This pipeline computes the correlation between significant copy number variation (cnv) genes and molecular subtypes.
Testing the association between copy number variation of 2 peak regions and 8 molecular subtypes across 66 patients, 4 significant findings detected with Q value < 0.25.
-
Amp Peak 1(8q11.23) cnvs correlated to 'MRNASEQ_CNMF' and 'MRNASEQ_CHIERARCHICAL'.
-
Amp Peak 2(15q22.31) cnvs correlated to 'MRNASEQ_CNMF' and 'MRNASEQ_CHIERARCHICAL'.
Table 1. Get Full Table Overview of the association between significant copy number variation of 2 regions and 8 molecular subtypes. Shown in the table are P values (Q values). Thresholded by Q value < 0.25, 4 significant findings detected.
|
Molecular subtypes |
CN CNMF |
METHLYATION CNMF |
MRNASEQ CNMF |
MRNASEQ CHIERARCHICAL |
MIRSEQ CNMF |
MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL |
MIRSEQ MATURE CNMF |
MIRSEQ MATURE CHIERARCHICAL |
||
| nCNV (%) | nWild-Type | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Chi-square test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Chi-square test | |
| Amp Peak 1(8q11 23) | 0 (0%) | 48 |
0.165 (1.00) |
0.377 (1.00) |
0.00906 (0.127) |
0.0143 (0.186) |
0.942 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.73 (1.00) |
0.753 (1.00) |
| Amp Peak 2(15q22 31) | 0 (0%) | 44 |
0.147 (1.00) |
0.732 (1.00) |
0.00546 (0.0873) |
0.00823 (0.124) |
0.645 (1.00) |
0.253 (1.00) |
0.845 (1.00) |
0.47 (1.00) |
P value = 0.00906 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.13
Table S1. Gene #1: 'Amp Peak 1(8q11.23)' versus Molecular Subtype #3: 'MRNASEQ_CNMF'
| nPatients | CLUS_1 | CLUS_2 | CLUS_3 | CLUS_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 19 | 22 | 15 | 10 |
| AMP PEAK 1(8Q11.23) CNV | 3 | 12 | 2 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 1(8Q11.23) WILD-TYPE | 16 | 10 | 13 | 9 |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image Gene #1: 'Amp Peak 1(8q11.23)' versus Molecular Subtype #3: 'MRNASEQ_CNMF'
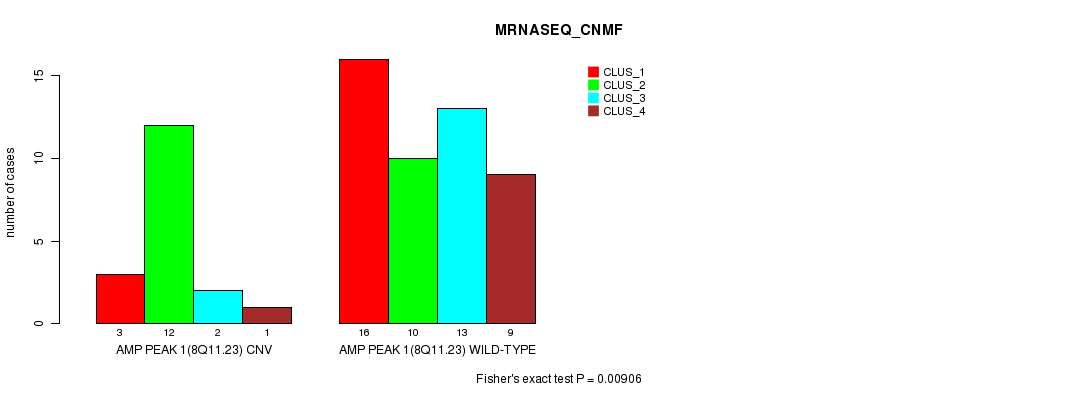
P value = 0.0143 (Chi-square test), Q value = 0.19
Table S2. Gene #1: 'Amp Peak 1(8q11.23)' versus Molecular Subtype #4: 'MRNASEQ_CHIERARCHICAL'
| nPatients | CLUS_1 | CLUS_2 | CLUS_3 | CLUS_4 | CLUS_5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 10 | 10 | 17 | 6 | 23 |
| AMP PEAK 1(8Q11.23) CNV | 2 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 4 |
| AMP PEAK 1(8Q11.23) WILD-TYPE | 8 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 19 |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image Gene #1: 'Amp Peak 1(8q11.23)' versus Molecular Subtype #4: 'MRNASEQ_CHIERARCHICAL'
