This pipeline computes the correlation between cancer subtypes identified by different molecular patterns and selected clinical features.
Testing the association between subtypes identified by 8 different clustering approaches and 8 clinical features across 155 patients, 7 significant findings detected with P value < 0.05 and Q value < 0.25.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes'. These subtypes do not correlate to any clinical features.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'METHLYATION CNMF'. These subtypes correlate to 'AGE'.
-
CNMF clustering analysis on sequencing-based mRNA expression data identified 5 subtypes that correlate to 'GENDER'.
-
Consensus hierarchical clustering analysis on sequencing-based mRNA expression data identified 4 subtypes that correlate to 'GENDER'.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRSEQ CNMF'. These subtypes correlate to 'AGE'.
-
4 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL'. These subtypes correlate to 'AGE'.
-
6 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes'. These subtypes correlate to 'AGE'.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes'. These subtypes correlate to 'AGE'.
Table 1. Get Full Table Overview of the association between subtypes identified by 8 different clustering approaches and 8 clinical features. Shown in the table are P values (Q values). Thresholded by P value < 0.05 and Q value < 0.25, 7 significant findings detected.
|
Clinical Features |
Time to Death |
AGE |
NEOPLASM DISEASESTAGE |
PATHOLOGY T STAGE |
PATHOLOGY N STAGE |
PATHOLOGY M STAGE |
GENDER |
COMPLETENESS OF RESECTION |
| Statistical Tests | logrank test | ANOVA | Chi-square test | Chi-square test | Fisher's exact test | Chi-square test | Fisher's exact test | Chi-square test |
| Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes |
0.0981 (1.00) |
0.61 (1.00) |
0.2 (1.00) |
0.153 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.89 (1.00) |
0.0129 (0.707) |
0.301 (1.00) |
| METHLYATION CNMF |
0.286 (1.00) |
0.000212 (0.0129) |
0.738 (1.00) |
0.933 (1.00) |
0.775 (1.00) |
0.324 (1.00) |
0.202 (1.00) |
0.803 (1.00) |
| RNAseq CNMF subtypes |
0.0124 (0.696) |
0.0154 (0.83) |
0.24 (1.00) |
0.0509 (1.00) |
0.456 (1.00) |
0.699 (1.00) |
5.98e-06 (0.000382) |
0.376 (1.00) |
| RNAseq cHierClus subtypes |
0.589 (1.00) |
0.00605 (0.345) |
0.51 (1.00) |
0.115 (1.00) |
0.412 (1.00) |
0.457 (1.00) |
0.00029 (0.0174) |
0.611 (1.00) |
| MIRSEQ CNMF |
0.141 (1.00) |
0.00106 (0.0627) |
0.605 (1.00) |
0.317 (1.00) |
0.181 (1.00) |
0.558 (1.00) |
0.894 (1.00) |
0.817 (1.00) |
| MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL |
0.33 (1.00) |
6.38e-05 (0.00395) |
0.83 (1.00) |
0.926 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.527 (1.00) |
0.038 (1.00) |
0.421 (1.00) |
| MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes |
0.541 (1.00) |
0.00198 (0.115) |
0.644 (1.00) |
0.619 (1.00) |
0.679 (1.00) |
0.526 (1.00) |
0.0309 (1.00) |
0.445 (1.00) |
| MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes |
0.144 (1.00) |
6.23e-06 (0.000393) |
0.461 (1.00) |
0.677 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.232 (1.00) |
0.289 (1.00) |
0.629 (1.00) |
Table S1. Description of clustering approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 43 | 58 | 48 |
P value = 0.0981 (logrank test), Q value = 1
Table S2. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 147 | 63 | 0.0 - 113.0 (14.1) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 21 | 0.1 - 101.0 (13.7) |
| subtype2 | 58 | 20 | 0.1 - 107.1 (18.8) |
| subtype3 | 47 | 22 | 0.0 - 113.0 (11.7) |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
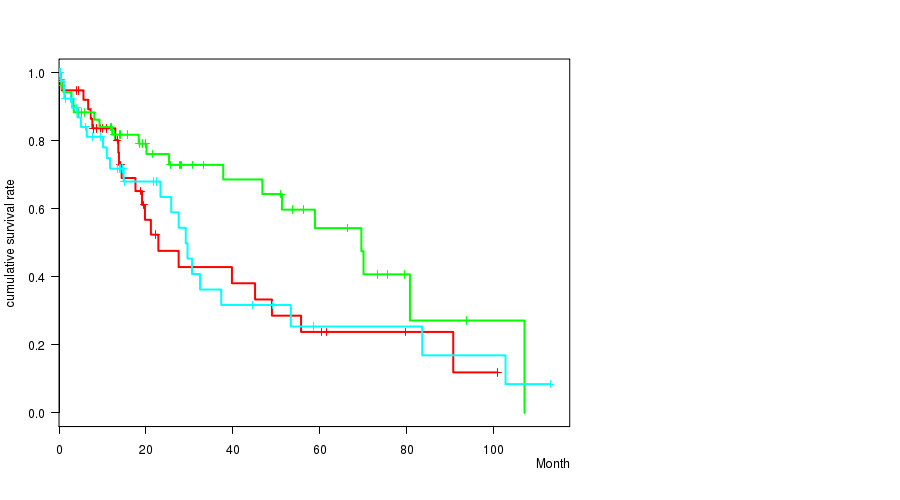
P value = 0.61 (ANOVA), Q value = 1
Table S3. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 147 | 61.6 (13.8) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 63.4 (13.5) |
| subtype2 | 57 | 61.0 (13.9) |
| subtype3 | 48 | 60.9 (14.0) |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
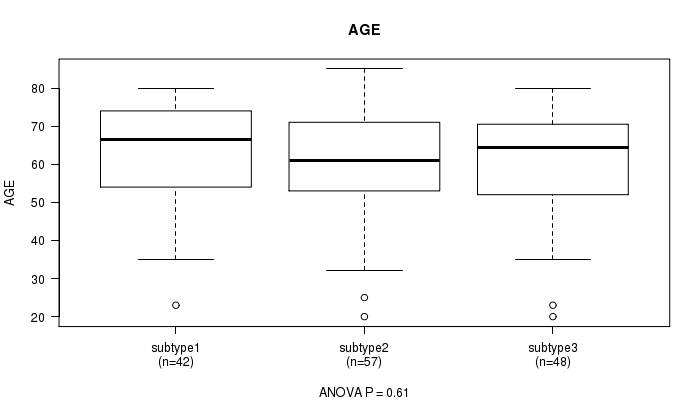
