |
0.967 (1.00) |
0.395 (1.00) |
0.724 (1.00) |
0.647 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.342 (1.00) |
0.842 (1.00) |
|
| BAGE2 | 4 (1%) | 289 |
0.961 (1.00) |
0.667 (1.00) |
0.612 (1.00) |
0.796 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.589 (1.00) |
|
| CNTNAP4 | 9 (3%) | 284 |
0.485 (1.00) |
0.5 (1.00) |
0.724 (1.00) |
0.51 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.513 (1.00) |
|
| CR1 | 10 (3%) | 283 |
0.594 (1.00) |
0.711 (1.00) |
0.743 (1.00) |
0.902 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.628 (1.00) |
0.777 (1.00) |
|
| STAG2 | 9 (3%) | 284 |
0.971 (1.00) |
0.0169 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.112 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.161 (1.00) |
|
| MSN | 4 (1%) | 289 |
0.63 (1.00) |
0.578 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.19 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.464 (1.00) |
|
| ABCB1 | 8 (3%) | 285 |
0.116 (1.00) |
0.582 (1.00) |
0.718 (1.00) |
0.882 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.603 (1.00) |
0.784 (1.00) |
|
| ADCY8 | 5 (2%) | 288 |
0.706 (1.00) |
0.582 (1.00) |
0.167 (1.00) |
0.262 (1.00) |
0.0753 (1.00) |
0.513 (1.00) |
0.0946 (1.00) |
|
| NPNT | 6 (2%) | 287 |
0.0806 (1.00) |
0.222 (1.00) |
0.668 (1.00) |
0.342 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.219 (1.00) |
|
| OR5H1 | 3 (1%) | 290 |
0.56 (1.00) |
0.566 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.519 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.38 (1.00) |
|
| SPAM1 | 5 (2%) | 288 |
0.27 (1.00) |
0.192 (1.00) |
0.661 (1.00) |
0.096 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.288 (1.00) |
|
| TPTE2 | 7 (2%) | 286 |
0.3 (1.00) |
0.309 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.48 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.599 (1.00) |
0.596 (1.00) |
P value = 0.000388 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.076
Table S1. Gene #4: 'BAP1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'TUMOR.STAGE'
| nPatients | I | II | III | IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 144 | 31 | 76 | 42 |
| BAP1 MUTATED | 5 | 5 | 7 | 10 |
| BAP1 WILD-TYPE | 139 | 26 | 69 | 32 |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image Gene #4: 'BAP1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'TUMOR.STAGE'
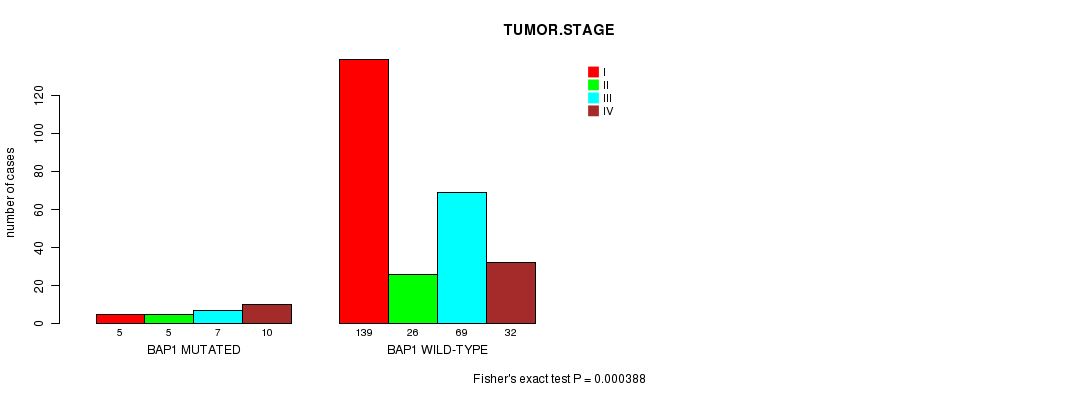
P value = 0.000354 (logrank test), Q value = 0.07
Table S2. Gene #8: 'TP53 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 291 | 77 | 0.1 - 109.6 (34.3) |
| TP53 MUTATED | 6 | 3 | 0.2 - 25.7 (9.8) |
| TP53 WILD-TYPE | 285 | 74 | 0.1 - 109.6 (35.2) |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image Gene #8: 'TP53 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
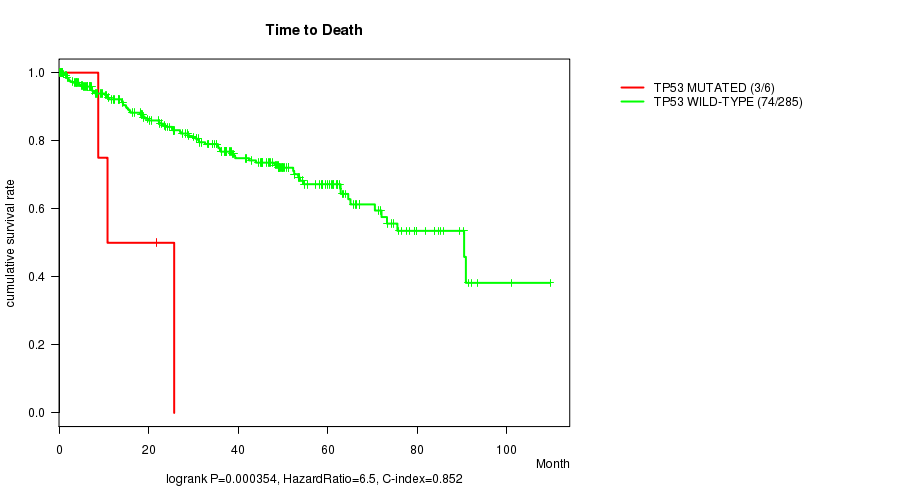
-
Mutation data file = KIRC-TP.mutsig.cluster.txt
-
Clinical data file = KIRC-TP.clin.merged.picked.txt
-
Number of patients = 293
-
Number of significantly mutated genes = 28
-
Number of selected clinical features = 8
-
Exclude genes that fewer than K tumors have mutations, K = 3
For survival clinical features, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of tumors with and without gene mutations were plotted and the statistical significance P values were estimated by logrank test (Bland and Altman 2004) using the 'survdiff' function in R
For continuous numerical clinical features, two-tailed Student's t test with unequal variance (Lehmann and Romano 2005) was applied to compare the clinical values between tumors with and without gene mutations using 't.test' function in R
For binary or multi-class clinical features (nominal or ordinal), two-tailed Fisher's exact tests (Fisher 1922) were used to estimate the P values using the 'fisher.test' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.
This is an experimental feature. The full results of the analysis summarized in this report can be downloaded from the TCGA Data Coordination Center.