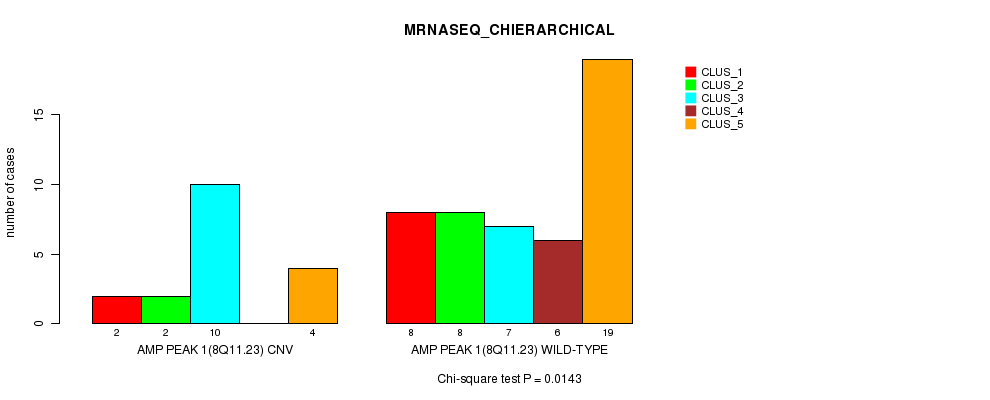
P value = 0.00546 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.087
Table S3. Gene #2: 'Amp Peak 2(15q22.31)' versus Molecular Subtype #3: 'MRNASEQ_CNMF'
| nPatients | CLUS_1 | CLUS_2 | CLUS_3 | CLUS_4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 19 | 22 | 15 | 10 |
| AMP PEAK 2(15Q22.31) CNV | 5 | 13 | 4 | 0 |
| AMP PEAK 2(15Q22.31) WILD-TYPE | 14 | 9 | 11 | 10 |
Figure S3. Get High-res Image Gene #2: 'Amp Peak 2(15q22.31)' versus Molecular Subtype #3: 'MRNASEQ_CNMF'
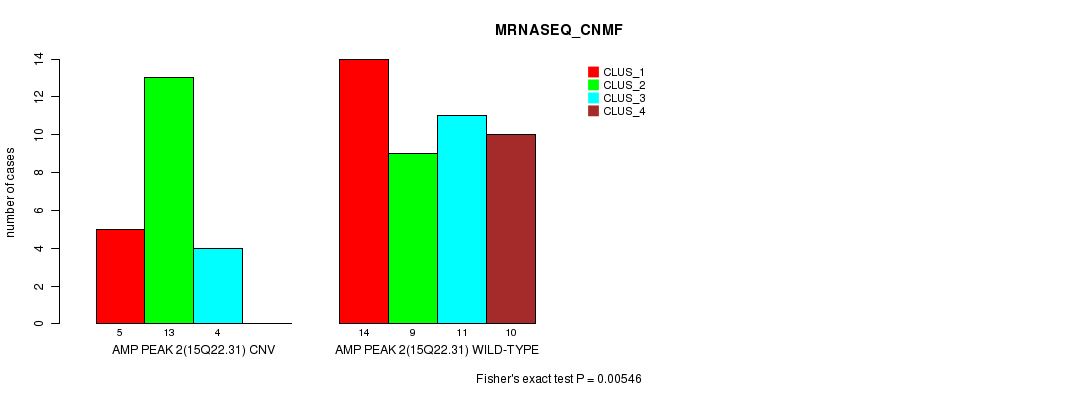
P value = 0.00823 (Chi-square test), Q value = 0.12
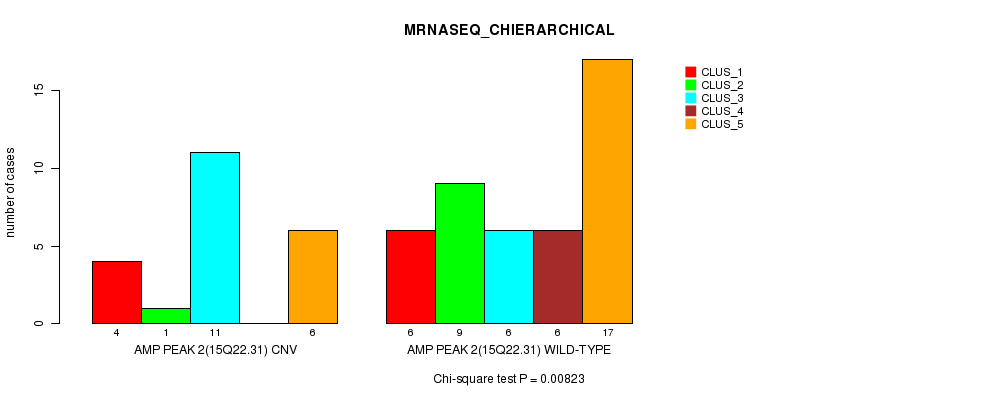
Table S4. Gene #2: 'Amp Peak 2(15q22.31)' versus Molecular Subtype #4: 'MRNASEQ_CHIERARCHICAL'
| nPatients | CLUS_1 | CLUS_2 | CLUS_3 | CLUS_4 | CLUS_5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 10 | 10 | 17 | 6 | 23 |
| AMP PEAK 2(15Q22.31) CNV | 4 | 1 | 11 | 0 | 6 |
| AMP PEAK 2(15Q22.31) WILD-TYPE | 6 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 17 |
Figure S4. Get High-res Image Gene #2: 'Amp Peak 2(15q22.31)' versus Molecular Subtype #4: 'MRNASEQ_CHIERARCHICAL'
-
Copy number data file = All Lesions File (all_lesions.conf_##.txt, where ## is the confidence level). The all lesions file is from GISTIC pipeline and summarizes the results from the GISTIC run. It contains data about the significant regions of amplification and deletion as well as which samples are amplified or deleted in each of these regions. The identified regions are listed down the first column, and the samples are listed across the first row, starting in column 10.
-
Molecular subtype file = KICH-TP.transferedmergedcluster.txt
-
Number of patients = 66
-
Number of copy number variation regions = 2
-
Number of molecular subtypes = 8
-
Exclude regions that fewer than K tumors have alterations, K = 3
For binary or multi-class clinical features (nominal or ordinal), two-tailed Fisher's exact tests (Fisher 1922) were used to estimate the P values using the 'fisher.test' function in R
For multi-class clinical features (nominal or ordinal), Chi-square tests (Greenwood and Nikulin 1996) were used to estimate the P values using the 'chisq.test' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.
This is an experimental feature. The full results of the analysis summarized in this report can be downloaded from the TCGA Data Coordination Center.