P value = 0.2 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S4. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE II | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA | STAGE IVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 58 | 36 | 2 | 30 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 21 | 9 | 0 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 25 | 11 | 0 | 13 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 12 | 16 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Figure S3. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
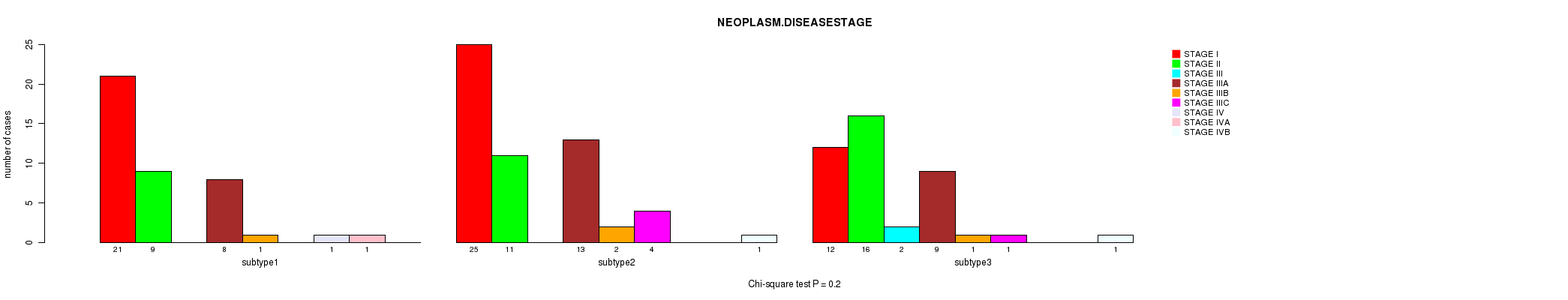
P value = 0.153 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S5. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 61 | 40 | 40 | 8 |
| subtype1 | 22 | 11 | 10 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 26 | 12 | 16 | 4 |
| subtype3 | 13 | 17 | 14 | 4 |
Figure S4. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
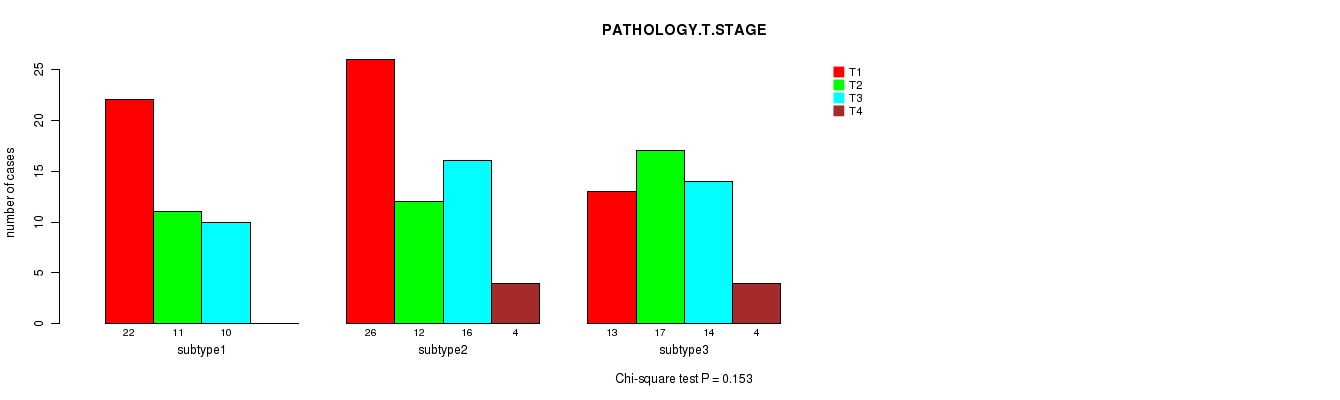
P value = 1 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S6. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 97 | 3 |
| subtype1 | 26 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 44 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 27 | 1 |
Figure S5. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
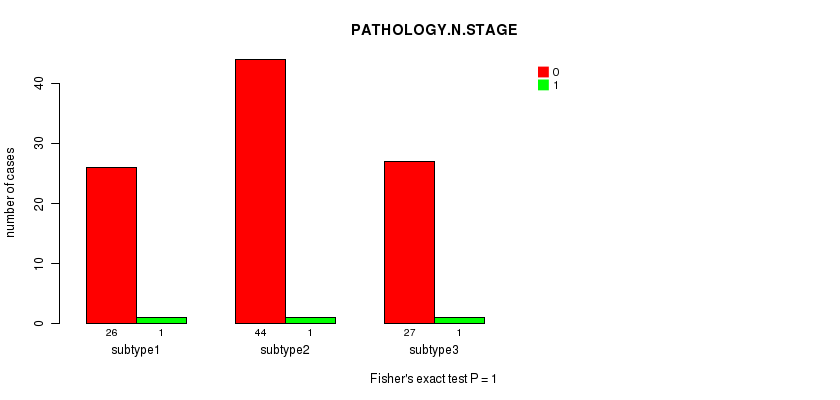
P value = 0.89 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S7. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
| nPatients | M0 | M1 | MX |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 115 | 3 | 31 |
| subtype1 | 31 | 1 | 11 |
| subtype2 | 47 | 1 | 10 |
| subtype3 | 37 | 1 | 10 |
Figure S6. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
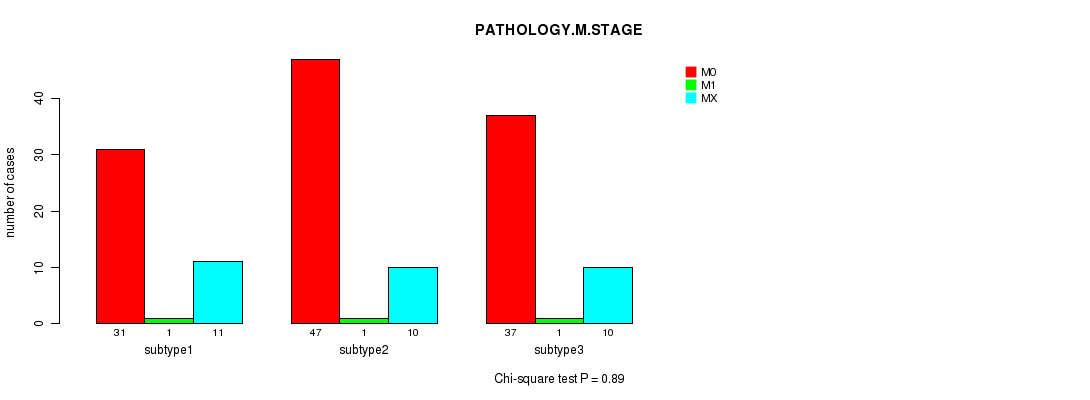
P value = 0.0129 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.71
Table S8. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 58 | 91 |
| subtype1 | 9 | 34 |
| subtype2 | 28 | 30 |
| subtype3 | 21 | 27 |
Figure S7. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
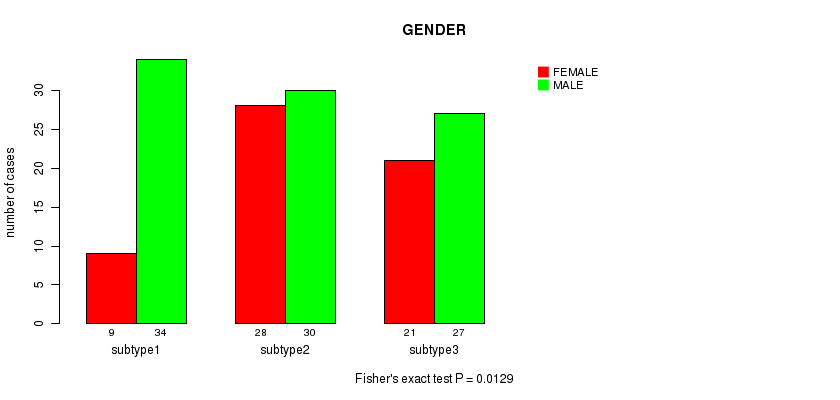
P value = 0.301 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S9. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 122 | 11 | 1 | 10 |
| subtype1 | 33 | 5 | 1 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 50 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 39 | 5 | 0 | 4 |
Figure S8. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
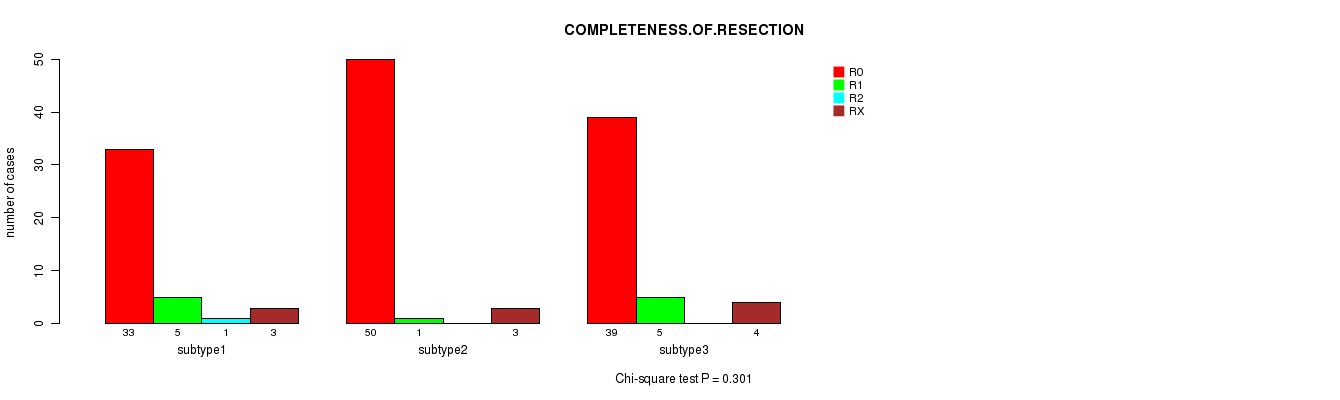
Table S10. Description of clustering approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 42 | 43 | 69 |
P value = 0.286 (logrank test), Q value = 1
Table S11. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 151 | 63 | 0.0 - 113.0 (13.9) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 14 | 0.1 - 107.1 (13.8) |
| subtype2 | 42 | 20 | 0.1 - 113.0 (13.2) |
| subtype3 | 67 | 29 | 0.0 - 102.7 (15.0) |
Figure S9. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
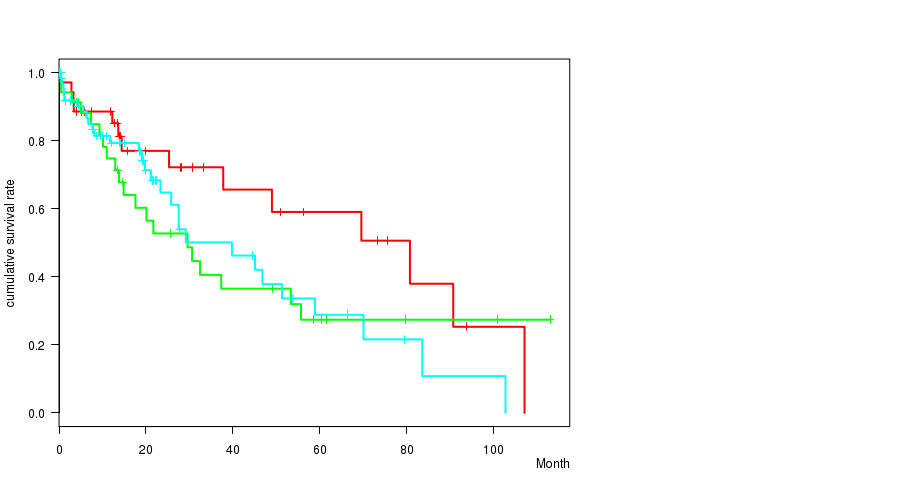
P value = 0.000212 (ANOVA), Q value = 0.013
Table S12. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 152 | 61.2 (14.2) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 56.0 (15.9) |
| subtype2 | 43 | 58.4 (15.7) |
| subtype3 | 67 | 66.3 (9.8) |
Figure S10. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
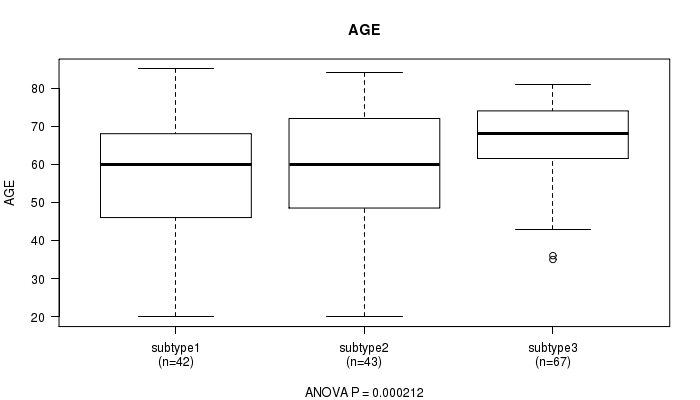
P value = 0.738 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S13. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE II | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA | STAGE IVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 58 | 36 | 2 | 34 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 15 | 9 | 0 | 11 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 28 | 17 | 1 | 14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Figure S11. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
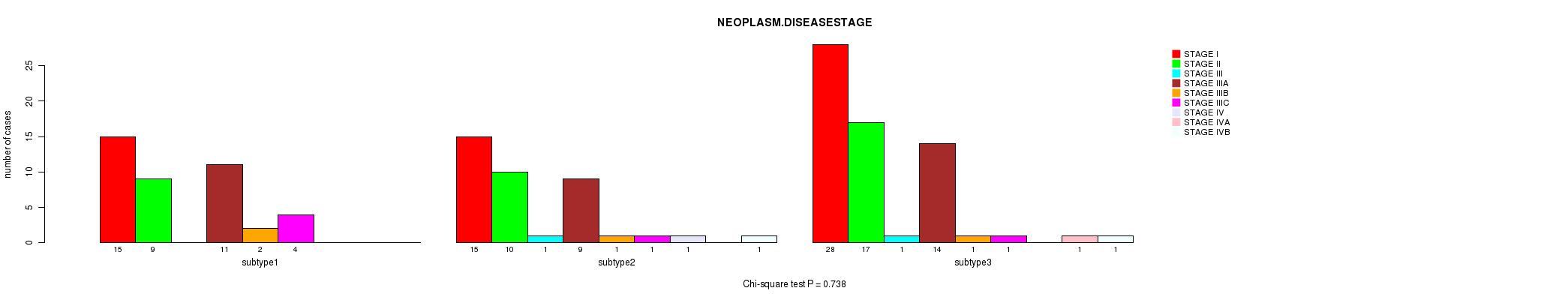
P value = 0.933 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S14. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 61 | 40 | 44 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 16 | 10 | 13 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 11 | 14 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 30 | 19 | 17 | 3 |
