This pipeline computes the correlation between cancer subtypes identified by different molecular patterns and selected clinical features.
Testing the association between subtypes identified by 10 different clustering approaches and 13 clinical features across 274 patients, 28 significant findings detected with P value < 0.05 and Q value < 0.25.
-
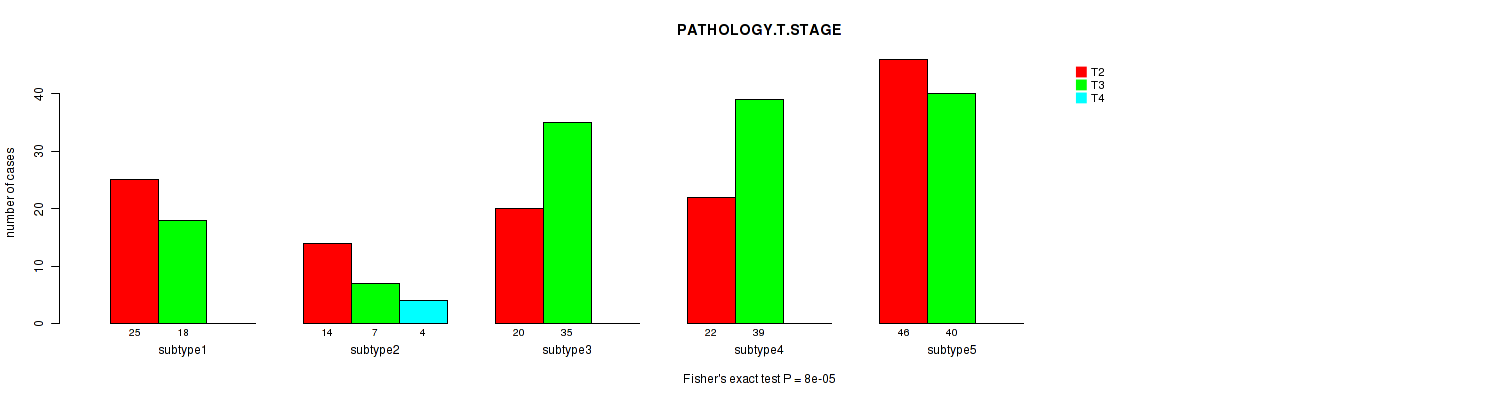
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes'. These subtypes correlate to 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE', 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE', 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION', 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES', 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED', 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY', and 'GLEASON_SCORE'.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'METHLYATION CNMF'. These subtypes correlate to 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED', 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY', 'GLEASON_SCORE', and 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'.
-
CNMF clustering analysis on RPPA data identified 3 subtypes that correlate to 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED', 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY', and 'GLEASON_SCORE'.
-
Consensus hierarchical clustering analysis on RPPA data identified 3 subtypes that correlate to 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED', 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY', and 'GLEASON_SCORE'.
-
CNMF clustering analysis on sequencing-based mRNA expression data identified 3 subtypes that do not correlate to any clinical features.
-
Consensus hierarchical clustering analysis on sequencing-based mRNA expression data identified 3 subtypes that correlate to 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'.
-
5 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRSEQ CNMF'. These subtypes correlate to 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE' and 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL'. These subtypes correlate to 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE', 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED', 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY', and 'GLEASON_SCORE'.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes'. These subtypes do not correlate to any clinical features.
-
5 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes'. These subtypes correlate to 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE', 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED', 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY', and 'GLEASON_SCORE'.
Table 1. Get Full Table Overview of the association between subtypes identified by 10 different clustering approaches and 13 clinical features. Shown in the table are P values (Q values). Thresholded by P value < 0.05 and Q value < 0.25, 28 significant findings detected.
|
Clinical Features |
Statistical Tests |
Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes |
METHLYATION CNMF |
RPPA CNMF subtypes |
RPPA cHierClus subtypes |
RNAseq CNMF subtypes |
RNAseq cHierClus subtypes |
MIRSEQ CNMF |
MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL |
MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes |
MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes |
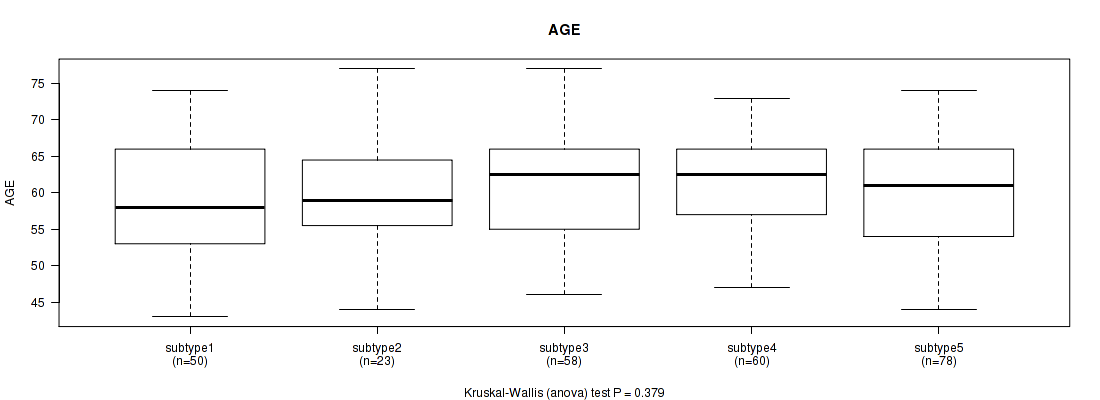
| AGE | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.215 (1.00) |
0.00373 (0.366) |
0.0791 (1.00) |
0.0149 (1.00) |
0.496 (1.00) |
0.57 (1.00) |
0.379 (1.00) |
0.301 (1.00) |
0.0573 (1.00) |
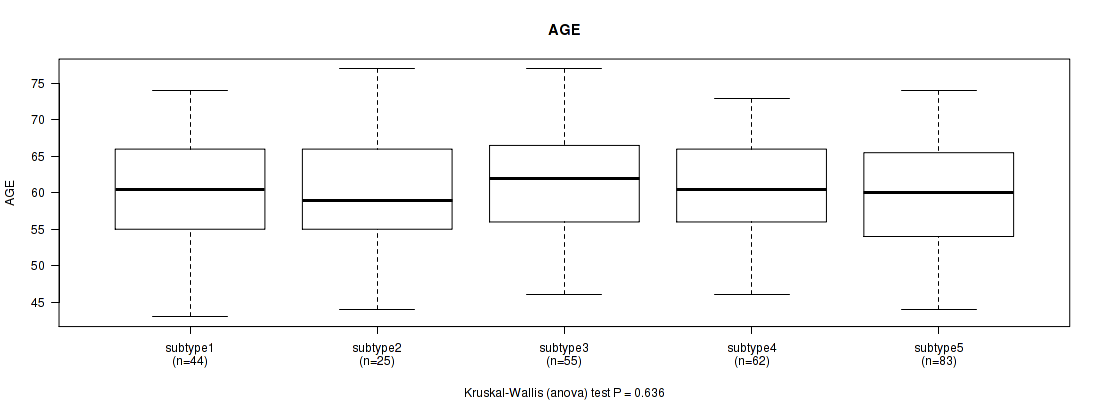