Figure S12. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
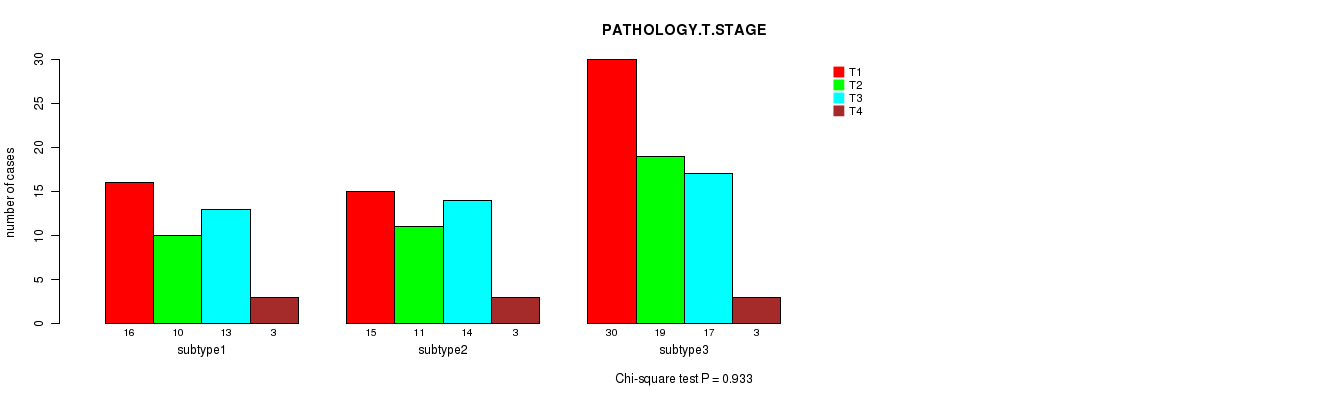
P value = 0.775 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S15. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 101 | 3 |
| subtype1 | 34 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 30 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 37 | 2 |
Figure S13. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
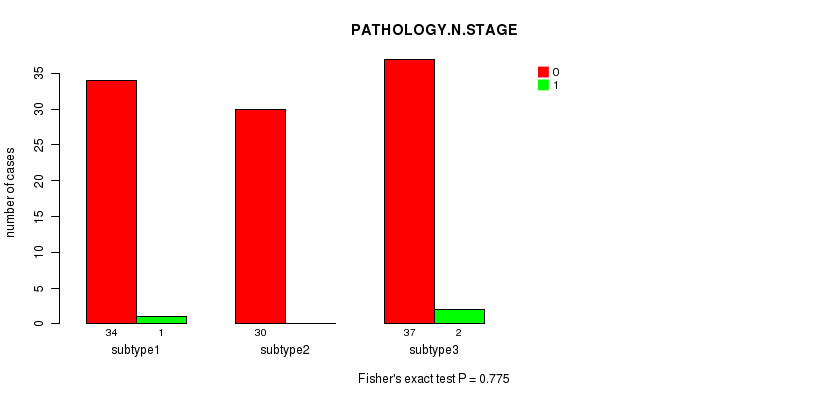
P value = 0.324 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S16. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
| nPatients | M0 | M1 | MX |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 121 | 3 | 30 |
| subtype1 | 35 | 0 | 7 |
| subtype2 | 35 | 2 | 6 |
| subtype3 | 51 | 1 | 17 |
Figure S14. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
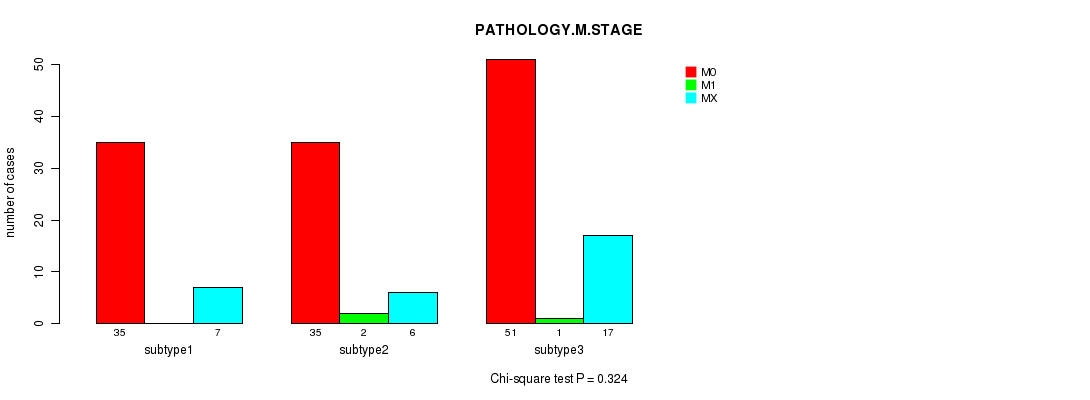
P value = 0.202 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S17. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 61 | 93 |
| subtype1 | 19 | 23 |
| subtype2 | 20 | 23 |
| subtype3 | 22 | 47 |
Figure S15. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
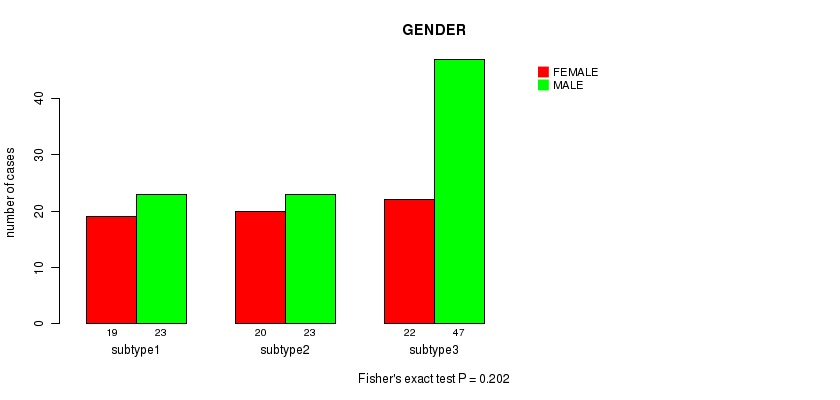
P value = 0.803 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S18. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 126 | 11 | 1 | 11 |
| subtype1 | 34 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 35 | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 57 | 5 | 0 | 5 |
Figure S16. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
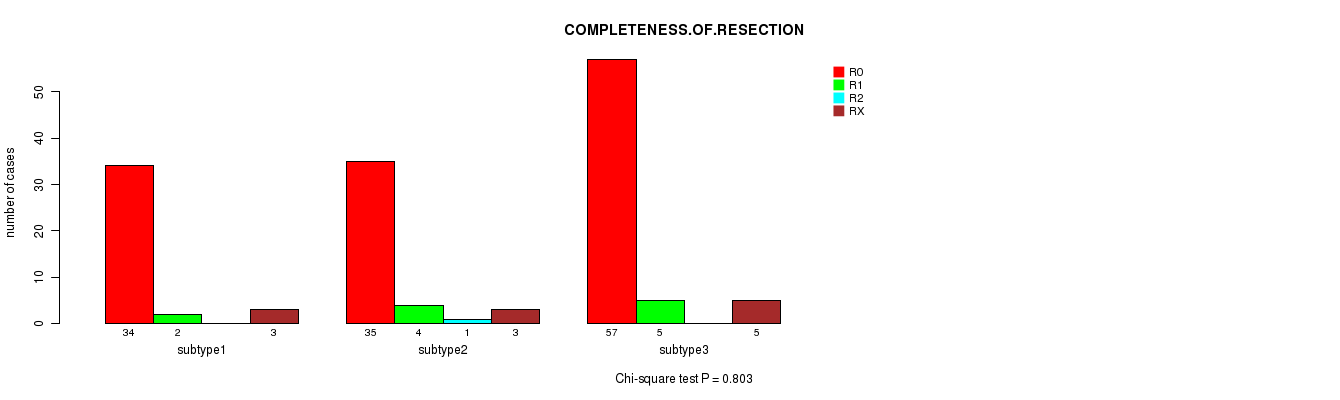
Table S19. Description of clustering approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 35 | 23 | 43 | 21 | 25 |
P value = 0.0124 (logrank test), Q value = 0.7
Table S20. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 145 | 62 | 0.0 - 113.0 (14.1) |
| subtype1 | 35 | 17 | 0.1 - 113.0 (15.8) |
| subtype2 | 22 | 13 | 0.1 - 45.1 (8.4) |
| subtype3 | 42 | 18 | 0.1 - 102.7 (20.3) |
| subtype4 | 21 | 7 | 0.0 - 80.8 (12.7) |
| subtype5 | 25 | 7 | 0.2 - 93.7 (13.6) |
Figure S17. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
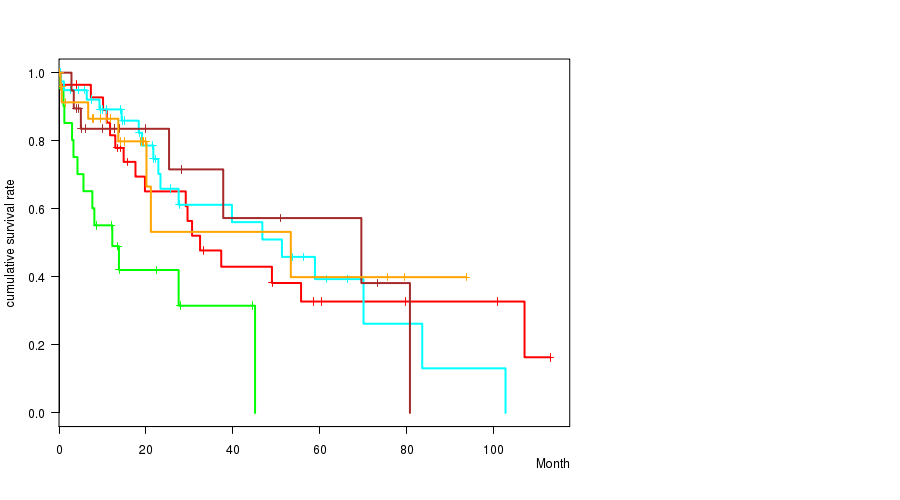
P value = 0.0154 (ANOVA), Q value = 0.83
Table S21. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 145 | 61.7 (13.8) |
| subtype1 | 35 | 57.7 (15.4) |
| subtype2 | 22 | 63.8 (12.3) |
| subtype3 | 42 | 66.4 (10.9) |
| subtype4 | 21 | 56.0 (15.0) |
| subtype5 | 25 | 62.6 (13.8) |
Figure S18. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
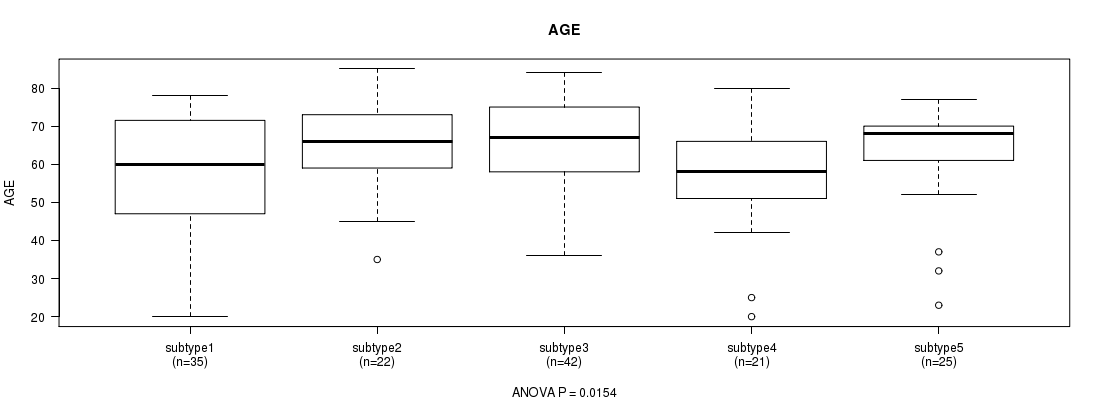
P value = 0.24 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S22. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE II | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA | STAGE IVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 57 | 34 | 2 | 31 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 8 | 12 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 23 | 5 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| subtype4 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 11 | 7 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Figure S19. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
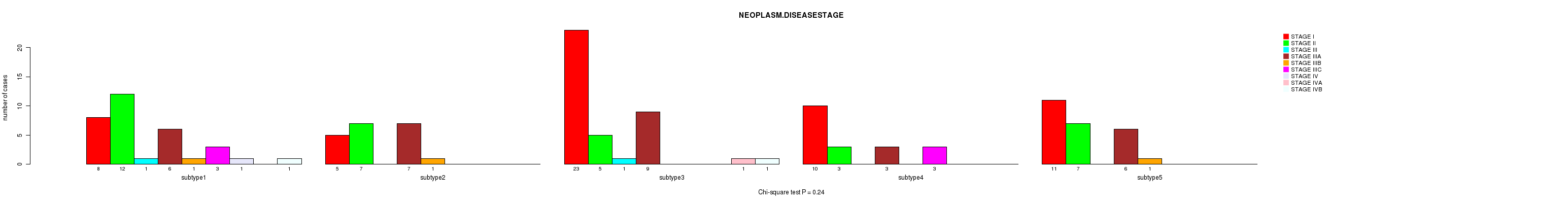
P value = 0.0509 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S23. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 60 | 38 | 40 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 9 | 14 | 10 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 24 | 5 | 11 | 3 |
| subtype4 | 11 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| subtype5 | 11 | 7 | 7 | 0 |
Figure S20. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
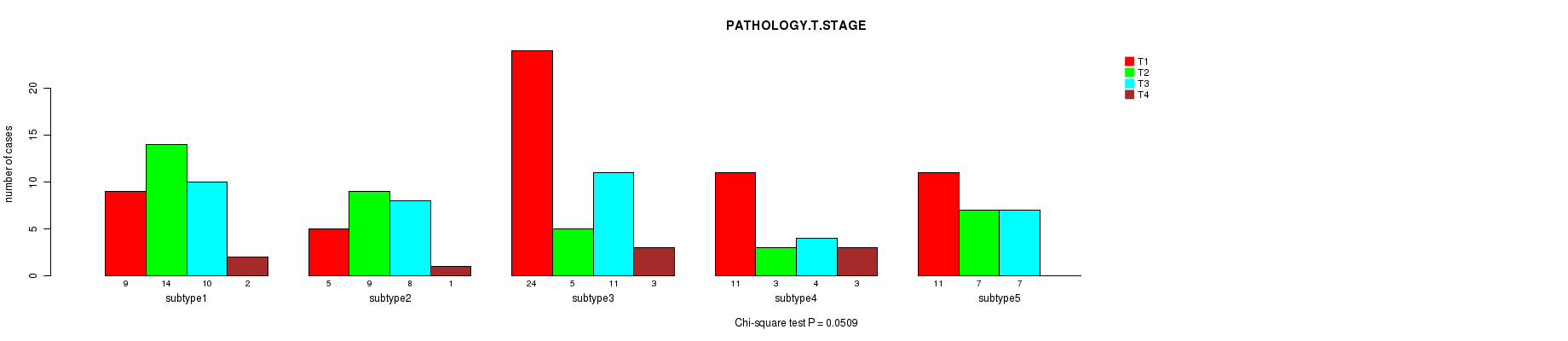
P value = 0.456 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S24. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 95 | 3 |
| subtype1 | 22 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 14 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 29 | 1 |
| subtype4 | 14 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 16 | 0 |
Figure S21. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
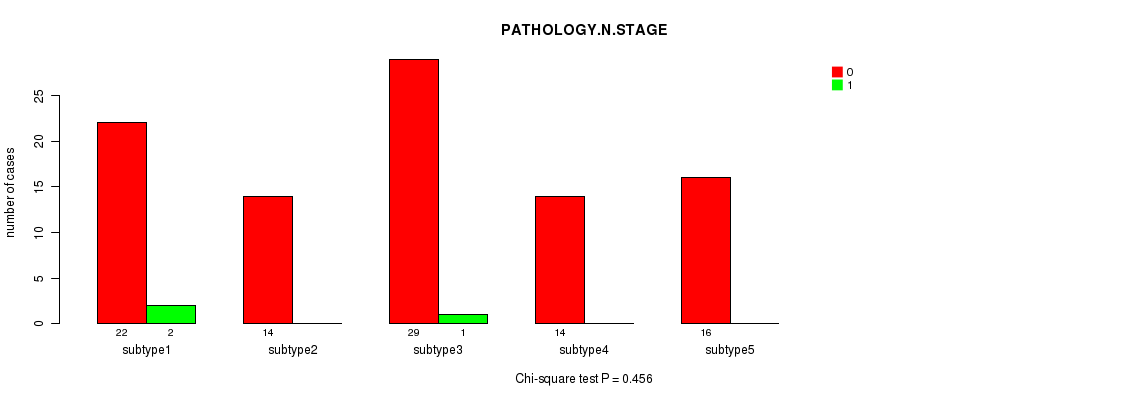
P value = 0.699 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S25. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
| nPatients | M0 | M1 | MX |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 113 | 3 | 31 |
| subtype1 | 28 | 2 | 5 |
| subtype2 | 17 | 0 | 6 |
| subtype3 | 33 | 1 | 9 |
| subtype4 | 15 | 0 | 6 |
| subtype5 | 20 | 0 | 5 |
Figure S22. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
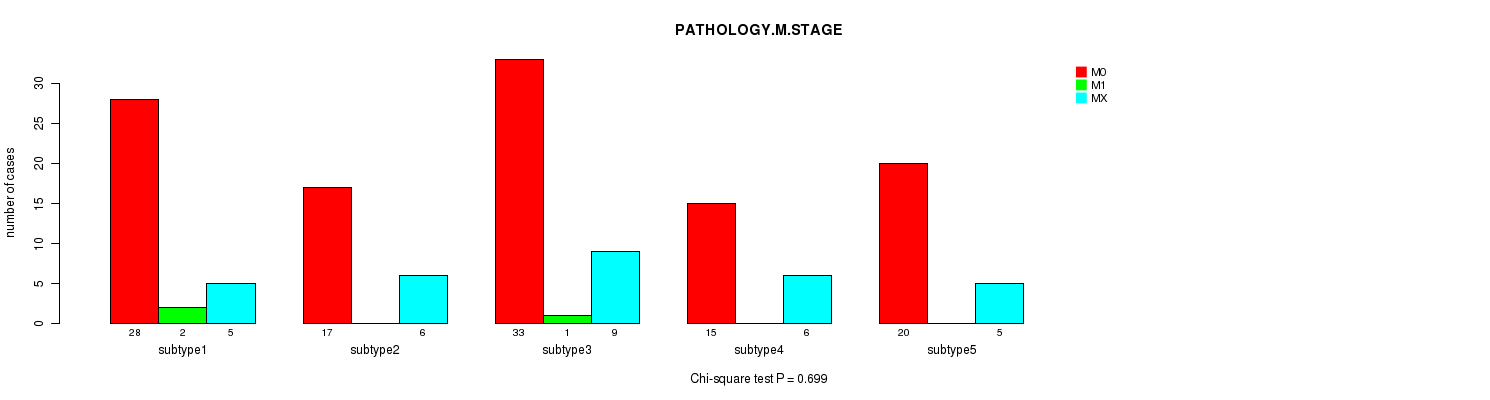
P value = 5.98e-06 (Chi-square test), Q value = 0.00038
Table S26. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 56 | 91 |
| subtype1 | 25 | 10 |
| subtype2 | 7 | 16 |
| subtype3 | 15 | 28 |
| subtype4 | 8 | 13 |
| subtype5 | 1 | 24 |
Figure S23. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
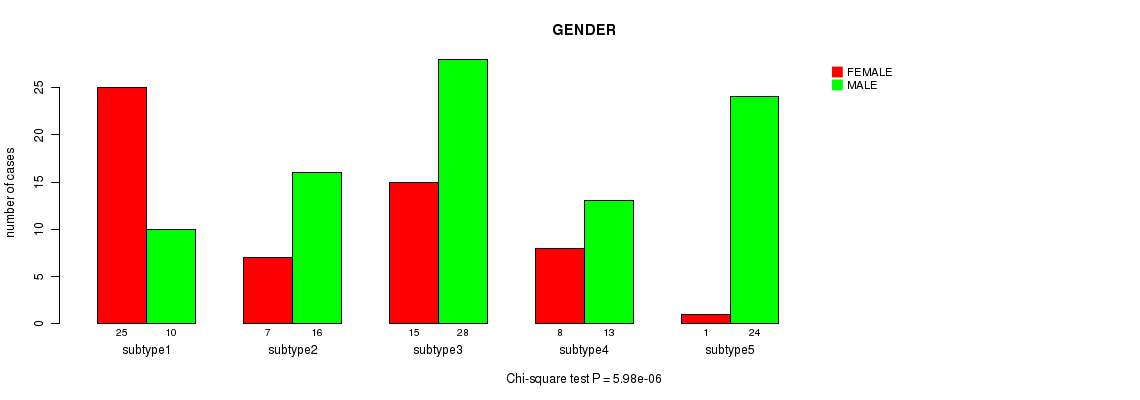
P value = 0.376 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S27. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 120 | 11 | 1 | 10 |
| subtype1 | 29 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 4 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 37 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype4 | 16 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype5 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Figure S24. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
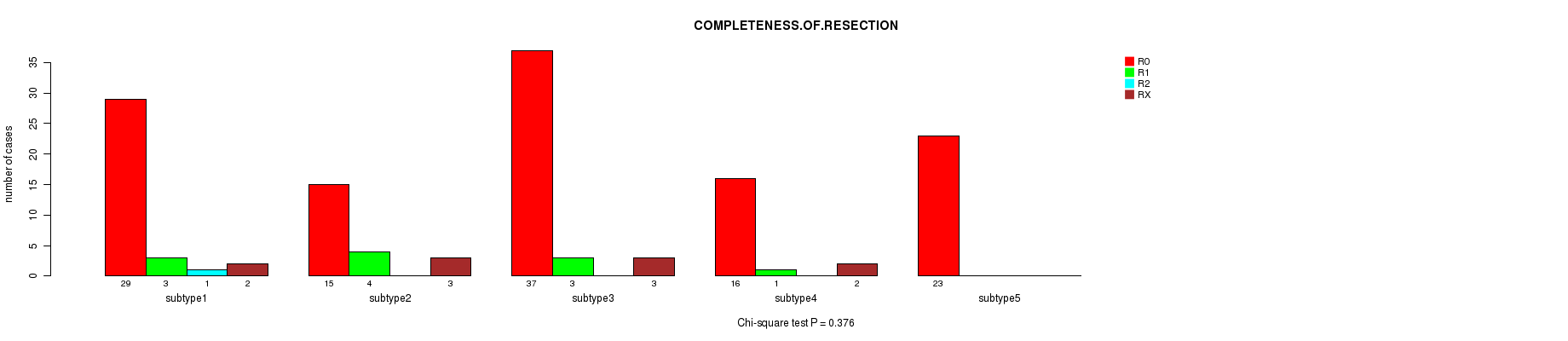
Table S28. Description of clustering approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 25 | 25 | 55 | 42 |
P value = 0.589 (logrank test), Q value = 1
Table S29. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 145 | 62 | 0.0 - 113.0 (14.1) |
| subtype1 | 24 | 9 | 0.0 - 80.8 (17.0) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 7 | 0.2 - 93.7 (14.1) |
| subtype3 | 54 | 27 | 0.1 - 113.0 (13.6) |
| subtype4 | 42 | 19 | 0.1 - 102.7 (14.5) |
Figure S25. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
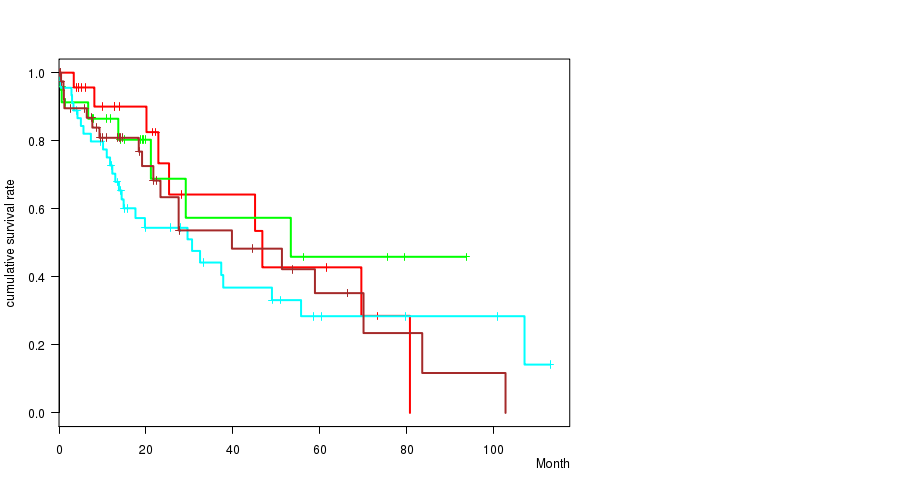
P value = 0.00605 (ANOVA), Q value = 0.34
Table S30. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 145 | 61.7 (13.8) |
| subtype1 | 24 | 61.7 (14.3) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 63.2 (13.3) |
| subtype3 | 55 | 57.2 (15.2) |
| subtype4 | 41 | 66.9 (9.7) |
Figure S26. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
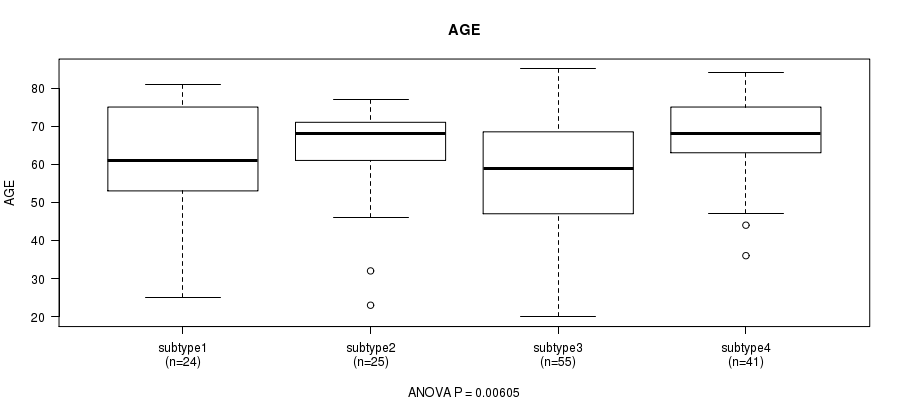
P value = 0.51 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S31. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE II | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA | STAGE IVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 57 | 34 | 2 | 31 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 14 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 11 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 14 | 15 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype4 | 18 | 8 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Figure S27. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
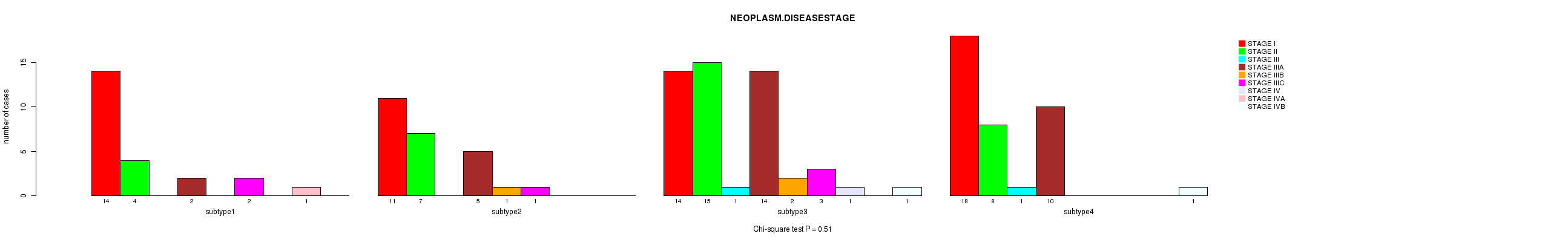
P value = 0.115 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S32. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 60 | 38 | 40 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 12 | 7 | 6 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 14 | 17 | 20 | 4 |
| subtype4 | 18 | 10 | 11 | 3 |
Figure S28. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
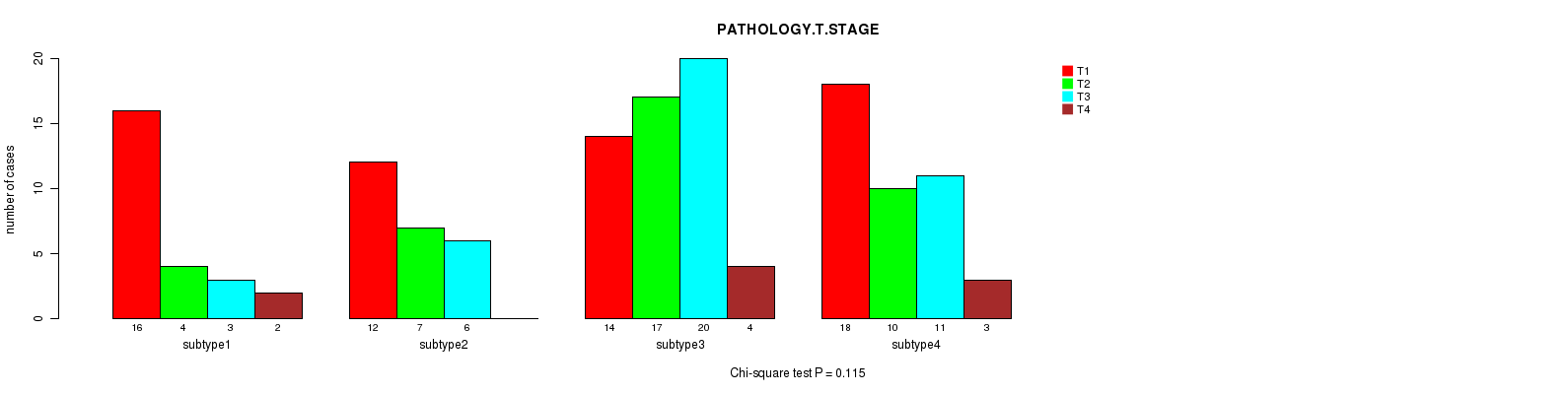
P value = 0.412 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S33. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 95 | 3 |
| subtype1 | 16 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 37 | 1 |
| subtype4 | 27 | 0 |
Figure S29. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
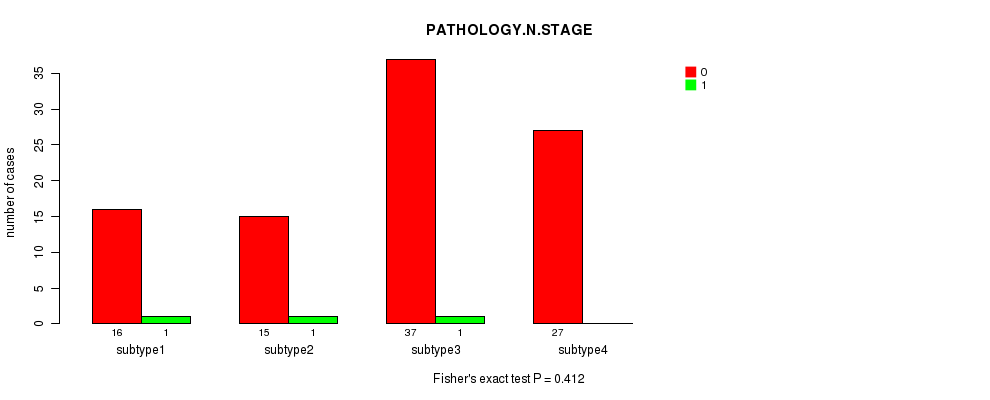
P value = 0.457 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S34. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
| nPatients | M0 | M1 | MX |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 113 | 3 | 31 |
| subtype1 | 16 | 0 | 9 |
| subtype2 | 20 | 0 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 44 | 2 | 9 |
| subtype4 | 33 | 1 | 8 |
Figure S30. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
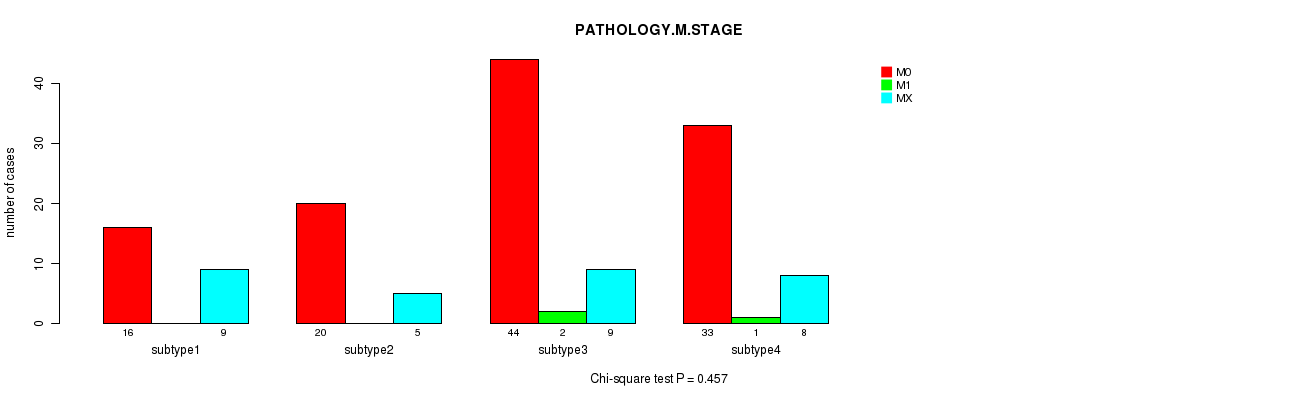