0.636 (1.00) |
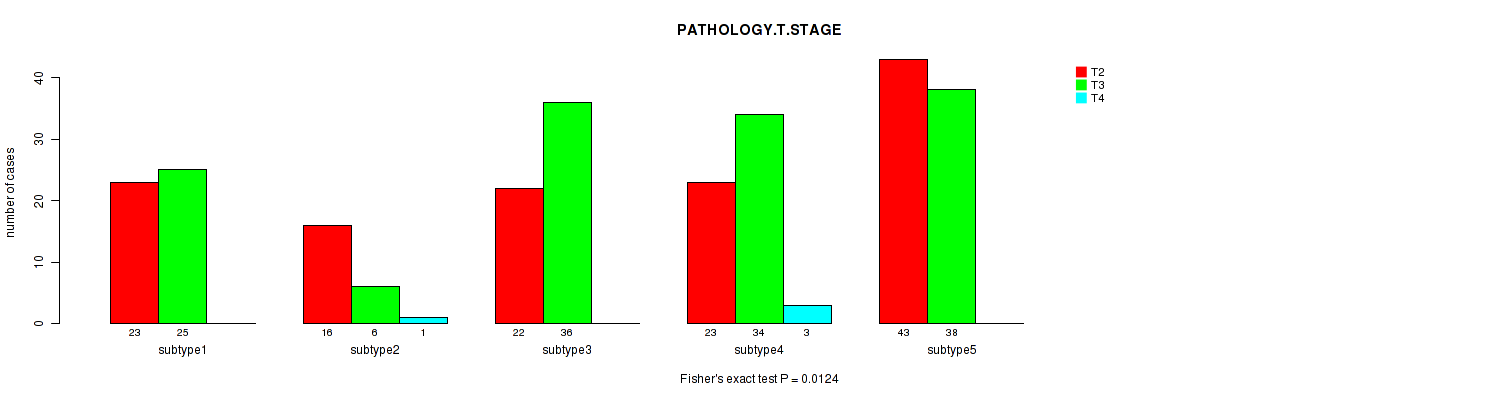
| PATHOLOGY T STAGE | Fisher's exact test |
2e-05 (0.00244) |
0.0486 (1.00) |
0.0061 (0.573) |
0.0204 (1.00) |
0.017 (1.00) |
0.0087 (0.783) |
0.0124 (1.00) |
0.00014 (0.0164) |
0.419 (1.00) |
8e-05 (0.00952) |
| PATHOLOGY N STAGE | Fisher's exact test |
0.00016 (0.0184) |
0.0138 (1.00) |
0.0542 (1.00) |
0.0163 (1.00) |
0.00909 (0.809) |
0.112 (1.00) |
0.193 (1.00) |
0.00299 (0.305) |
0.113 (1.00) |
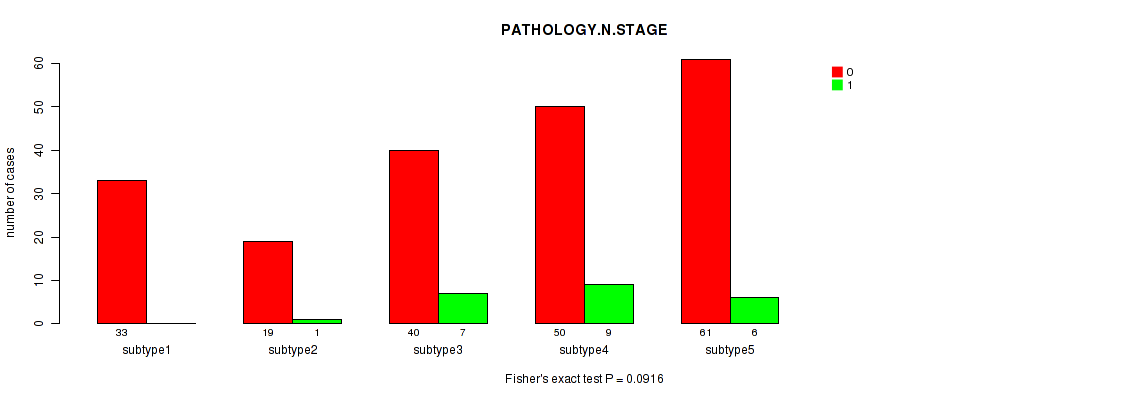
0.0916 (1.00) |
| HISTOLOGICAL TYPE | Fisher's exact test |
0.828 (1.00) |
0.678 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.336 (1.00) |
0.284 (1.00) |
0.33 (1.00) |
0.00064 (0.0691) |
0.577 (1.00) |
0.0408 (1.00) |
0.014 (1.00) |
| COMPLETENESS OF RESECTION | Fisher's exact test |
0.00112 (0.119) |
0.461 (1.00) |
0.0204 (1.00) |
0.00354 (0.35) |
0.438 (1.00) |
0.251 (1.00) |
0.0301 (1.00) |
0.768 (1.00) |
0.435 (1.00) |
0.588 (1.00) |
| NUMBER OF LYMPH NODES | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.000169 (0.0193) |
0.0235 (1.00) |
0.0381 (1.00) |
0.0119 (1.00) |
0.016 (1.00) |
0.0887 (1.00) |
0.148 (1.00) |
0.00463 (0.444) |
0.0953 (1.00) |
0.134 (1.00) |
| GLEASON SCORE COMBINED | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
1.39e-09 (1.8e-07) |
0.00111 (0.119) |
0.00011 (0.013) |
4.87e-05 (0.00584) |
0.0543 (1.00) |
0.0062 (0.577) |
0.0301 (1.00) |
8.63e-06 (0.00109) |
0.0034 (0.34) |
0.000299 (0.0332) |
| GLEASON SCORE PRIMARY | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
2.38e-09 (3.04e-07) |
0.000468 (0.051) |
1.56e-05 (0.00194) |
1.14e-05 (0.00142) |
0.00443 (0.43) |
0.000183 (0.0207) |
0.000358 (0.0394) |
1.63e-05 (0.00201) |
0.00568 (0.54) |
0.00148 (0.154) |
| GLEASON SCORE SECONDARY | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.0806 (1.00) |
0.423 (1.00) |
0.45 (1.00) |
0.157 (1.00) |
0.831 (1.00) |
0.45 (1.00) |
0.25 (1.00) |
0.28 (1.00) |
0.333 (1.00) |
0.264 (1.00) |
| GLEASON SCORE | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
2.08e-10 (2.71e-08) |
0.0015 (0.154) |
4.74e-05 (0.00573) |
7.53e-06 (0.000956) |
0.0301 (1.00) |
0.0124 (1.00) |
0.034 (1.00) |
0.00014 (0.0164) |
0.00761 (0.7) |
0.00113 (0.119) |
| PSA RESULT PREOP | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.0202 (1.00) |
0.000198 (0.0222) |
0.0443 (1.00) |
0.0303 (1.00) |
0.00335 (0.338) |
0.02 (1.00) |
0.0118 (1.00) |
0.188 (1.00) |
0.775 (1.00) |
0.0185 (1.00) |
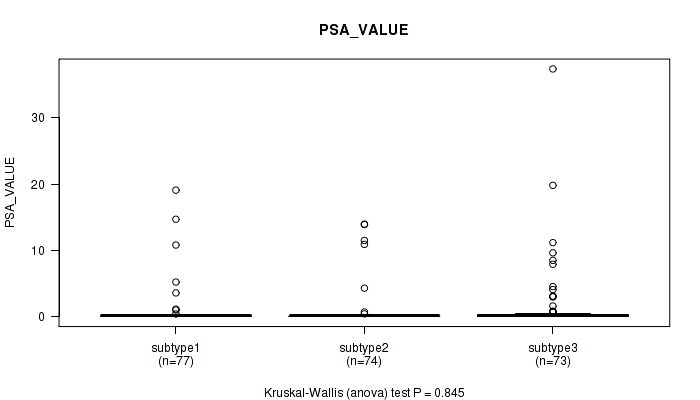
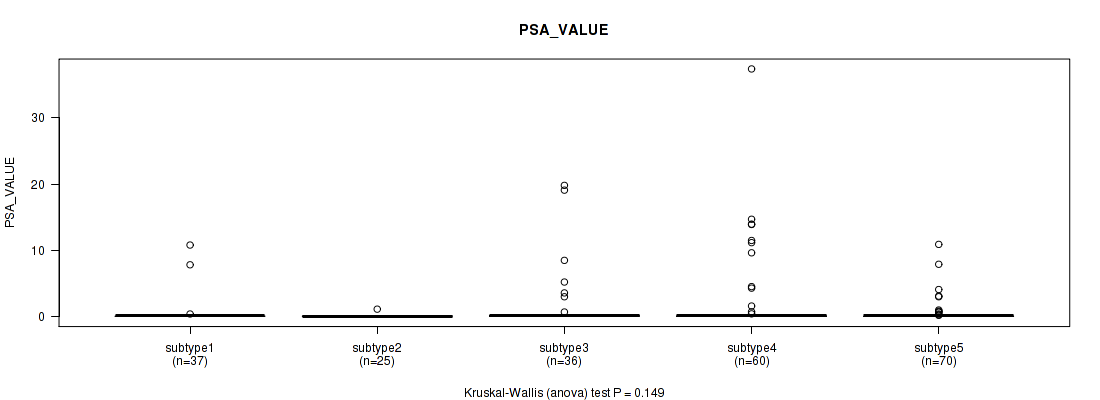
| PSA VALUE | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.241 (1.00) |
0.367 (1.00) |
0.163 (1.00) |
0.434 (1.00) |
0.264 (1.00) |
0.845 (1.00) |
0.131 (1.00) |
0.0193 (1.00) |
0.668 (1.00) |
0.149 (1.00) |
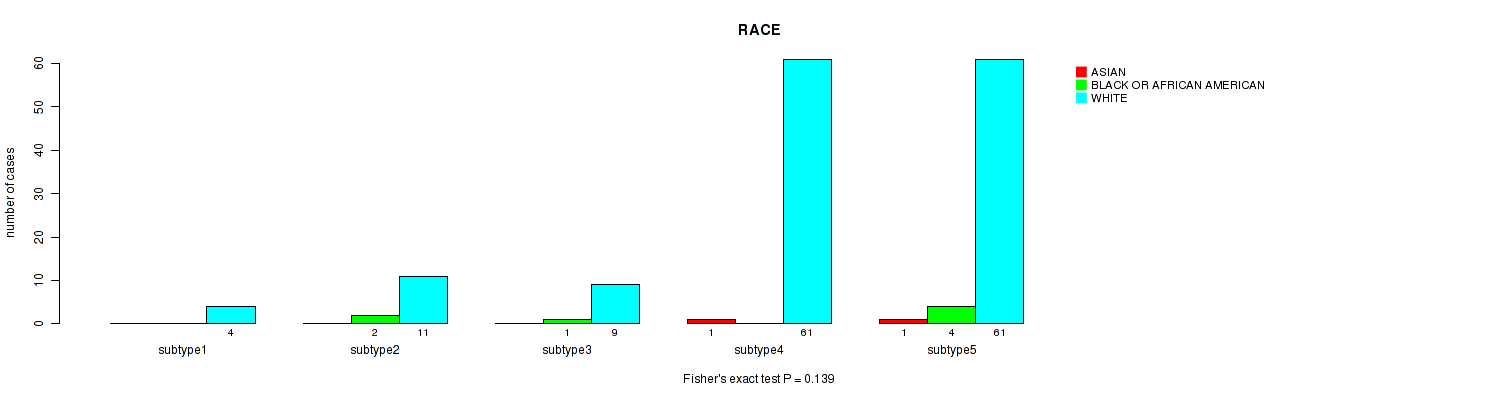
| RACE | Fisher's exact test |
0.782 (1.00) |
0.745 (1.00) |
0.0271 (1.00) |
0.00836 (0.761) |
0.329 (1.00) |
0.0104 (0.916) |
0.417 (1.00) |
0.824 (1.00) |
0.828 (1.00) |
0.139 (1.00) |
Table S1. Description of clustering approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 165 | 59 | 47 |
P value = 0.215 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S2. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 268 | 60.3 (7.0) |
| subtype1 | 162 | 59.8 (6.9) |
| subtype2 | 59 | 61.3 (6.5) |
| subtype3 | 47 | 60.7 (7.7) |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
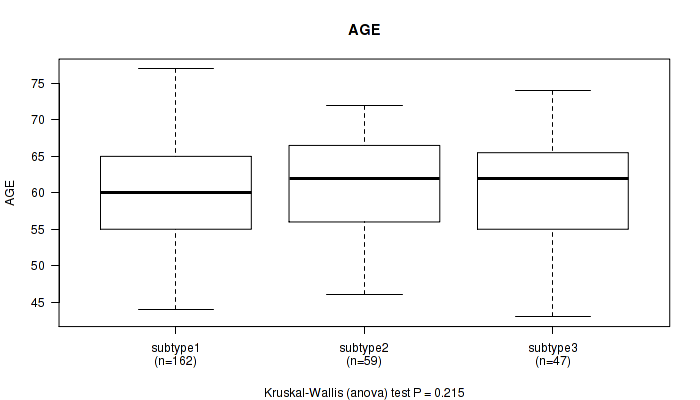
P value = 2e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0024
Table S3. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 128 | 136 | 5 |
| subtype1 | 89 | 72 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 12 | 45 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 27 | 19 | 1 |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