P value = 0.00029 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.017
Table S35. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 56 | 91 |
| subtype1 | 6 | 19 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 23 |
| subtype3 | 29 | 26 |
| subtype4 | 19 | 23 |
Figure S31. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
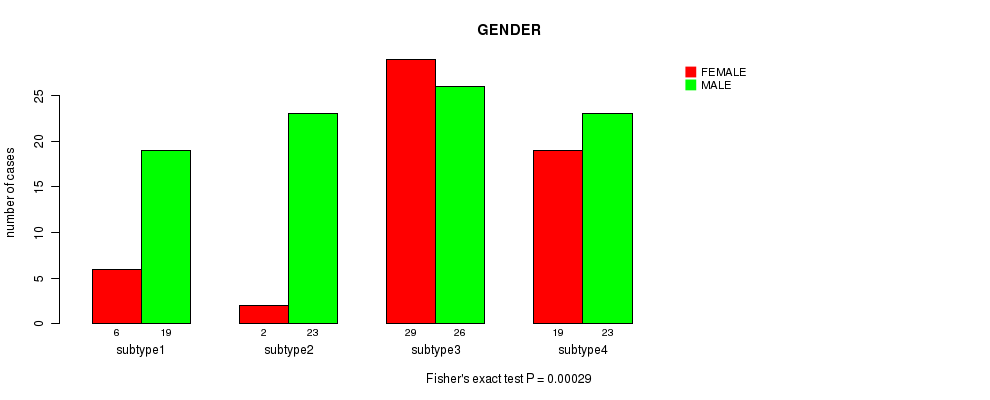
P value = 0.611 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S36. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 120 | 11 | 1 | 10 |
| subtype1 | 20 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 43 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| subtype4 | 34 | 4 | 0 | 4 |
Figure S32. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
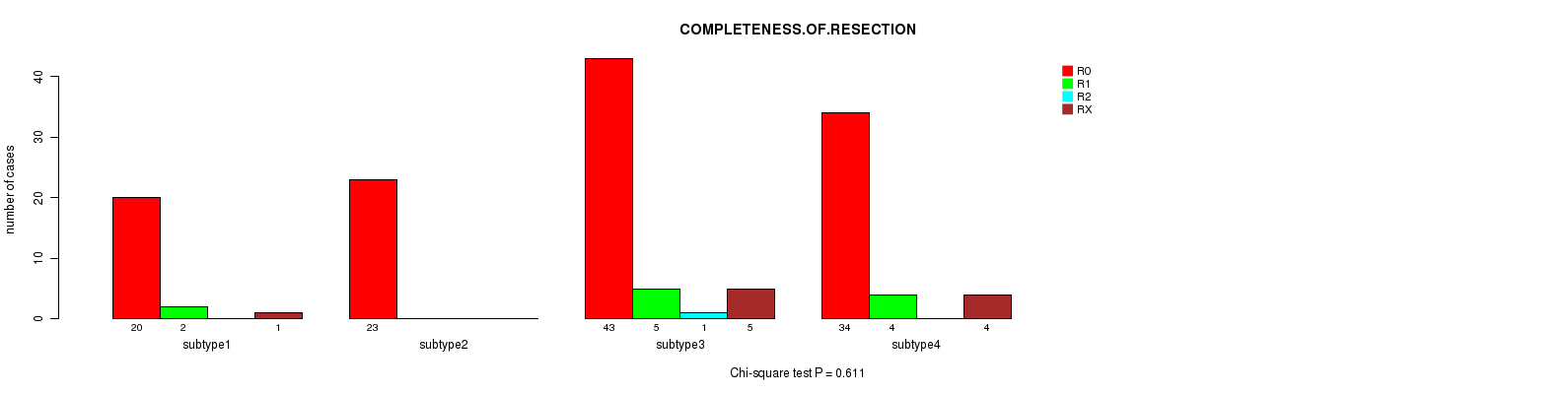
Table S37. Description of clustering approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 56 | 33 | 61 |
P value = 0.141 (logrank test), Q value = 1
Table S38. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 147 | 61 | 0.0 - 113.0 (13.9) |
| subtype1 | 55 | 19 | 0.1 - 101.0 (14.4) |
| subtype2 | 32 | 18 | 0.0 - 102.7 (10.0) |
| subtype3 | 60 | 24 | 0.2 - 113.0 (14.0) |
Figure S33. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
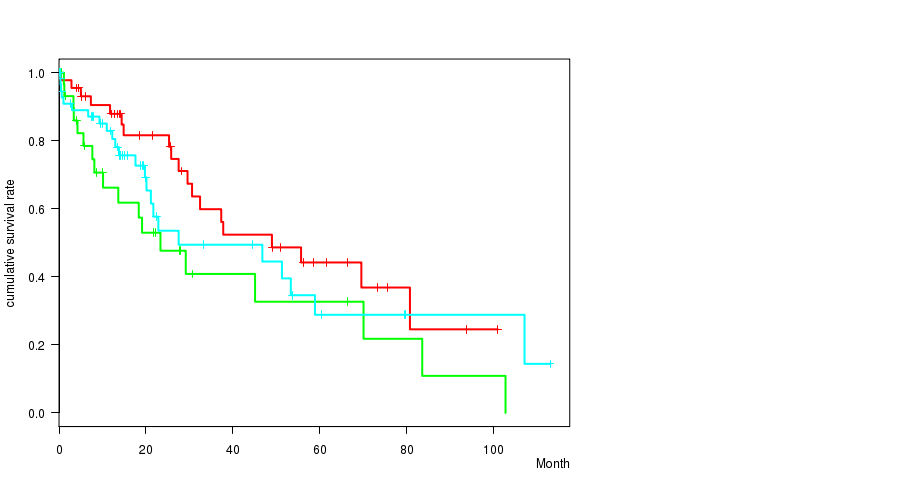
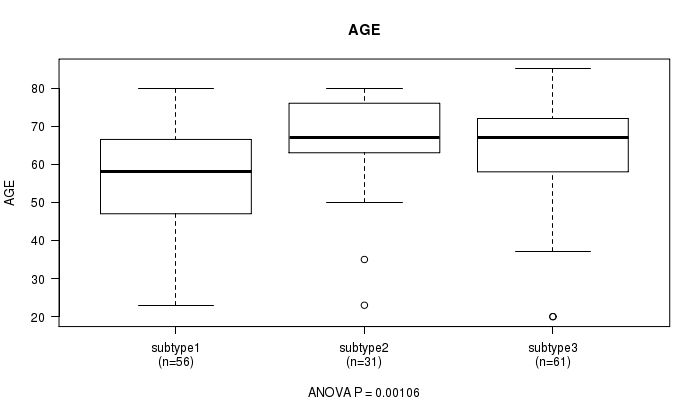
P value = 0.00106 (ANOVA), Q value = 0.063
Table S39. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 148 | 61.3 (14.2) |
| subtype1 | 56 | 55.9 (14.2) |
| subtype2 | 31 | 65.8 (12.8) |
| subtype3 | 61 | 63.9 (13.4) |
Figure S34. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
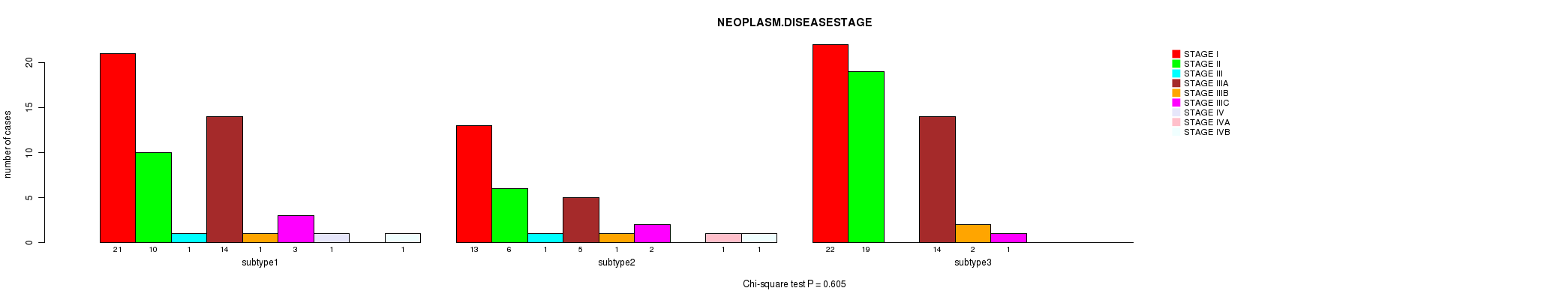
P value = 0.605 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S40. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE II | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA | STAGE IVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 56 | 35 | 2 | 33 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 21 | 10 | 1 | 14 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 13 | 6 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 22 | 19 | 0 | 14 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Figure S35. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
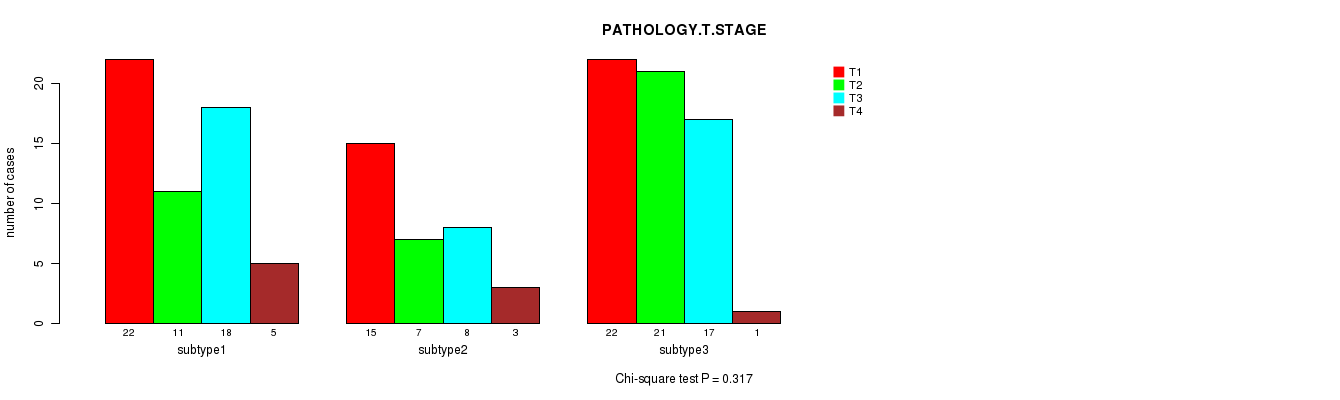
P value = 0.317 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S41. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 59 | 39 | 43 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 22 | 11 | 18 | 5 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 7 | 8 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 22 | 21 | 17 | 1 |
Figure S36. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
P value = 0.181 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S42. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 98 | 3 |
| subtype1 | 39 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 22 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 37 | 1 |
Figure S37. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
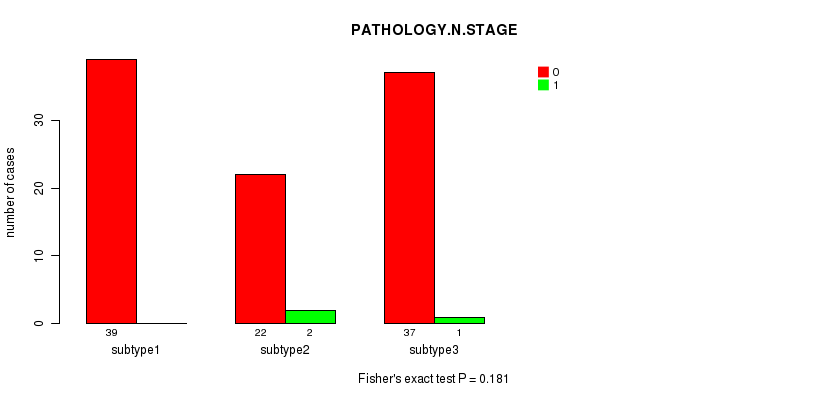
P value = 0.558 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S43. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
| nPatients | M0 | M1 | MX |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 118 | 3 | 29 |
| subtype1 | 45 | 2 | 9 |
| subtype2 | 24 | 1 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 49 | 0 | 12 |
Figure S38. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
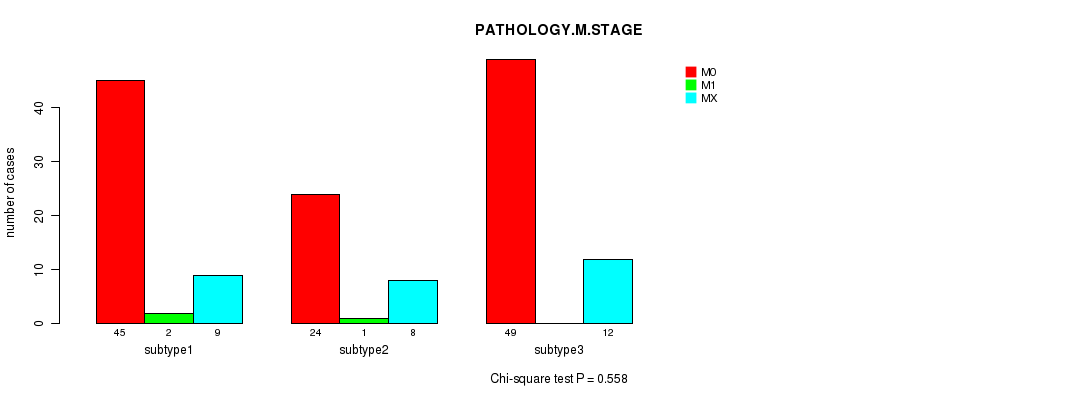
P value = 0.894 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S44. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 58 | 92 |
| subtype1 | 21 | 35 |
| subtype2 | 12 | 21 |
| subtype3 | 25 | 36 |
Figure S39. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
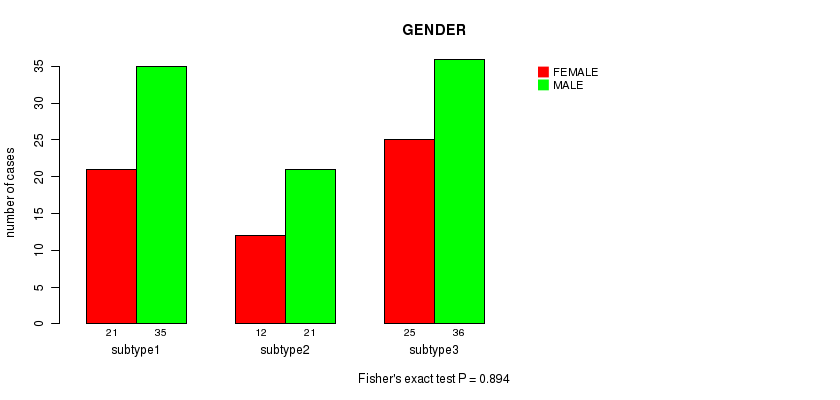
P value = 0.817 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S45. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 122 | 11 | 1 | 11 |
| subtype1 | 46 | 4 | 1 | 5 |
| subtype2 | 24 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 52 | 4 | 0 | 3 |
Figure S40. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
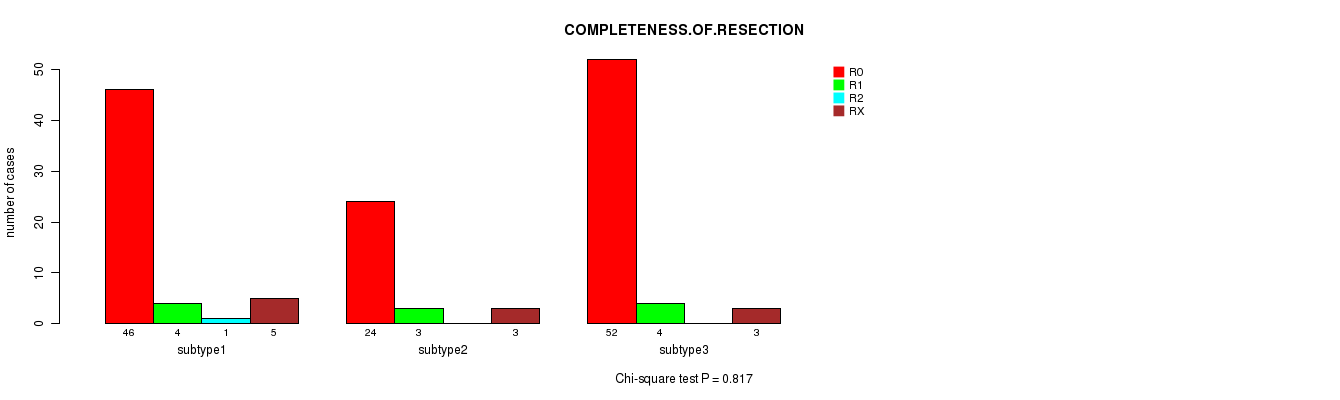