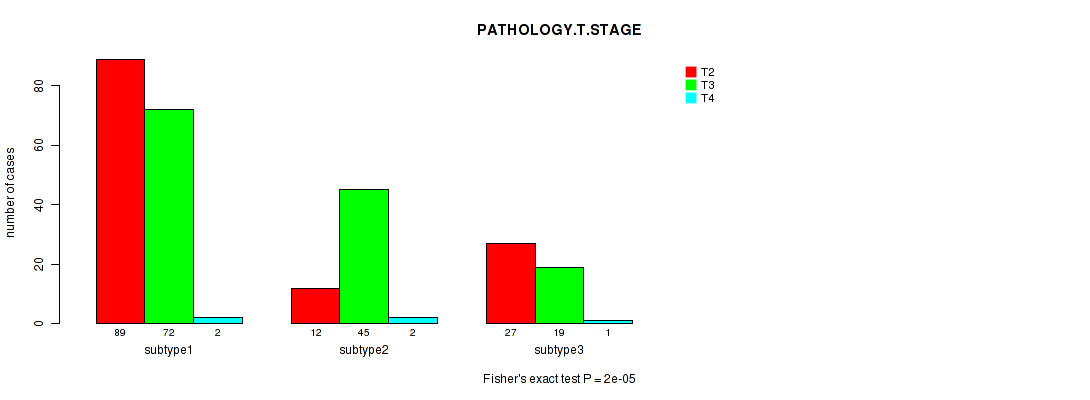
P value = 0.00016 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.018
Table S4. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 201 | 24 |
| subtype1 | 123 | 5 |
| subtype2 | 43 | 14 |
| subtype3 | 35 | 5 |
Figure S3. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
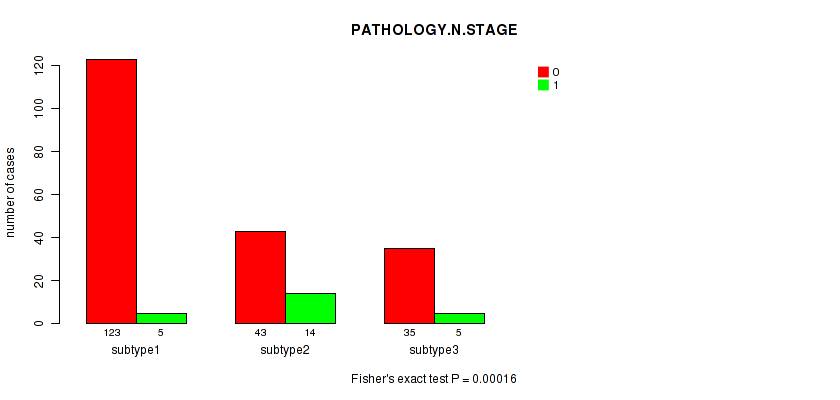
P value = 0.828 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S5. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 5 | 266 |
| subtype1 | 4 | 161 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 58 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 47 |
Figure S4. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
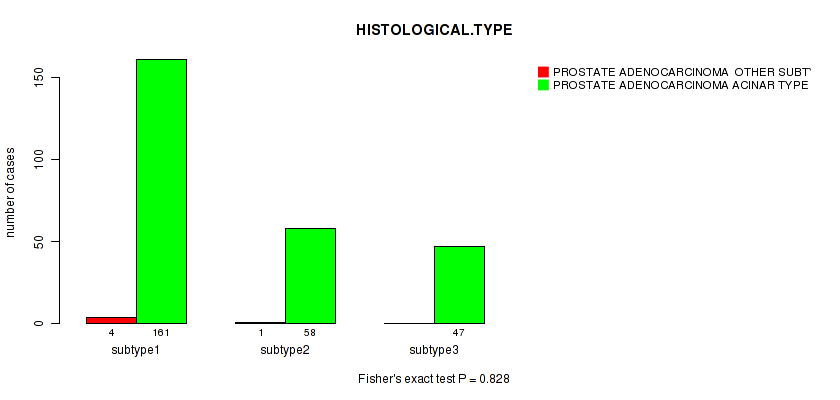
P value = 0.00112 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.12
Table S6. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 192 | 57 | 3 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 129 | 21 | 2 | 5 |
| subtype2 | 35 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 28 | 16 | 1 | 1 |
Figure S5. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
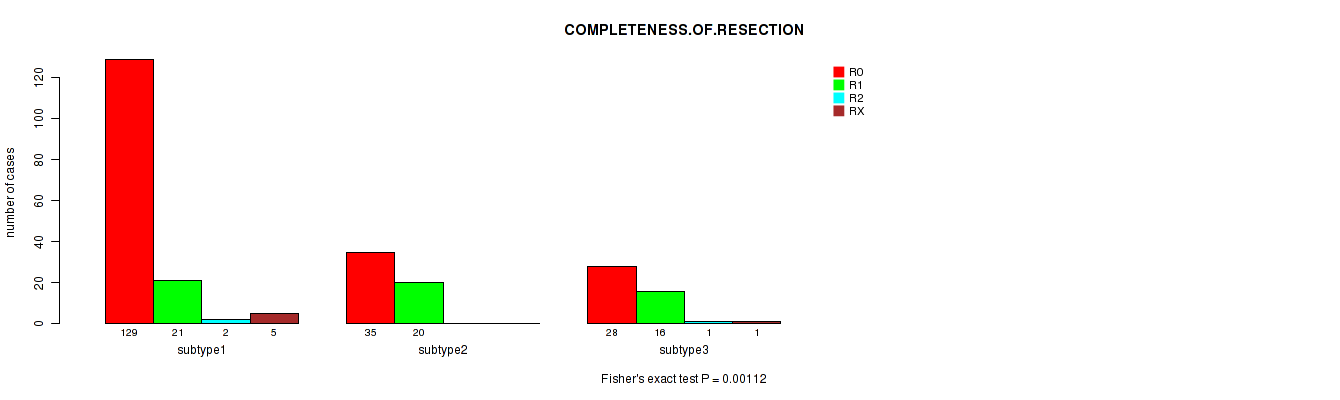
P value = 0.000169 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.019
Table S7. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 223 | 0.2 (1.2) |
| subtype1 | 126 | 0.1 (0.4) |
| subtype2 | 57 | 0.7 (2.2) |
| subtype3 | 40 | 0.1 (0.3) |
Figure S6. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
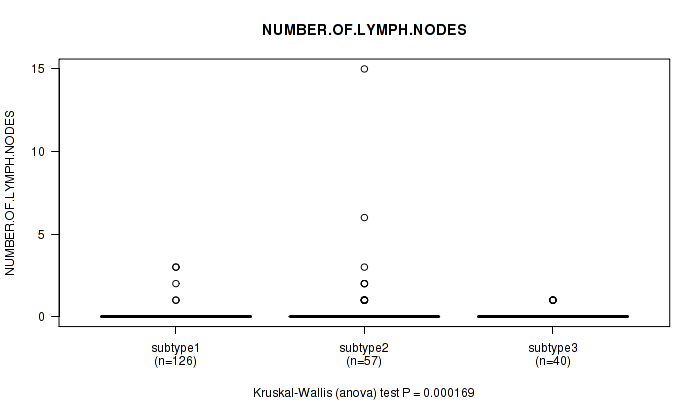
P value = 1.39e-09 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1.8e-07
Table S8. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 271 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 165 | 7.1 (0.7) |
| subtype2 | 59 | 7.9 (0.9) |
| subtype3 | 47 | 7.2 (0.6) |
Figure S7. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
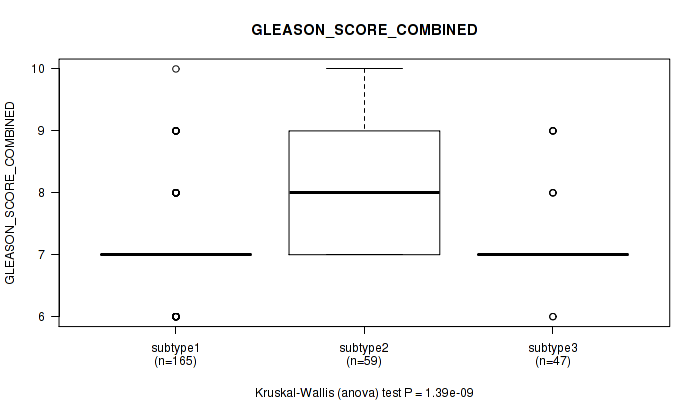
P value = 2.38e-09 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 3e-07
Table S9. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 271 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 165 | 3.4 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 59 | 3.9 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 47 | 3.4 (0.5) |
Figure S8. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
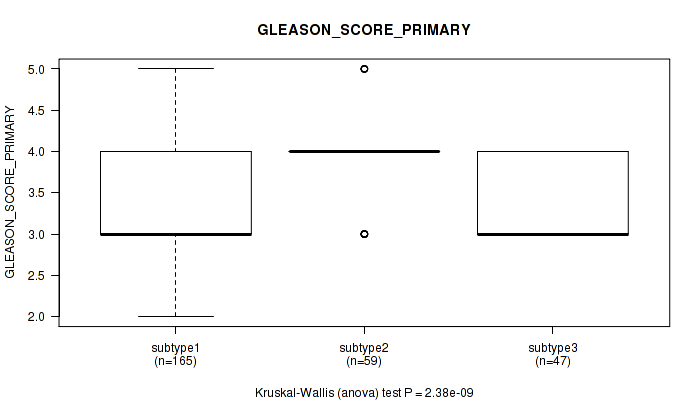
P value = 0.0806 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S10. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 271 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 165 | 3.7 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 59 | 4.0 (0.7) |
| subtype3 | 47 | 3.8 (0.6) |
Figure S9. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
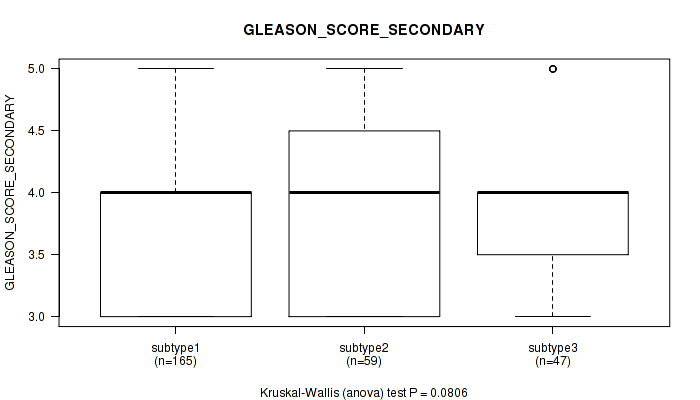
P value = 2.08e-10 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 2.7e-08
Table S11. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 271 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 165 | 7.1 (0.7) |
| subtype2 | 59 | 8.0 (0.9) |
| subtype3 | 47 | 7.2 (0.7) |
Figure S10. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
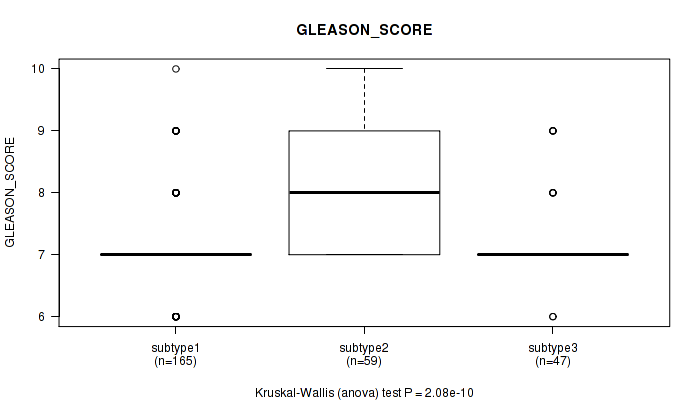
P value = 0.0202 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S12. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 269 | 10.4 (11.0) |
| subtype1 | 164 | 9.3 (10.7) |
| subtype2 | 59 | 14.1 (13.6) |
| subtype3 | 46 | 9.4 (6.8) |
Figure S11. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
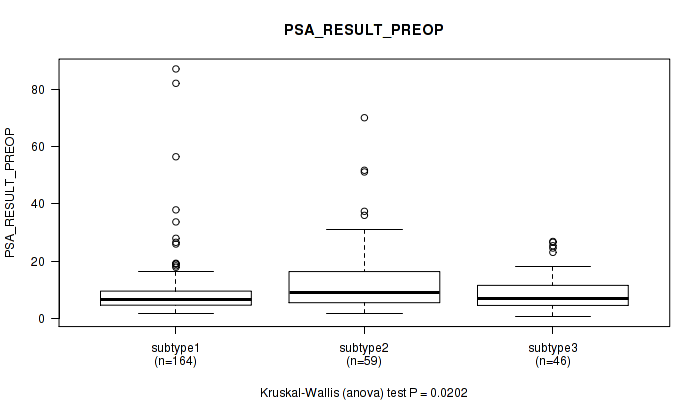
P value = 0.241 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S13. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 226 | 1.1 (3.9) |
| subtype1 | 144 | 0.8 (2.8) |
| subtype2 | 46 | 2.1 (6.5) |
| subtype3 | 36 | 1.0 (3.1) |
Figure S12. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
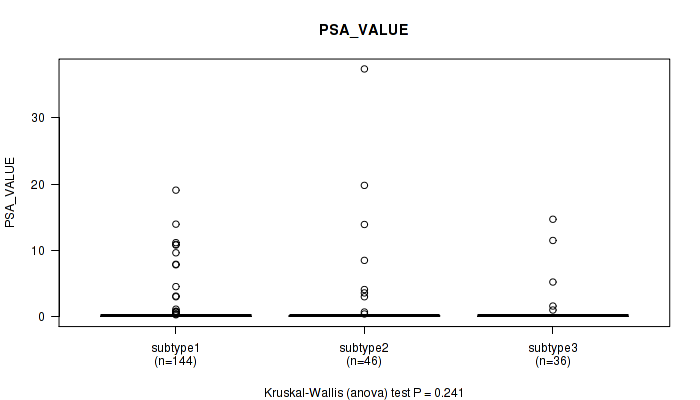
P value = 0.782 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S14. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 7 | 146 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 3 | 87 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 2 | 32 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 2 | 27 |
Figure S13. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
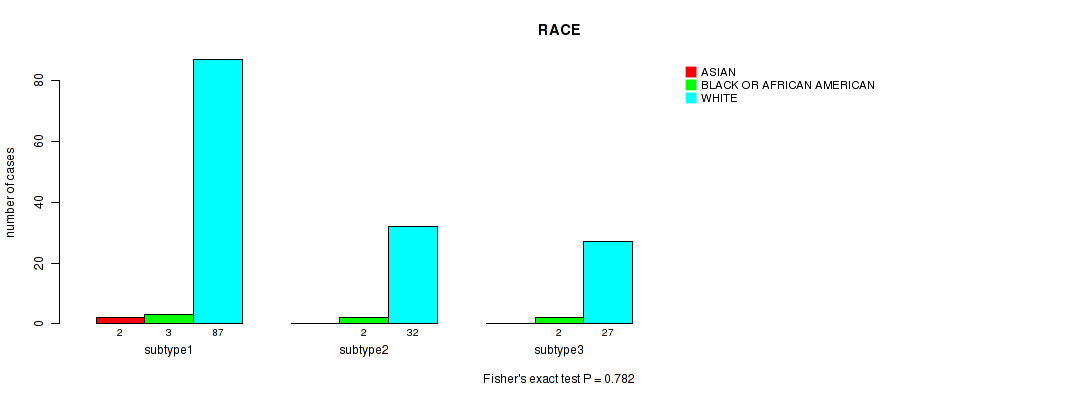
Table S15. Description of clustering approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 75 | 89 | 101 |
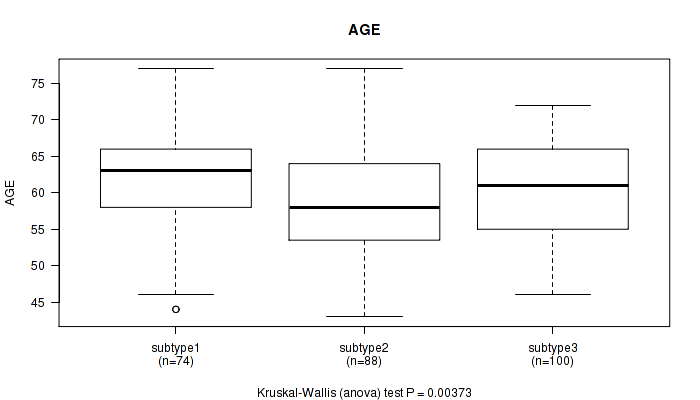
P value = 0.00373 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.37
Table S16. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 262 | 60.2 (7.0) |
| subtype1 | 74 | 61.9 (7.0) |
| subtype2 | 88 | 58.5 (7.0) |
| subtype3 | 100 | 60.5 (6.8) |
Figure S14. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
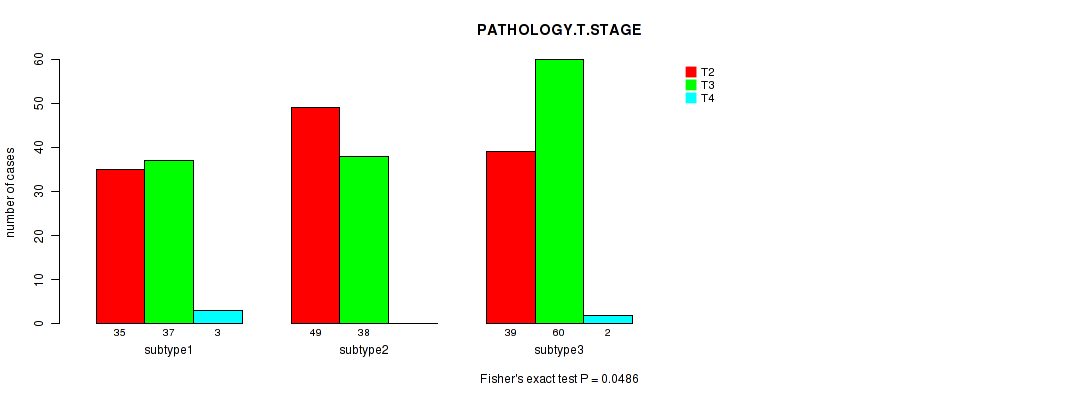
P value = 0.0486 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S17. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 123 | 135 | 5 |
| subtype1 | 35 | 37 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 49 | 38 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 39 | 60 | 2 |
Figure S15. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
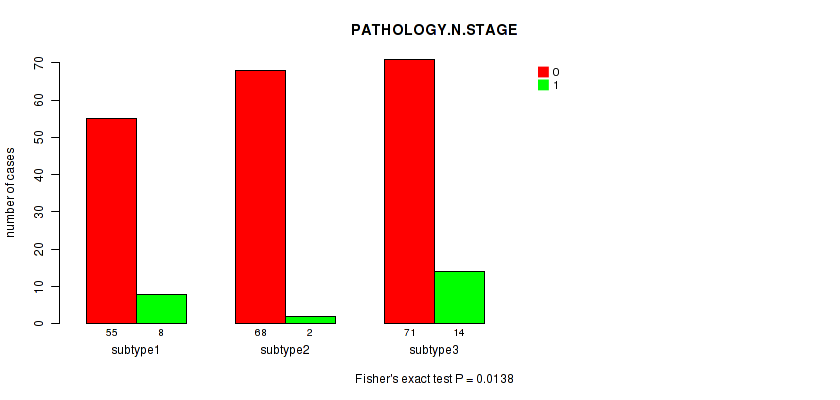
P value = 0.0138 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S18. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 194 | 24 |
| subtype1 | 55 | 8 |
| subtype2 | 68 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 71 | 14 |
Figure S16. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
P value = 0.678 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S19. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 259 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 73 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 88 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 98 |
Figure S17. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
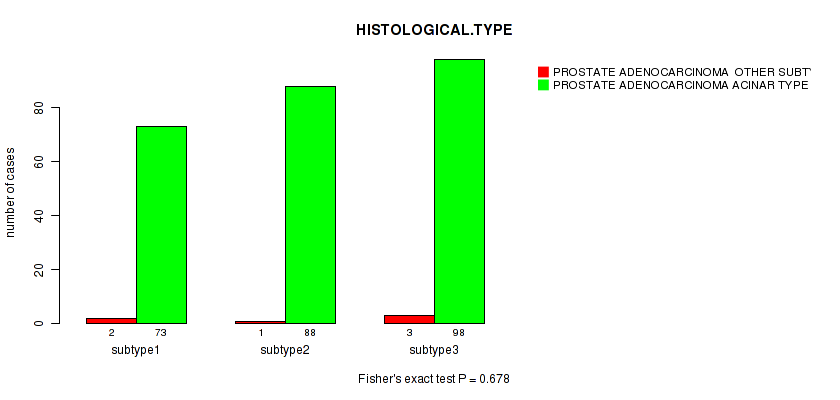
P value = 0.461 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S20. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 188 | 56 | 2 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 49 | 21 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 66 | 16 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 73 | 19 | 2 | 3 |
Figure S18. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
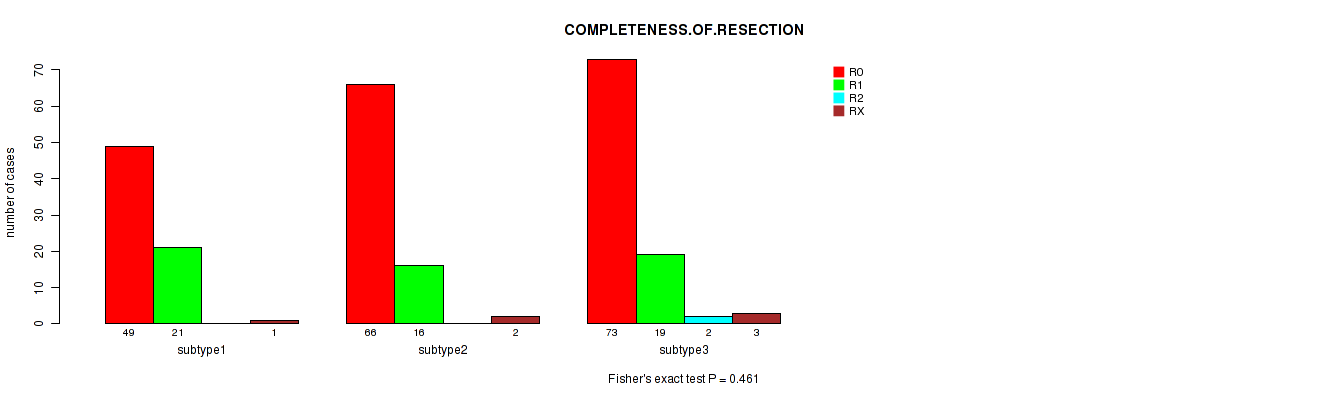
P value = 0.0235 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S21. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 216 | 0.2 (1.2) |
| subtype1 | 63 | 0.2 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 68 | 0.0 (0.2) |
| subtype3 | 85 | 0.5 (1.8) |
Figure S19. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
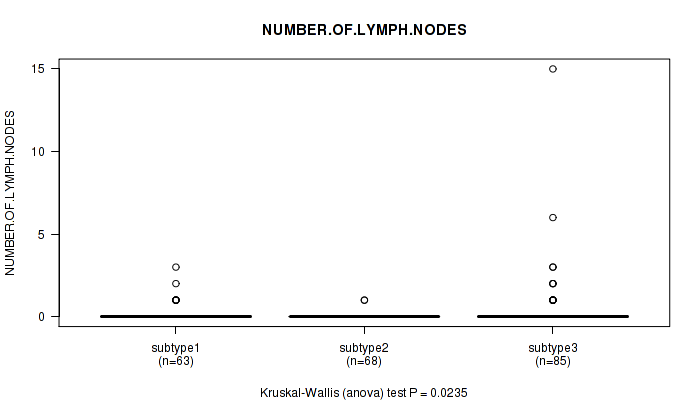
P value = 0.00111 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.12
Table S22. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 265 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 75 | 7.5 (0.9) |
| subtype2 | 89 | 7.0 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 101 | 7.4 (0.9) |
Figure S20. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
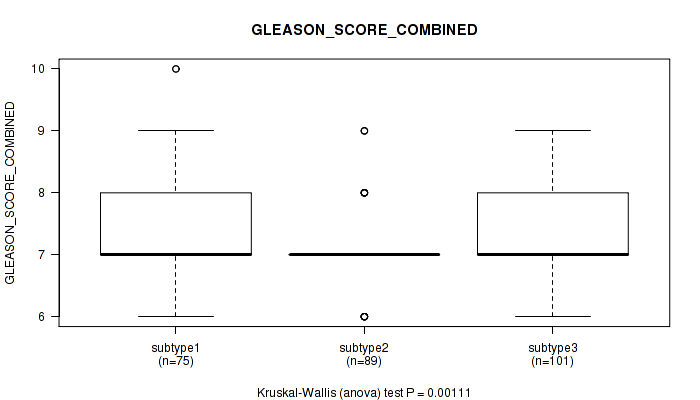
P value = 0.000468 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.051
Table S23. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 265 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 75 | 3.7 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 89 | 3.3 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 101 | 3.5 (0.6) |