Table S46. Description of clustering approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 15 | 67 | 26 | 42 |
P value = 0.33 (logrank test), Q value = 1
Table S47. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 147 | 61 | 0.0 - 113.0 (13.9) |
| subtype1 | 15 | 9 | 0.0 - 83.6 (10.0) |
| subtype2 | 66 | 27 | 0.1 - 101.0 (14.1) |
| subtype3 | 25 | 7 | 0.3 - 93.7 (11.0) |
| subtype4 | 41 | 18 | 0.1 - 113.0 (15.0) |
Figure S41. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
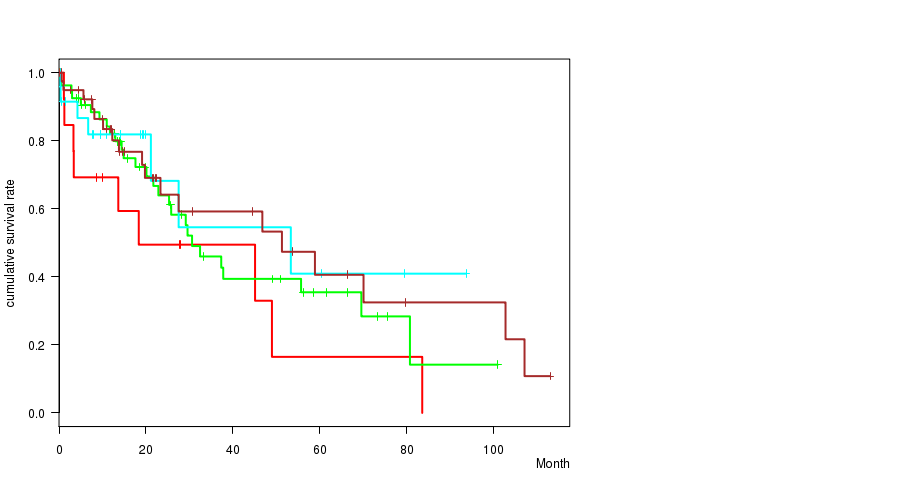
P value = 6.38e-05 (ANOVA), Q value = 0.004
Table S48. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 148 | 61.3 (14.2) |
| subtype1 | 15 | 62.1 (14.1) |
| subtype2 | 67 | 55.6 (14.9) |
| subtype3 | 26 | 66.6 (12.0) |
| subtype4 | 40 | 66.9 (10.5) |
Figure S42. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
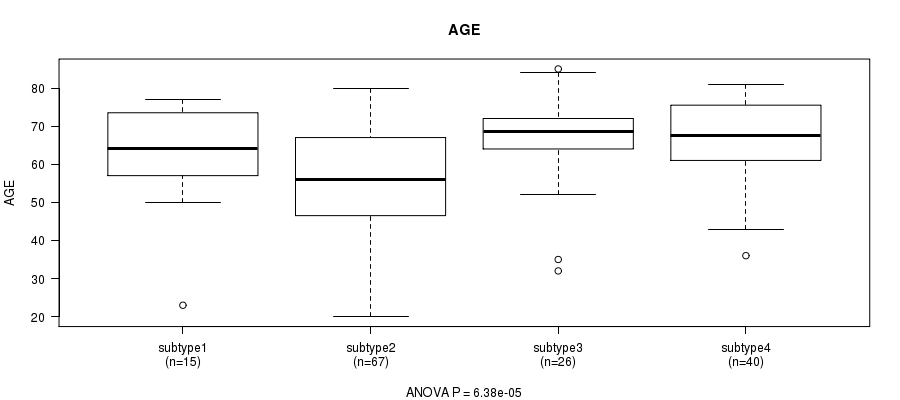
P value = 0.83 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S49. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE II | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA | STAGE IVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 56 | 35 | 2 | 33 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 25 | 14 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 11 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 15 | 12 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Figure S43. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
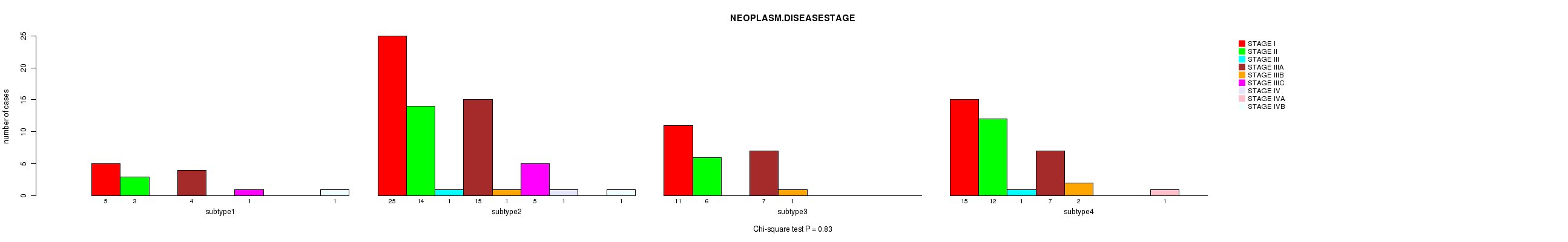
P value = 0.926 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S50. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 59 | 39 | 43 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 27 | 16 | 19 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 11 | 7 | 8 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 16 | 12 | 12 | 2 |
Figure S44. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
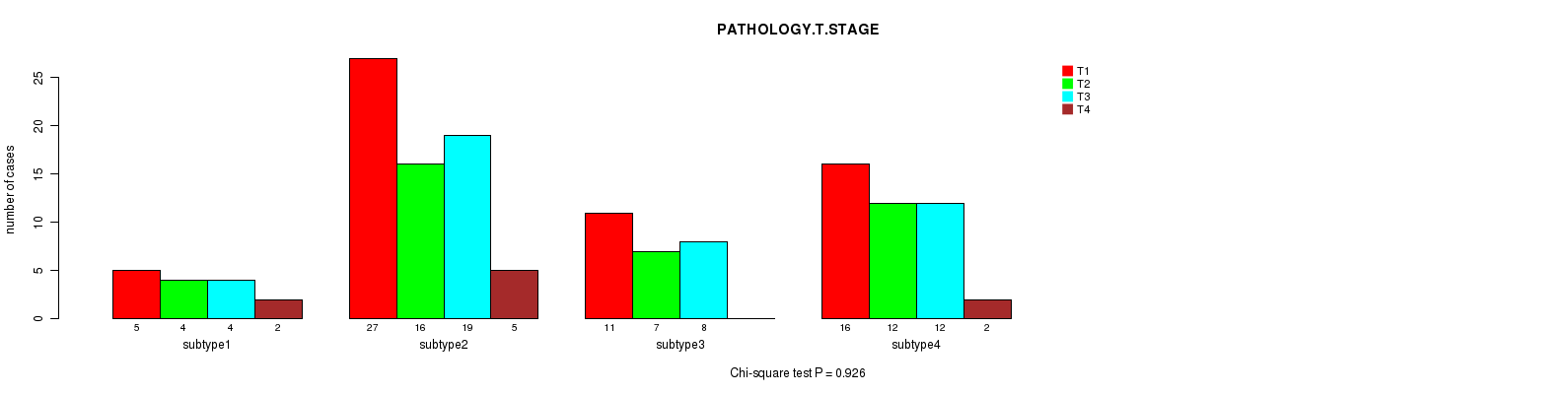
P value = 1 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S51. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 98 | 3 |
| subtype1 | 11 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 46 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 17 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 24 | 1 |
Figure S45. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
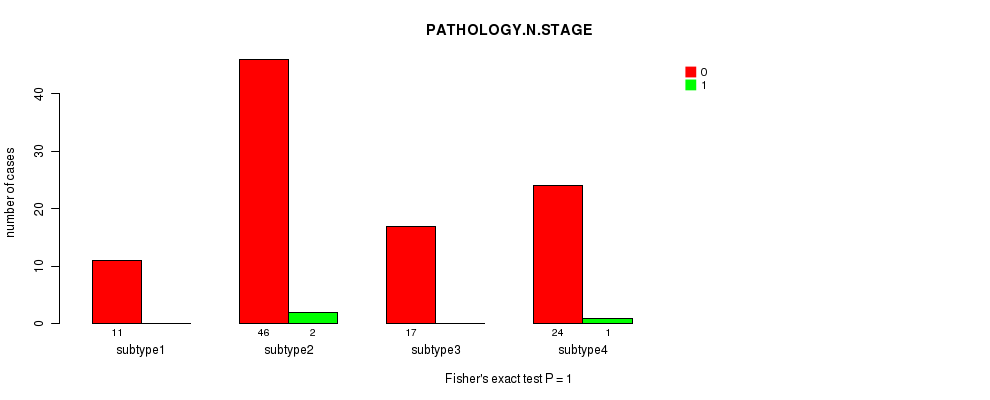
P value = 0.527 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S52. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
| nPatients | M0 | M1 | MX |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 118 | 3 | 29 |
| subtype1 | 10 | 1 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 54 | 2 | 11 |
| subtype3 | 22 | 0 | 4 |
| subtype4 | 32 | 0 | 10 |
Figure S46. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
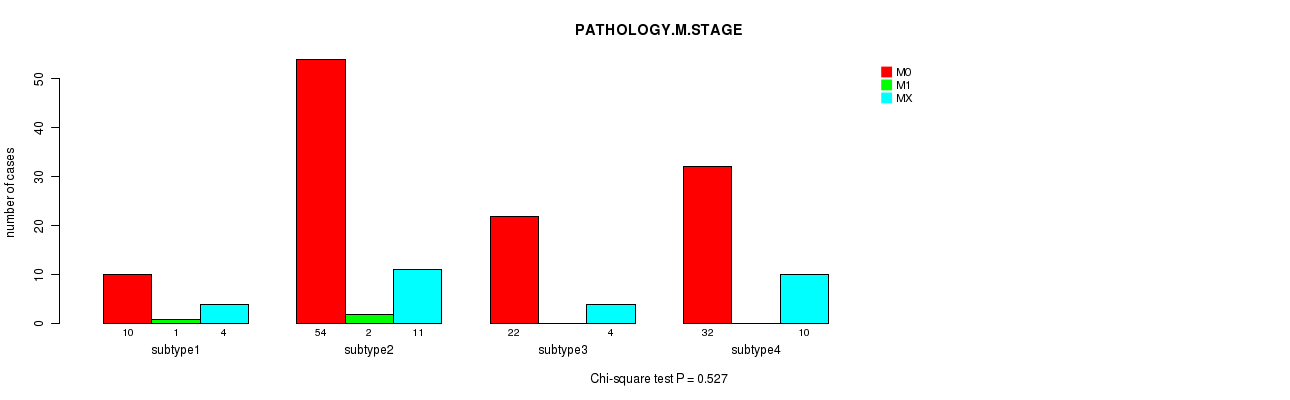
P value = 0.038 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S53. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 58 | 92 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 10 |
| subtype2 | 31 | 36 |
| subtype3 | 4 | 22 |
| subtype4 | 18 | 24 |
Figure S47. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
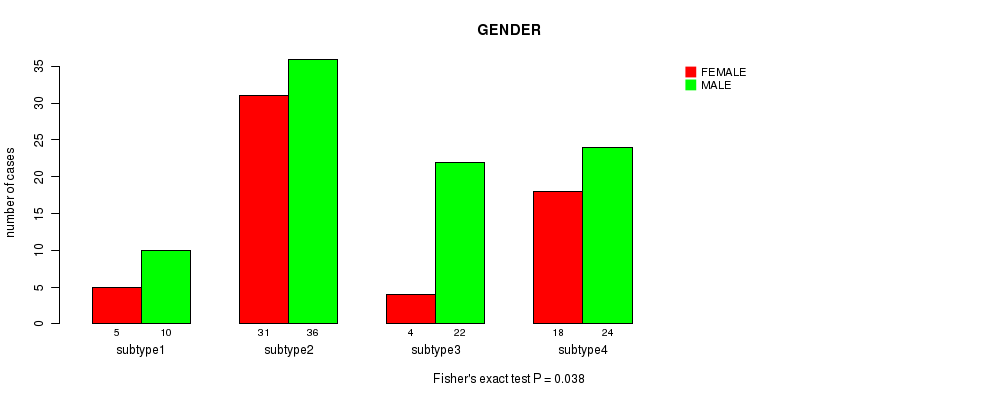
P value = 0.421 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S54. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 122 | 11 | 1 | 11 |
| subtype1 | 9 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 57 | 3 | 1 | 6 |
| subtype3 | 20 | 3 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype4 | 36 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
Figure S48. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
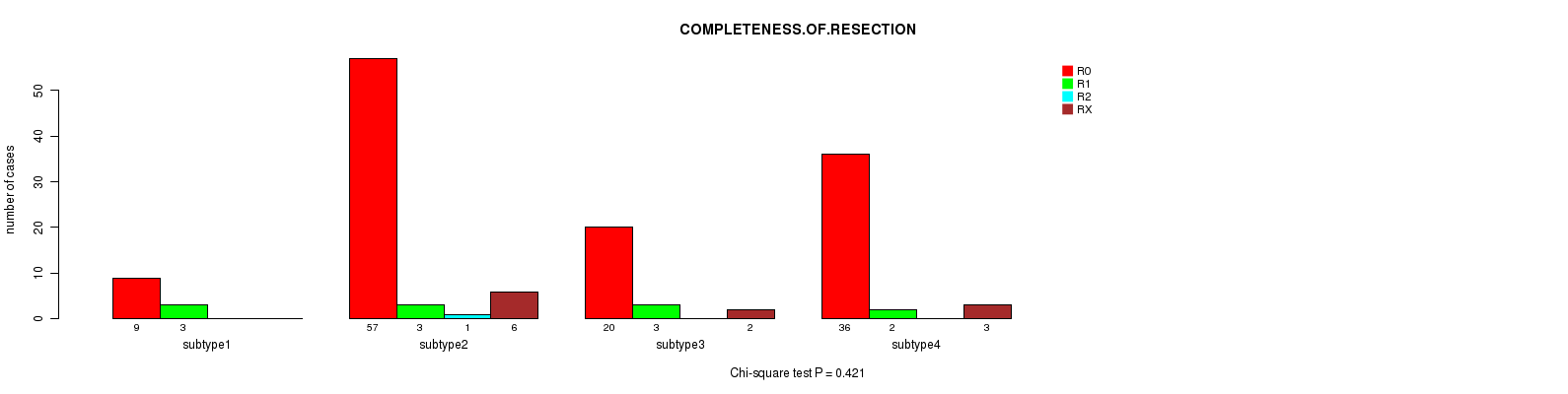
Table S55. Description of clustering approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 15 | 12 | 30 | 25 | 32 | 36 |
P value = 0.541 (logrank test), Q value = 1
Table S56. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 147 | 61 | 0.0 - 113.0 (13.9) |
| subtype1 | 14 | 4 | 0.1 - 75.7 (8.7) |
| subtype2 | 12 | 8 | 0.0 - 83.6 (11.8) |
| subtype3 | 30 | 14 | 0.1 - 101.0 (15.4) |
| subtype4 | 25 | 8 | 0.1 - 80.8 (12.8) |
| subtype5 | 30 | 13 | 0.2 - 113.0 (14.4) |