Figure S21. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
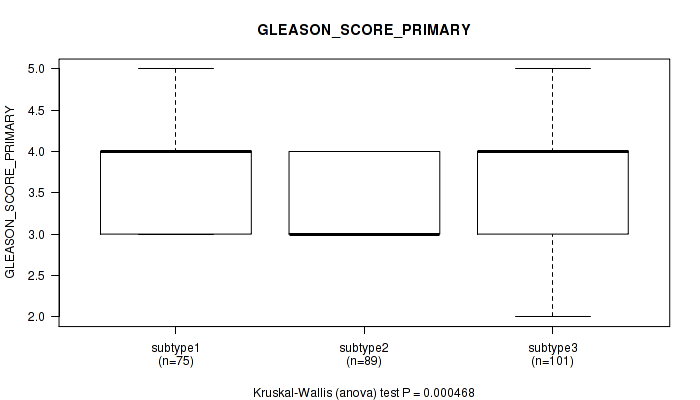
P value = 0.423 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S24. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 265 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 75 | 3.9 (0.7) |
| subtype2 | 89 | 3.7 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 101 | 3.8 (0.6) |
Figure S22. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
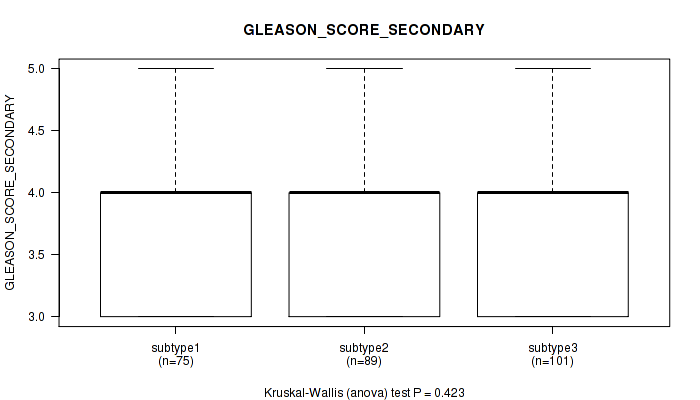
P value = 0.0015 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.15
Table S25. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 265 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 75 | 7.6 (1.0) |
| subtype2 | 89 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 101 | 7.4 (0.9) |
Figure S23. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
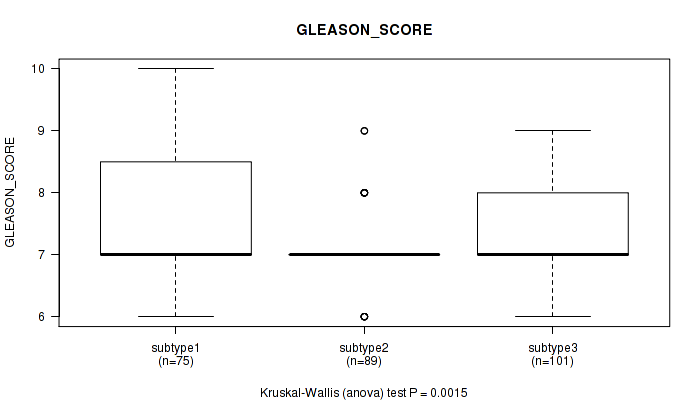
P value = 0.000198 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.022
Table S26. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 263 | 10.3 (10.5) |
| subtype1 | 75 | 14.8 (15.4) |
| subtype2 | 89 | 6.9 (3.7) |
| subtype3 | 99 | 9.9 (8.7) |
Figure S24. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
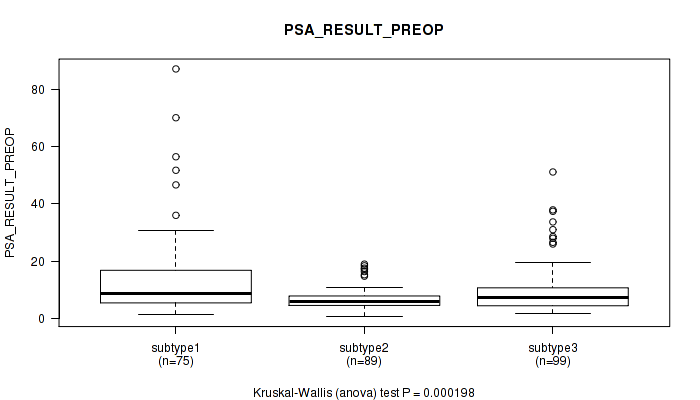
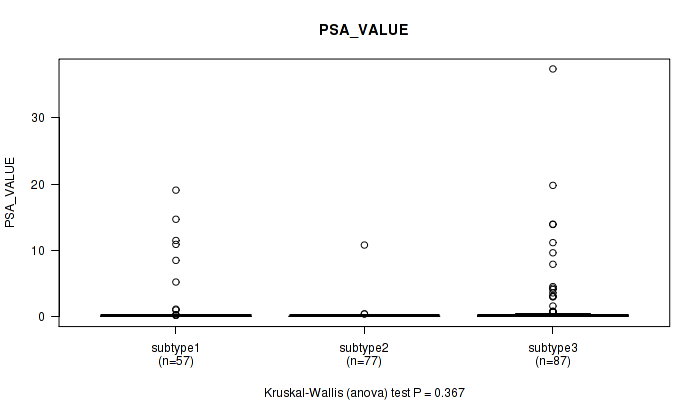
P value = 0.367 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S27. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 221 | 1.1 (3.9) |
| subtype1 | 57 | 1.3 (3.9) |
| subtype2 | 77 | 0.2 (1.2) |
| subtype3 | 87 | 1.7 (5.2) |
Figure S25. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
P value = 0.745 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S28. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 7 | 147 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 3 | 40 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 1 | 48 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 3 | 59 |
Figure S26. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
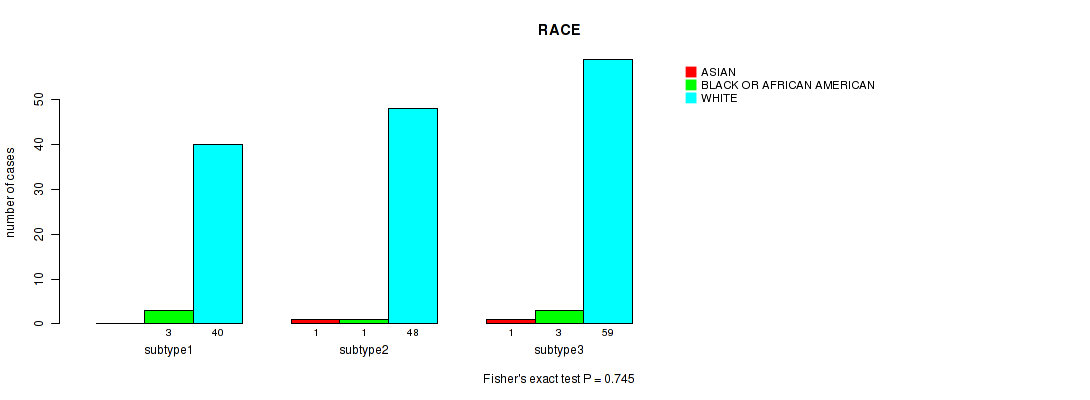
Table S29. Description of clustering approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 42 | 55 | 61 |
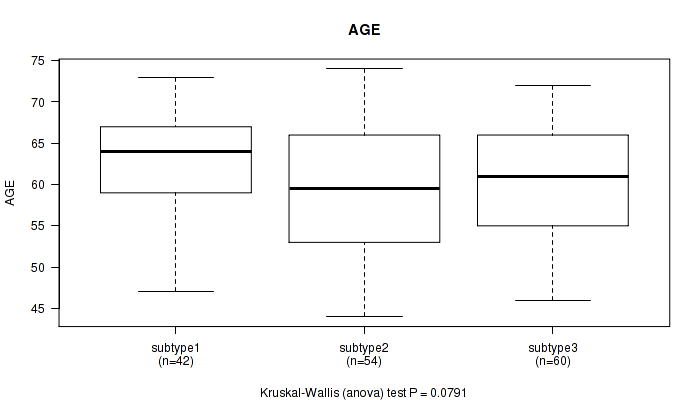
P value = 0.0791 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S30. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 156 | 60.6 (7.1) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 62.7 (6.3) |
| subtype2 | 54 | 59.2 (7.8) |
| subtype3 | 60 | 60.4 (6.7) |
Figure S27. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
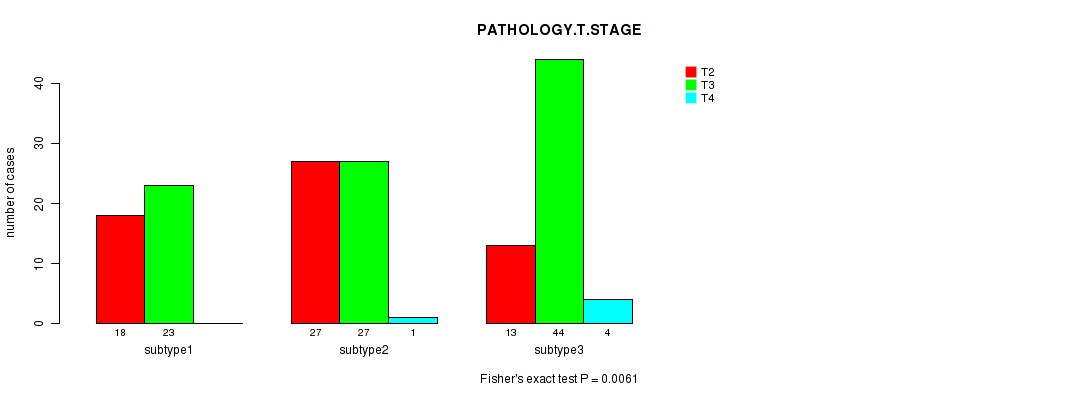
P value = 0.0061 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.57
Table S31. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 58 | 94 | 5 |
| subtype1 | 18 | 23 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 27 | 27 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 13 | 44 | 4 |
Figure S28. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
P value = 0.0542 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S32. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 123 | 17 |
| subtype1 | 38 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 43 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 42 | 11 |
Figure S29. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
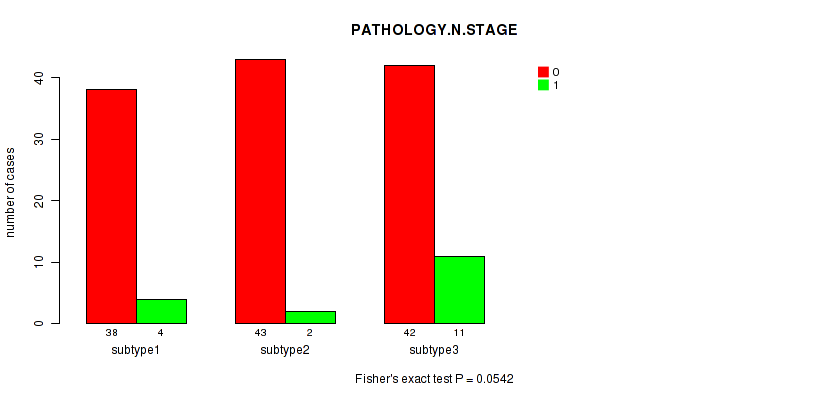
P value = 1 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S33. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 156 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 42 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 54 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 60 |