| subtype6 | 36 | 14 | 0.3 - 107.1 (12.5) |
Figure S49. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
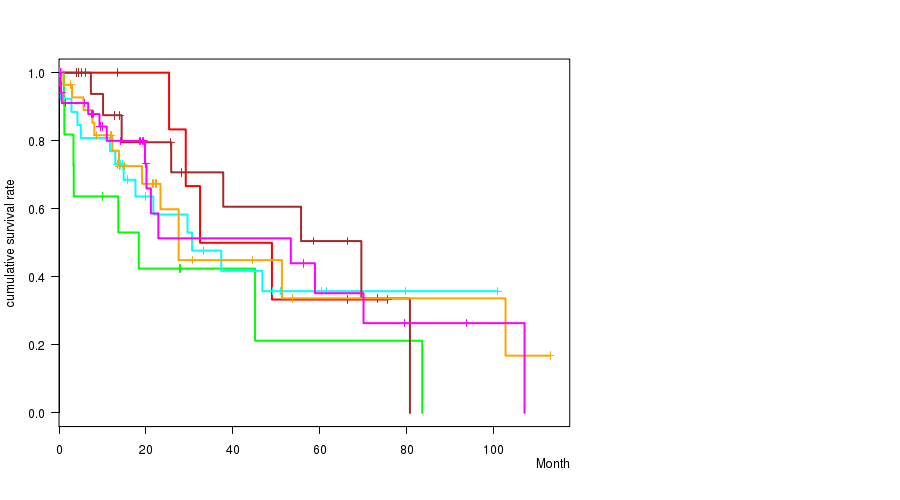
P value = 0.00198 (ANOVA), Q value = 0.11
Table S57. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 148 | 61.3 (14.2) |
| subtype1 | 15 | 55.5 (15.4) |
| subtype2 | 12 | 61.3 (15.5) |
| subtype3 | 30 | 57.0 (17.6) |
| subtype4 | 25 | 56.2 (13.0) |
| subtype5 | 30 | 68.3 (8.3) |
| subtype6 | 36 | 64.8 (11.6) |
Figure S50. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
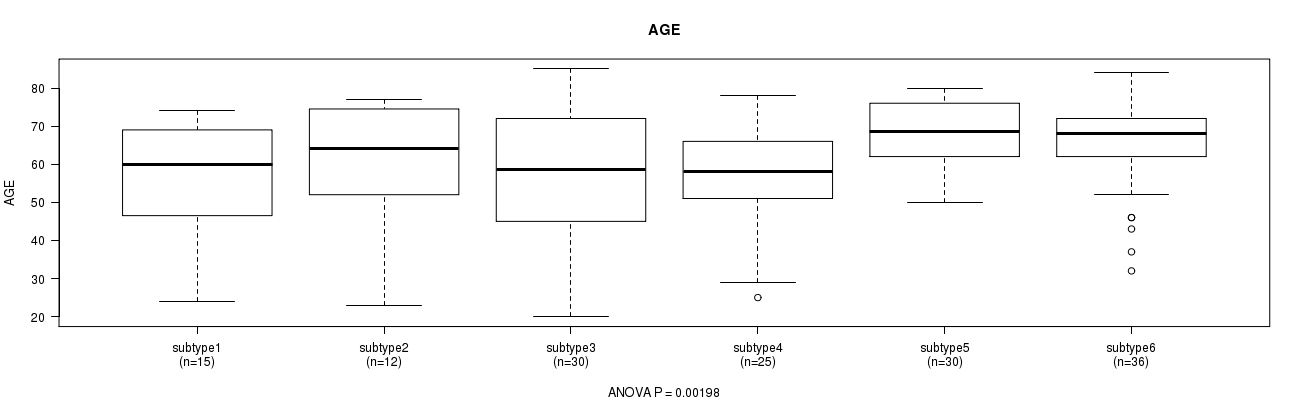
P value = 0.644 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S58. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE II | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA | STAGE IVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 56 | 35 | 2 | 33 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype4 | 11 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 10 | 8 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| subtype6 | 19 | 9 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Figure S51. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
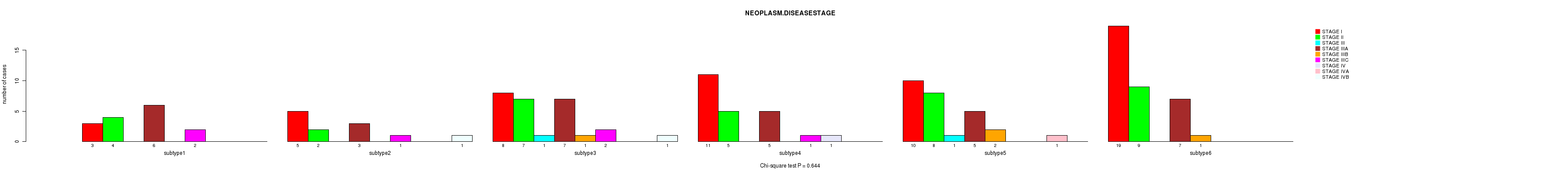
P value = 0.619 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S59. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 59 | 39 | 43 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 2 |
| subtype4 | 12 | 5 | 7 | 1 |
| subtype5 | 11 | 10 | 8 | 3 |
| subtype6 | 19 | 9 | 8 | 0 |
Figure S52. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
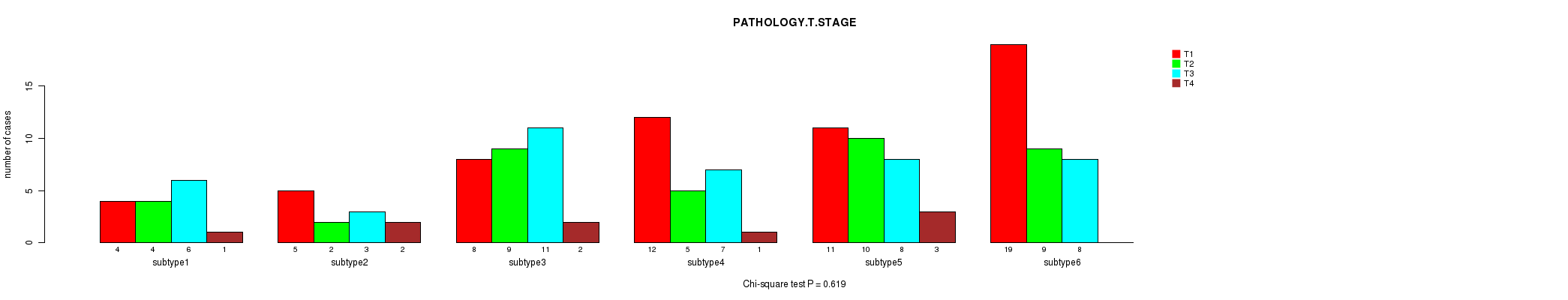
P value = 0.679 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S60. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 98 | 3 |
| subtype1 | 11 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 10 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 22 | 1 |
| subtype4 | 15 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 18 | 1 |
| subtype6 | 22 | 0 |
Figure S53. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
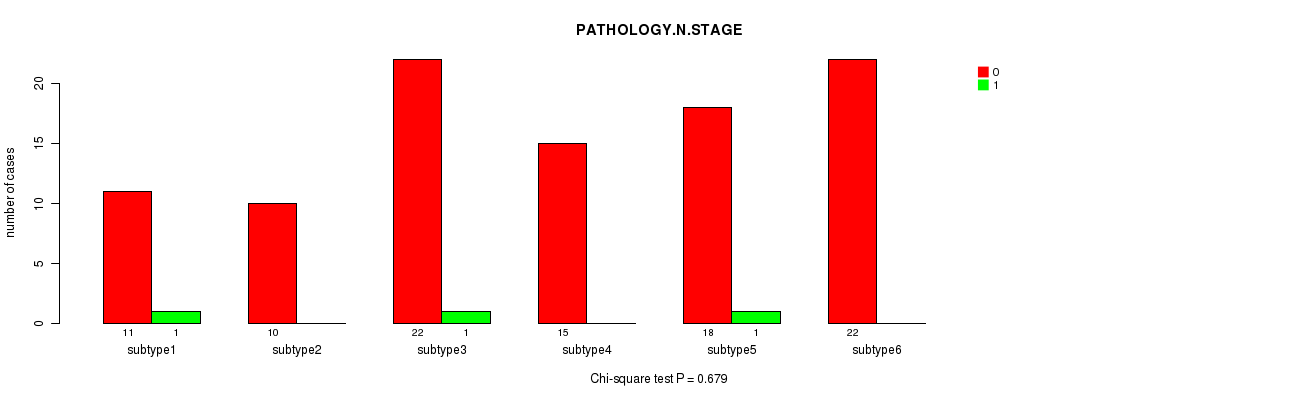
P value = 0.526 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S61. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
| nPatients | M0 | M1 | MX |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 118 | 3 | 29 |
| subtype1 | 14 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 8 | 1 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 25 | 1 | 4 |
| subtype4 | 19 | 1 | 5 |
| subtype5 | 23 | 0 | 9 |
| subtype6 | 29 | 0 | 7 |
Figure S54. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
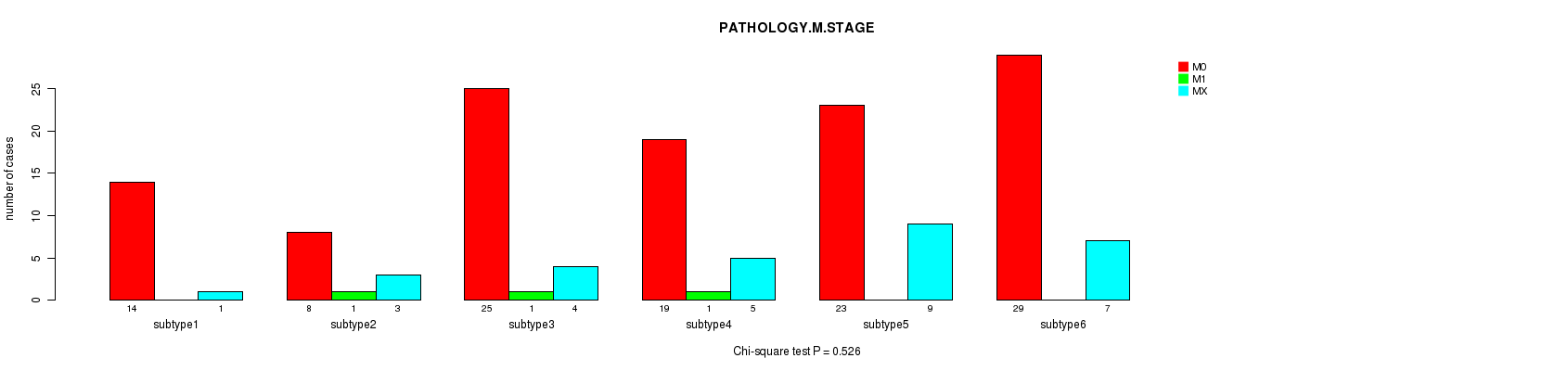
P value = 0.0309 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S62. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 58 | 92 |
| subtype1 | 7 | 8 |
| subtype2 | 4 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 19 | 11 |
| subtype4 | 7 | 18 |
| subtype5 | 12 | 20 |
| subtype6 | 9 | 27 |
Figure S55. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
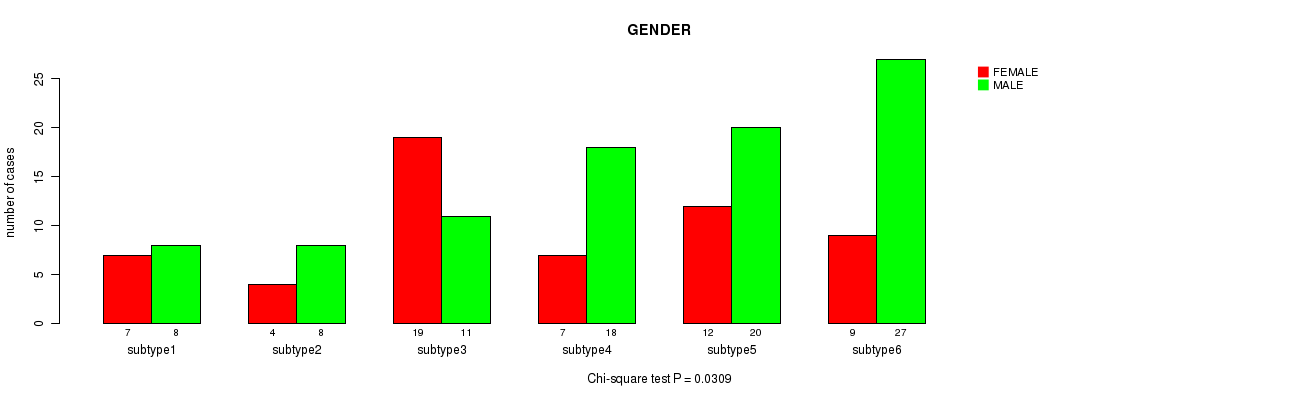
P value = 0.445 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S63. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 122 | 11 | 1 | 11 |
| subtype1 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 25 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype4 | 22 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| subtype5 | 23 | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| subtype6 | 33 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Figure S56. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
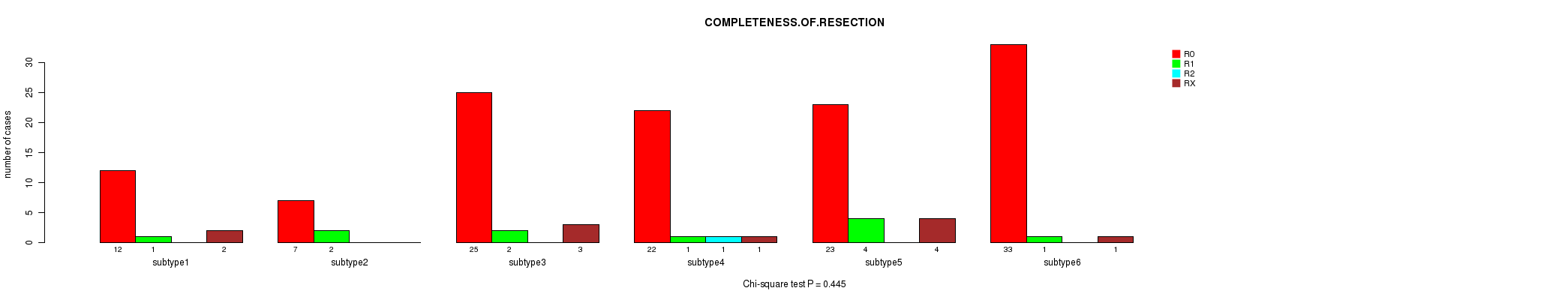
Table S64. Description of clustering approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 13 | 69 | 68 |
P value = 0.144 (logrank test), Q value = 1
Table S65. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 147 | 61 | 0.0 - 113.0 (13.9) |
| subtype1 | 13 | 8 | 0.0 - 83.6 (10.0) |
| subtype2 | 67 | 25 | 0.2 - 113.0 (14.2) |
| subtype3 | 67 | 28 | 0.1 - 101.0 (13.9) |
Figure S57. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
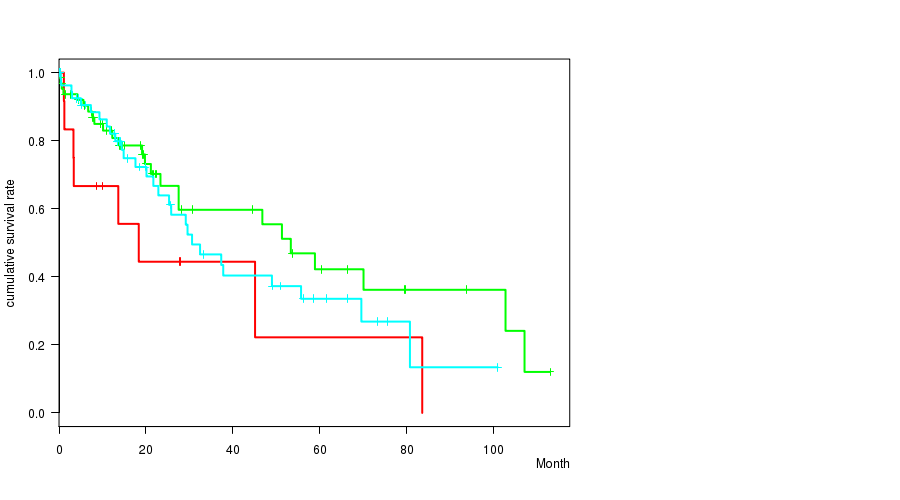
P value = 6.23e-06 (ANOVA), Q value = 0.00039
Table S66. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 148 | 61.3 (14.2) |
| subtype1 | 13 | 61.3 (14.8) |
| subtype2 | 67 | 67.1 (10.4) |
| subtype3 | 68 | 55.5 (15.1) |
Figure S58. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'AGE'
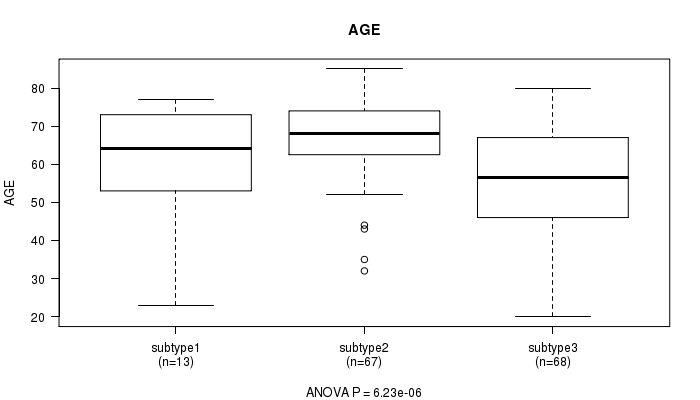
P value = 0.461 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S67. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE II | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA | STAGE IVB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 56 | 35 | 2 | 33 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 27 | 19 | 1 | 13 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 24 | 14 | 1 | 17 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Figure S59. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM.DISEASESTAGE'
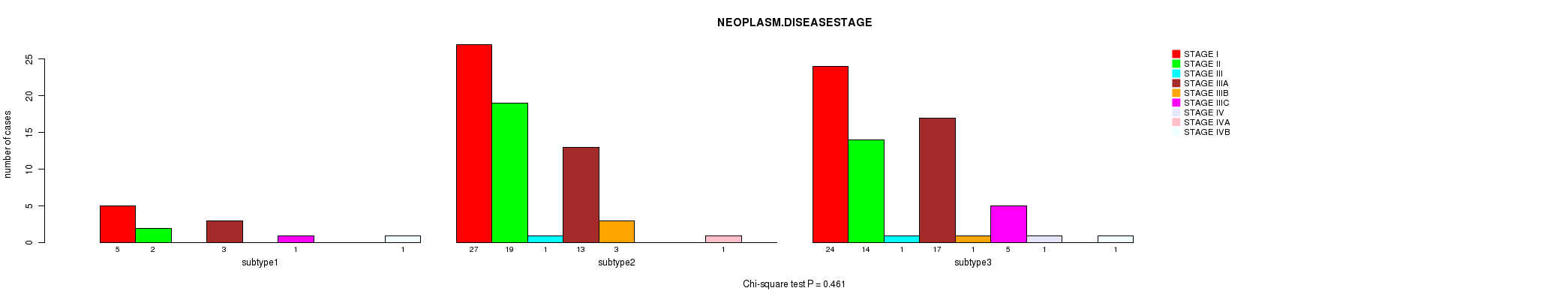
P value = 0.677 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S68. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 59 | 39 | 43 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 28 | 20 | 19 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 26 | 16 | 21 | 5 |
Figure S60. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
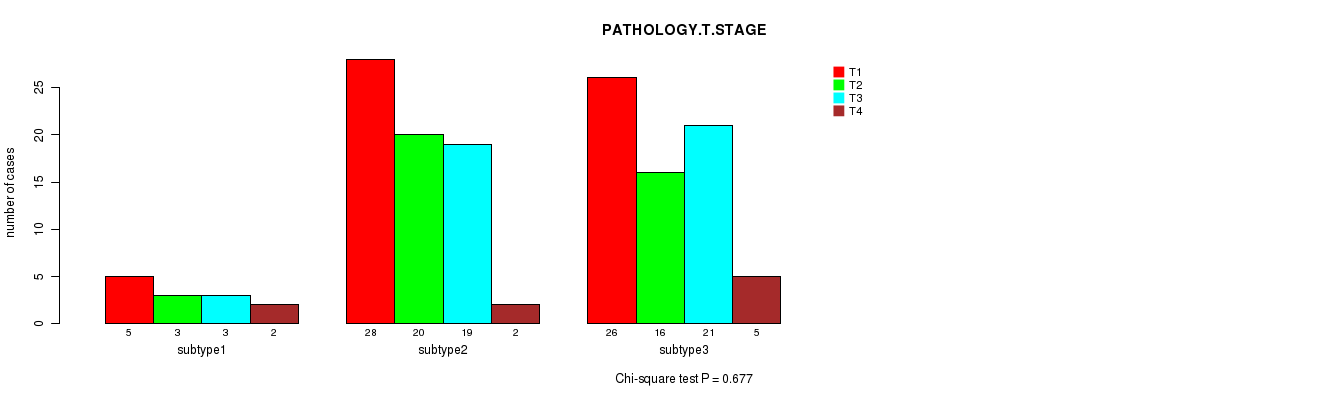
P value = 1 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S69. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 98 | 3 |
| subtype1 | 10 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 42 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 46 | 2 |
Figure S61. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
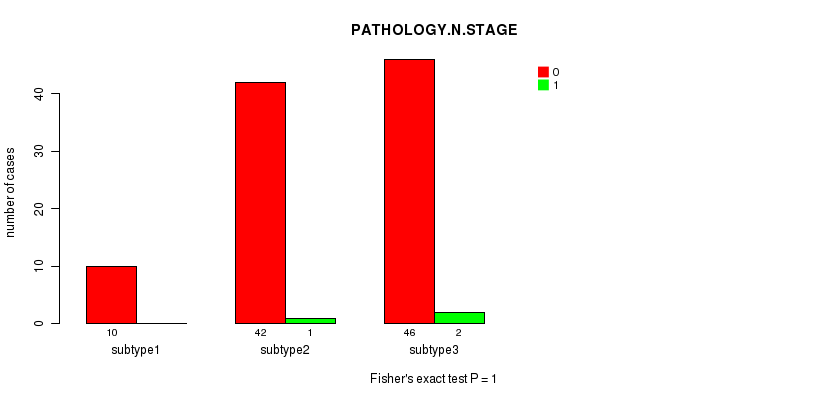
P value = 0.232 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S70. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
| nPatients | M0 | M1 | MX |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 118 | 3 | 29 |
| subtype1 | 8 | 1 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 55 | 0 | 14 |
| subtype3 | 55 | 2 | 11 |
Figure S62. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY.M.STAGE'
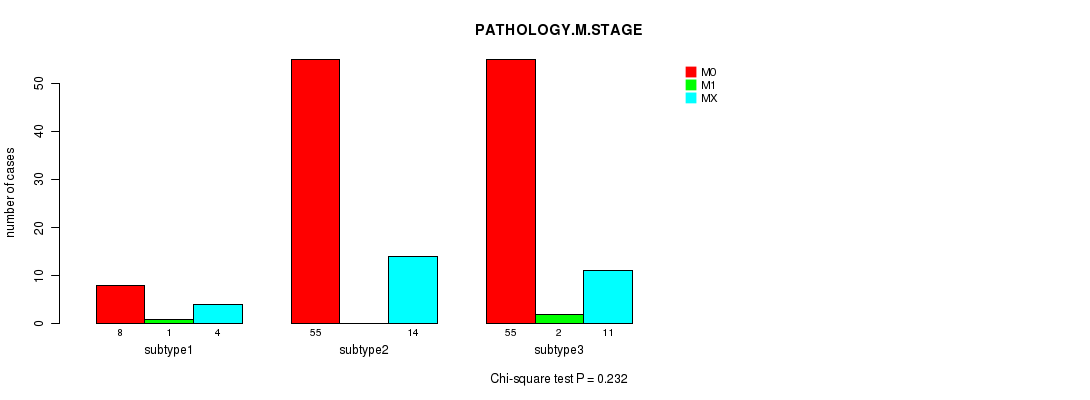
P value = 0.289 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S71. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 58 | 92 |
| subtype1 | 4 | 9 |
| subtype2 | 23 | 46 |
| subtype3 | 31 | 37 |
Figure S63. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
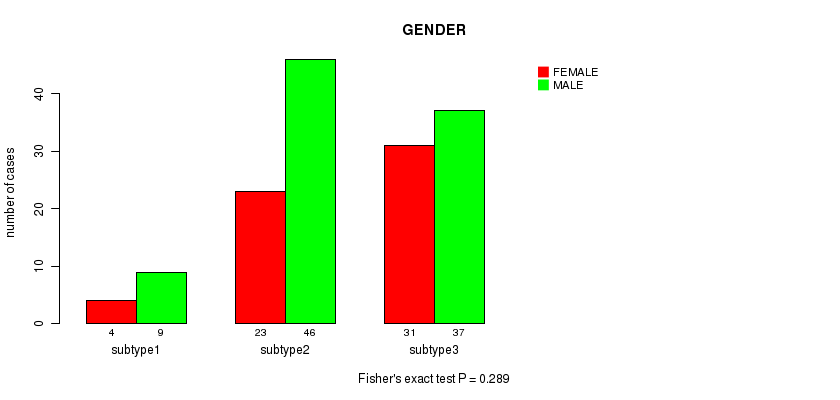
P value = 0.629 (Chi-square test), Q value = 1
Table S72. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 122 | 11 | 1 | 11 |
| subtype1 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 57 | 5 | 0 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 57 | 4 | 1 | 6 |
Figure S64. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
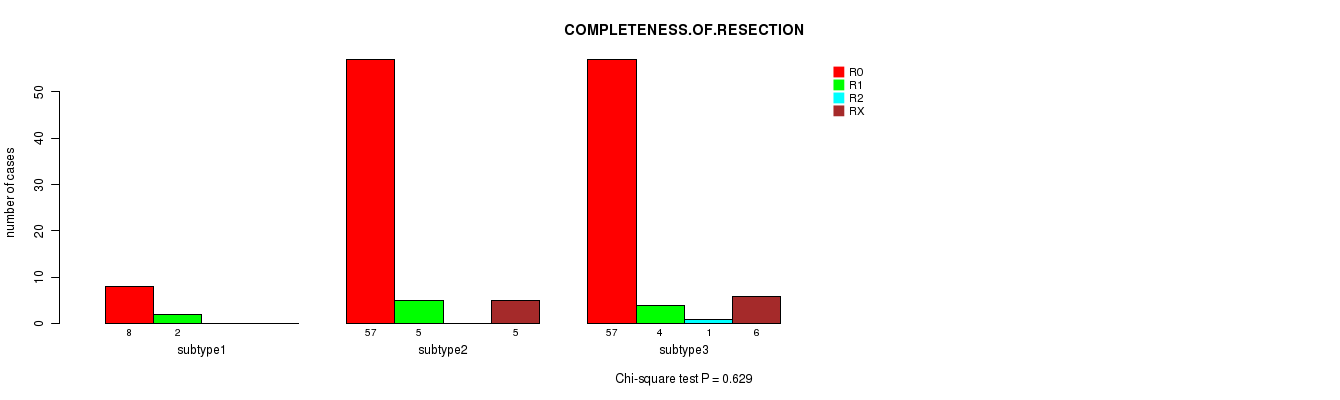
-
Cluster data file = LIHC-TP.mergedcluster.txt
-
Clinical data file = LIHC-TP.merged_data.txt
-
Number of patients = 155
-
Number of clustering approaches = 8
-
Number of selected clinical features = 8
-
Exclude small clusters that include fewer than K patients, K = 3
consensus non-negative matrix factorization clustering approach (Brunet et al. 2004)
Resampling-based clustering method (Monti et al. 2003)
For survival clinical features, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of tumors with and without gene mutations were plotted and the statistical significance P values were estimated by logrank test (Bland and Altman 2004) using the 'survdiff' function in R
For continuous numerical clinical features, one-way analysis of variance (Howell 2002) was applied to compare the clinical values between tumor subtypes using 'anova' function in R
For multi-class clinical features (nominal or ordinal), Chi-square tests (Greenwood and Nikulin 1996) were used to estimate the P values using the 'chisq.test' function in R
For binary clinical features, two-tailed Fisher's exact tests (Fisher 1922) were used to estimate the P values using the 'fisher.test' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.
In addition to the links below, the full results of the analysis summarized in this report can also be downloaded programmatically using firehose_get, or interactively from either the Broad GDAC website or TCGA Data Coordination Center Portal.