Figure S30. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
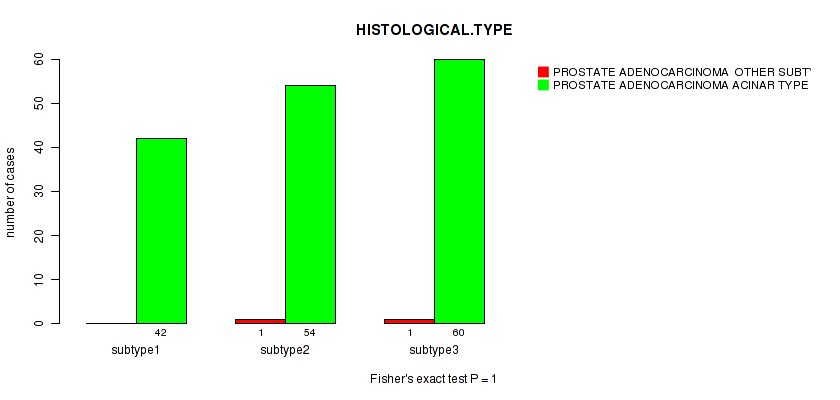
P value = 0.0204 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S34. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 111 | 33 | 1 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 36 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 40 | 9 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 35 | 20 | 1 | 1 |
Figure S31. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
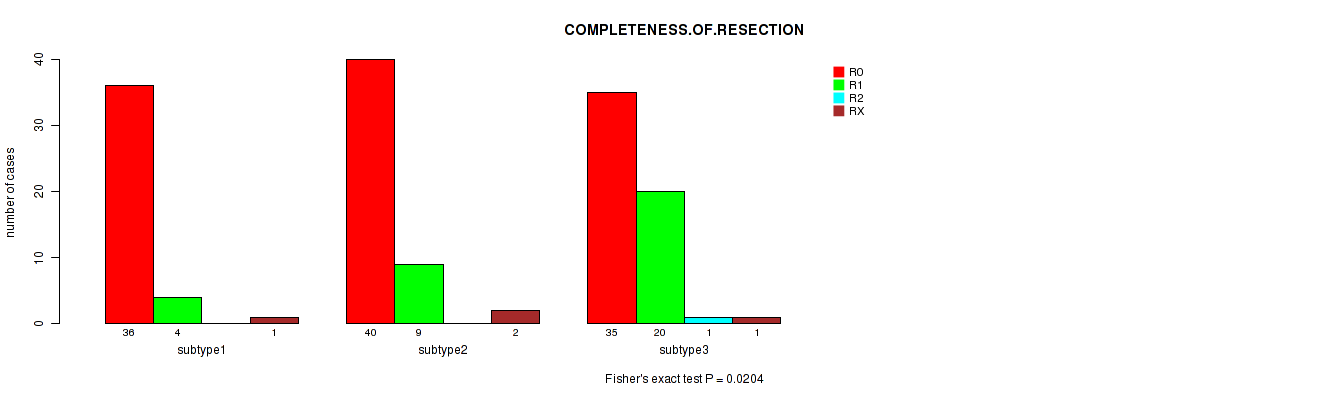
P value = 0.0381 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S35. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 140 | 0.2 (0.7) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 0.1 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 45 | 0.1 (0.3) |
| subtype3 | 53 | 0.4 (1.1) |
Figure S32. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
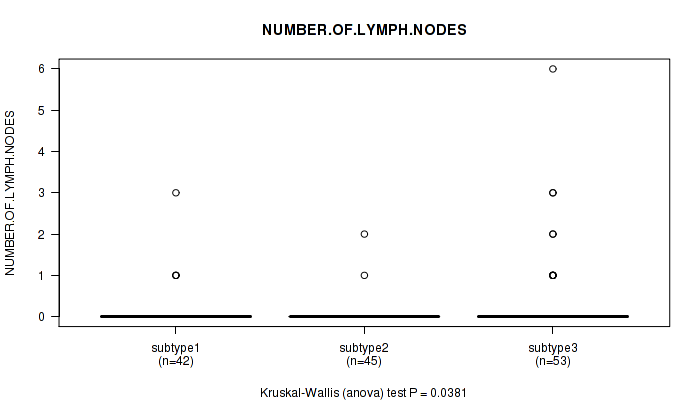
P value = 0.00011 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.013
Table S36. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 158 | 7.4 (0.9) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 7.1 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 55 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype3 | 61 | 7.8 (1.0) |
Figure S33. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
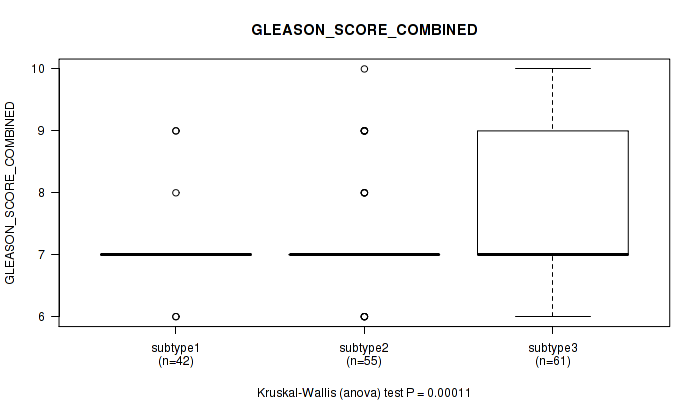
P value = 1.56e-05 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.0019
Table S37. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 158 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 3.3 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 55 | 3.4 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 61 | 3.8 (0.6) |
Figure S34. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
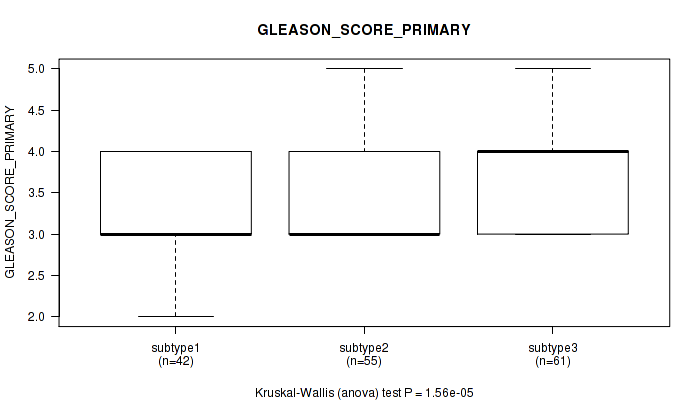
P value = 0.45 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S38. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 158 | 3.9 (0.7) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 3.7 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 55 | 3.9 (0.7) |
| subtype3 | 61 | 3.9 (0.8) |
Figure S35. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
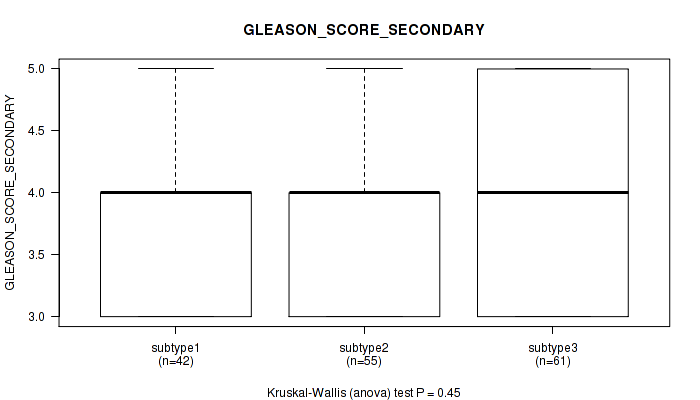
P value = 4.74e-05 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.0057
Table S39. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 158 | 7.4 (0.9) |
| subtype1 | 42 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 55 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype3 | 61 | 7.9 (1.0) |
Figure S36. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
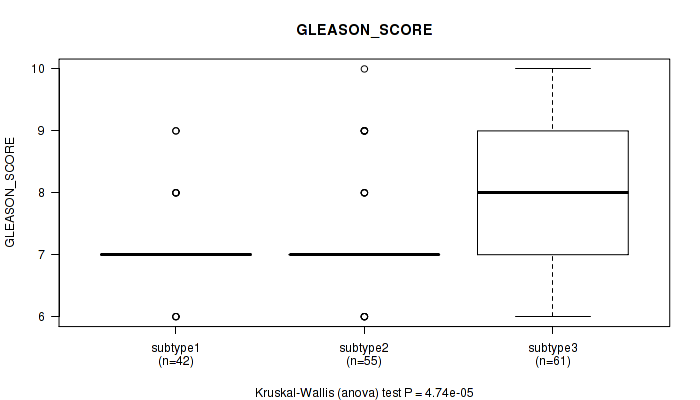
P value = 0.0443 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S40. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 156 | 11.3 (11.2) |
| subtype1 | 41 | 8.3 (5.0) |
| subtype2 | 54 | 10.5 (13.4) |
| subtype3 | 61 | 14.0 (11.7) |
Figure S37. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
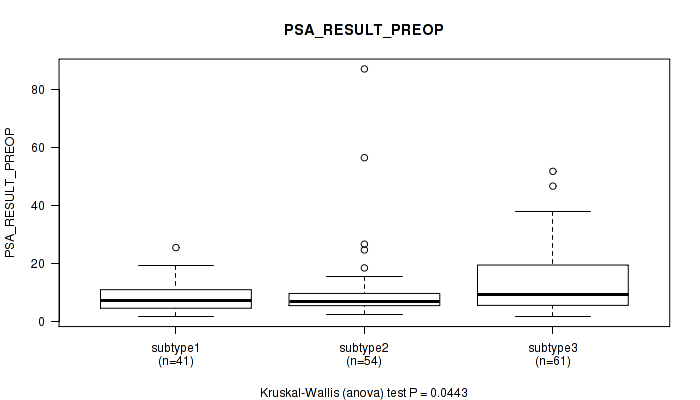
P value = 0.163 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S41. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 143 | 1.4 (4.5) |
| subtype1 | 41 | 1.0 (2.8) |
| subtype2 | 49 | 0.8 (3.4) |
| subtype3 | 53 | 2.4 (6.0) |
Figure S38. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
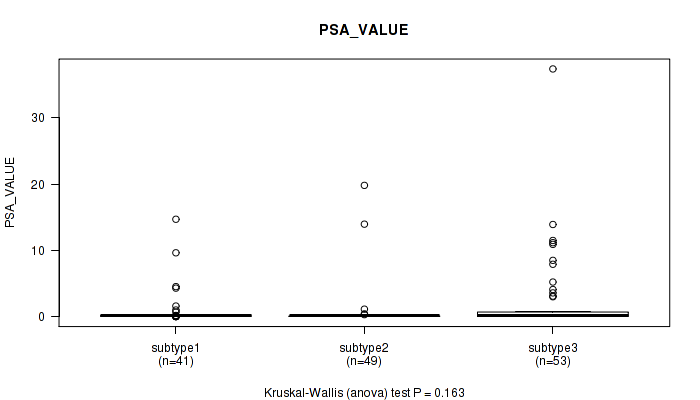
P value = 0.0271 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S42. Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 6 | 121 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 0 | 39 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 1 | 42 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 5 | 40 |
Figure S39. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RPPA CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
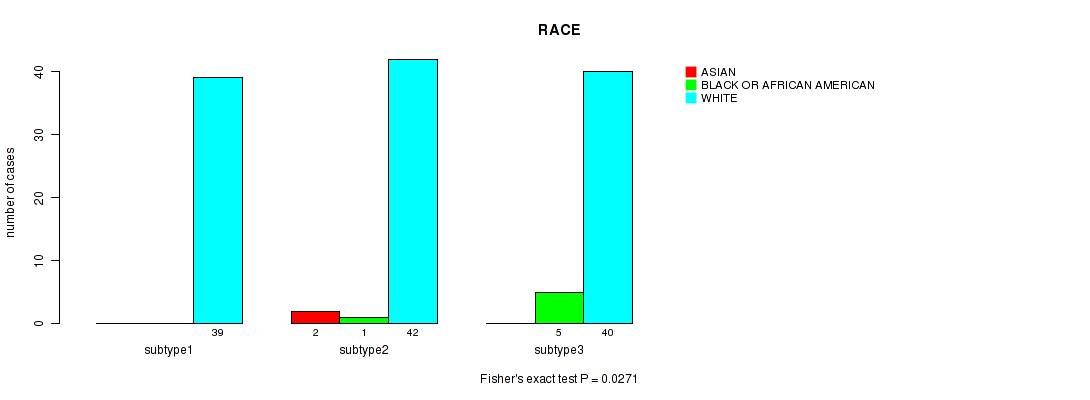
Table S43. Description of clustering approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 48 | 64 | 46 |
P value = 0.0149 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
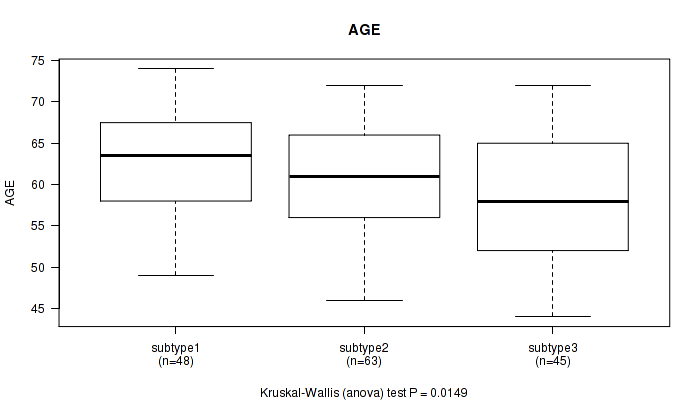
Table S44. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 156 | 60.6 (7.1) |
| subtype1 | 48 | 63.0 (6.2) |
| subtype2 | 63 | 60.5 (6.7) |
| subtype3 | 45 | 58.2 (7.8) |
Figure S40. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
P value = 0.0204 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S45. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 58 | 94 | 5 |
| subtype1 | 22 | 25 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 45 | 4 |
| subtype3 | 21 | 24 | 1 |
Figure S41. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
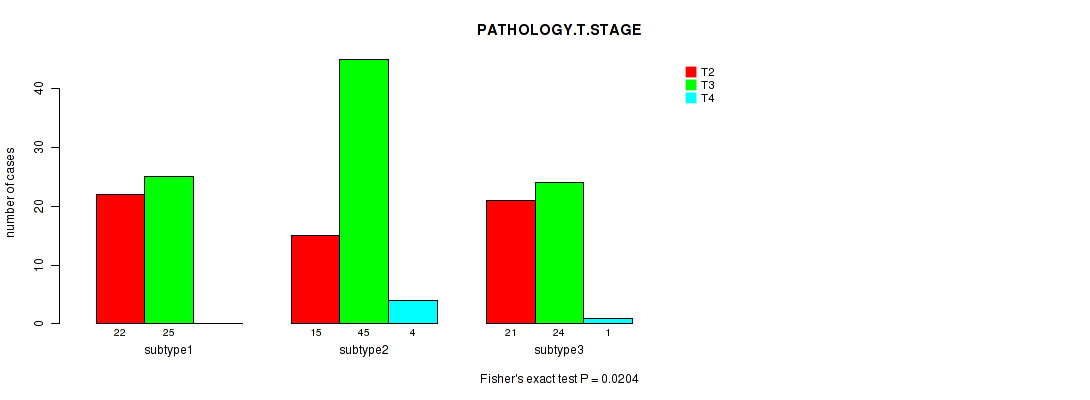
P value = 0.0163 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S46. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 123 | 17 |
| subtype1 | 43 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 43 | 12 |
| subtype3 | 37 | 1 |
Figure S42. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
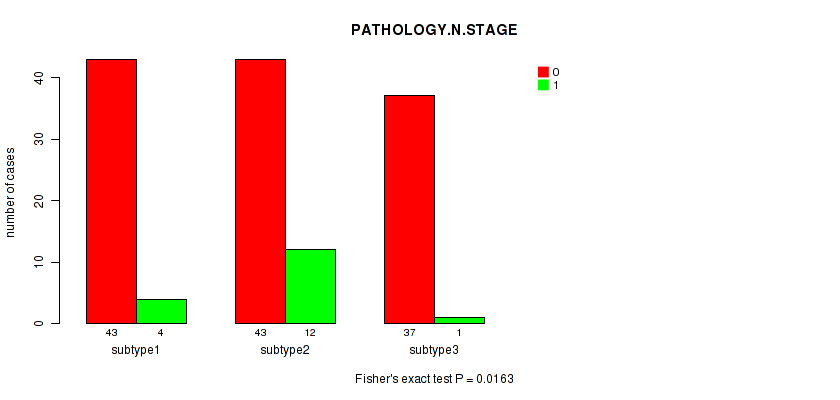
P value = 0.336 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S47. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 156 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 48 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 62 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 46 |
Figure S43. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
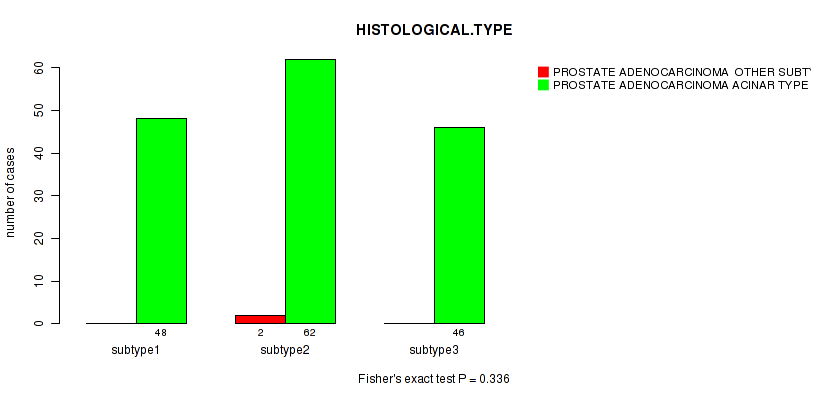
P value = 0.00354 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.35
Table S48. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 111 | 33 | 1 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 43 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 35 | 20 | 1 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 33 | 9 | 0 | 1 |
Figure S44. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
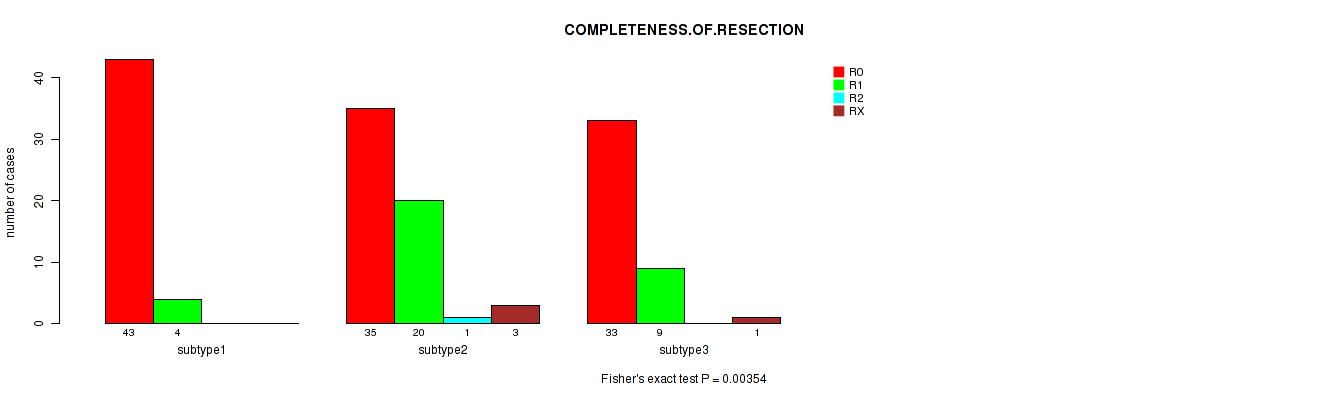
P value = 0.0119 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S49. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 140 | 0.2 (0.7) |
| subtype1 | 47 | 0.1 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 55 | 0.4 (1.1) |
| subtype3 | 38 | 0.0 (0.2) |
Figure S45. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
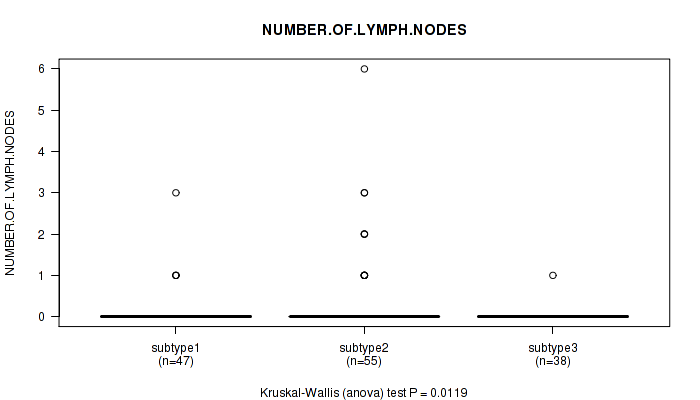
P value = 4.87e-05 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.0058
Table S50. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 158 | 7.4 (0.9) |
| subtype1 | 48 | 7.0 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 64 | 7.8 (1.0) |
| subtype3 | 46 | 7.3 (0.9) |
Figure S46. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
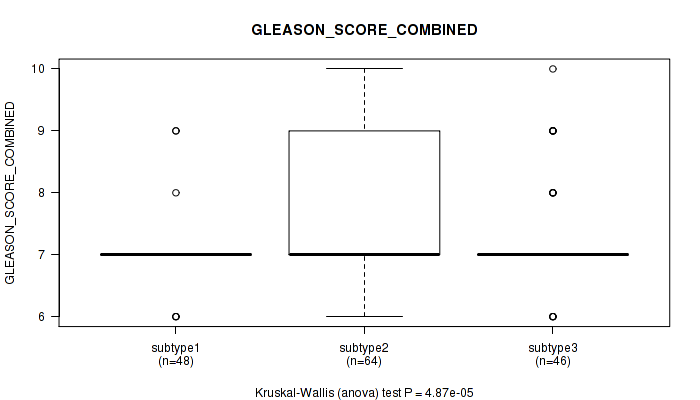
P value = 1.14e-05 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.0014
Table S51. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 158 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 48 | 3.4 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 64 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 46 | 3.4 (0.5) |
Figure S47. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
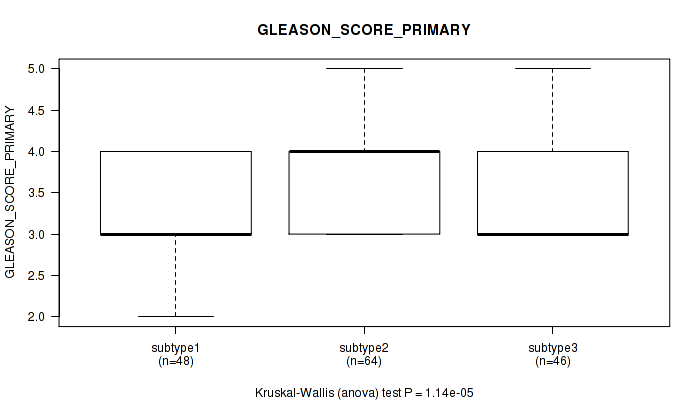
P value = 0.157 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S52. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 158 | 3.9 (0.7) |
| subtype1 | 48 | 3.7 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 64 | 3.9 (0.8) |
| subtype3 | 46 | 3.9 (0.6) |
Figure S48. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
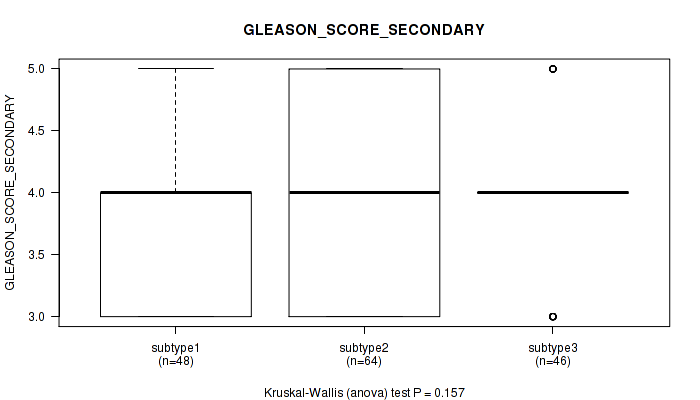
P value = 7.53e-06 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.00096
Table S53. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 158 | 7.4 (0.9) |
| subtype1 | 48 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 64 | 7.9 (1.0) |
| subtype3 | 46 | 7.3 (0.9) |
Figure S49. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
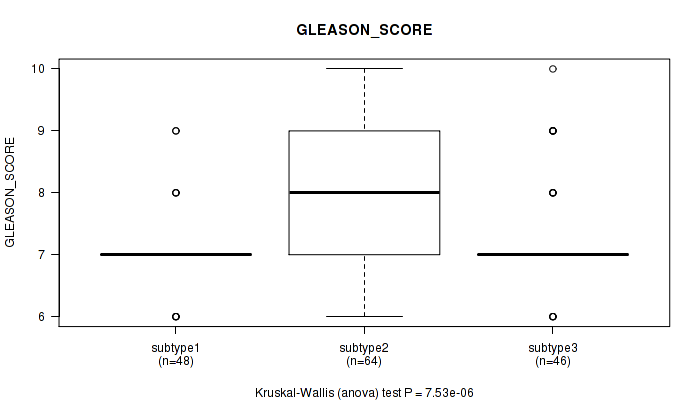
P value = 0.0303 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S54. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 156 | 11.3 (11.2) |
| subtype1 | 47 | 8.9 (6.4) |
| subtype2 | 64 | 14.1 (12.3) |
| subtype3 | 45 | 9.7 (12.9) |
Figure S50. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
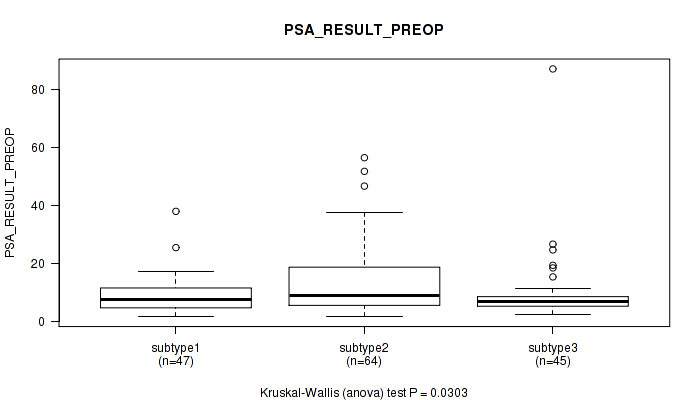
P value = 0.434 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S55. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 143 | 1.4 (4.5) |
| subtype1 | 47 | 1.4 (3.7) |
| subtype2 | 55 | 2.0 (5.7) |
| subtype3 | 41 | 0.6 (3.1) |
Figure S51. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
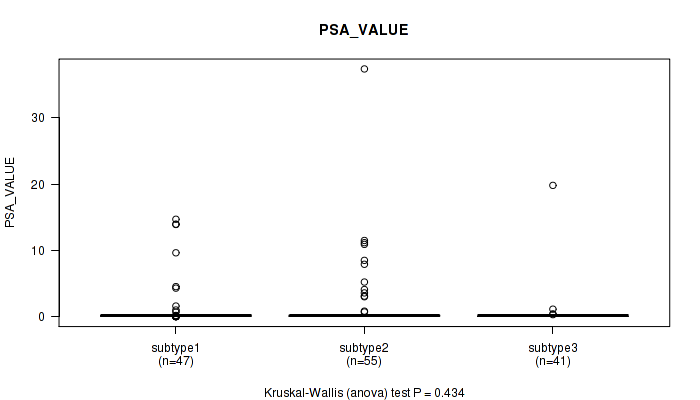
P value = 0.00836 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.76
Table S56. Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 6 | 121 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 0 | 45 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 5 | 40 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 1 | 36 |
Figure S52. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RPPA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
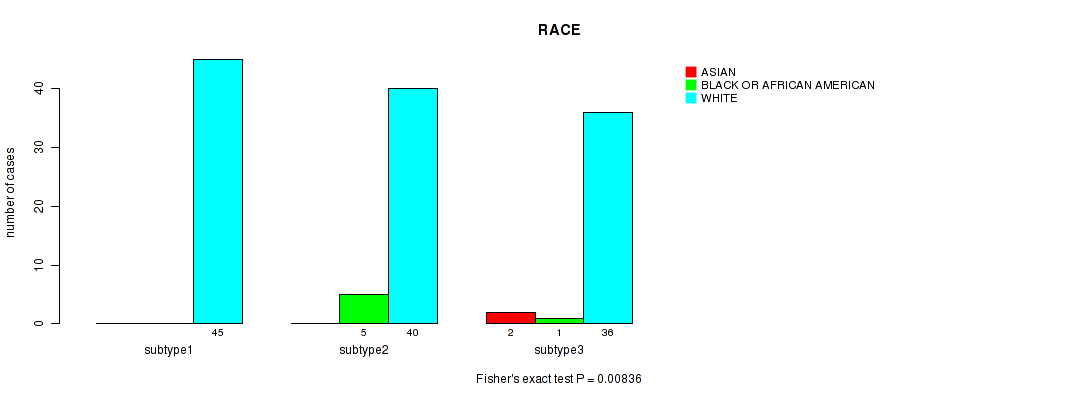
Table S57. Description of clustering approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 86 | 85 | 97 |
P value = 0.496 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
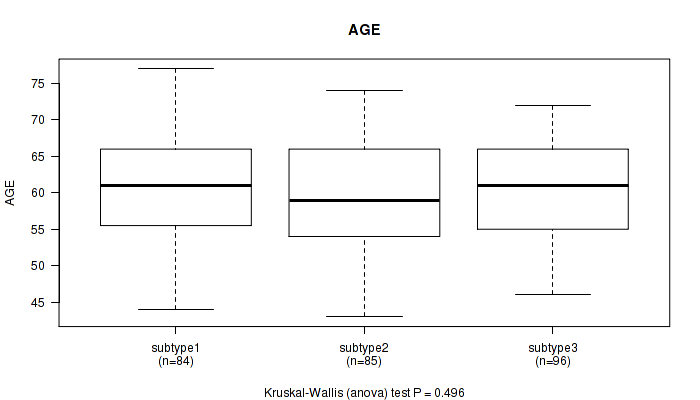
Table S58. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 265 | 60.2 (7.0) |
| subtype1 | 84 | 60.7 (7.0) |
| subtype2 | 85 | 59.5 (7.1) |
| subtype3 | 96 | 60.4 (6.8) |
Figure S53. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
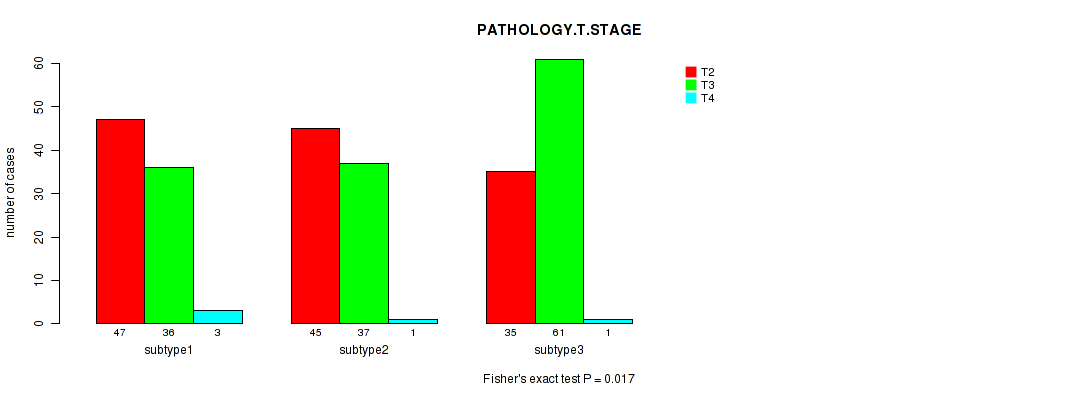
P value = 0.017 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S59. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 127 | 134 | 5 |
| subtype1 | 47 | 36 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 45 | 37 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 35 | 61 | 1 |
Figure S54. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
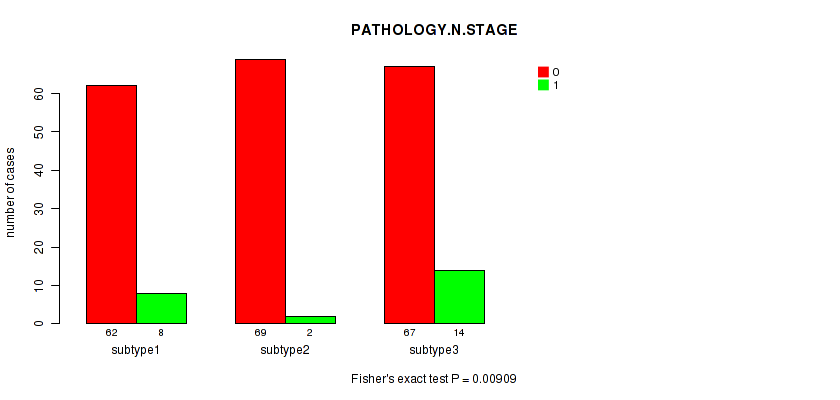
P value = 0.00909 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.81
Table S60. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 198 | 24 |
| subtype1 | 62 | 8 |
| subtype2 | 69 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 67 | 14 |
Figure S55. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
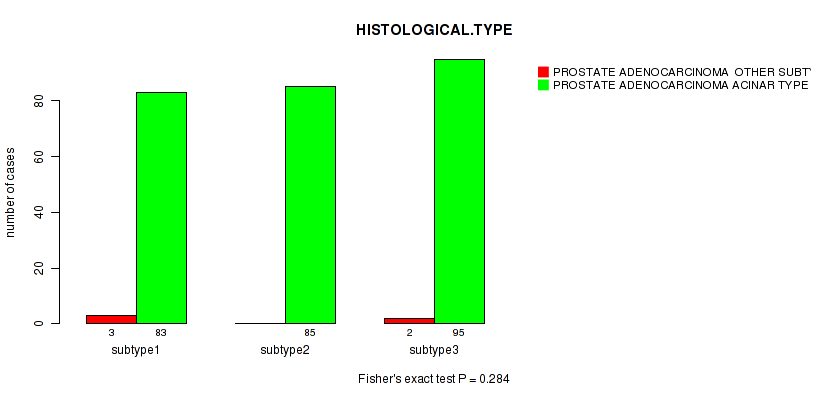
P value = 0.284 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S61. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 5 | 263 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 83 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 85 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 95 |
Figure S56. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
P value = 0.438 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S62. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 190 | 56 | 3 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 57 | 24 | 1 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 63 | 14 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 70 | 18 | 2 | 3 |
Figure S57. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
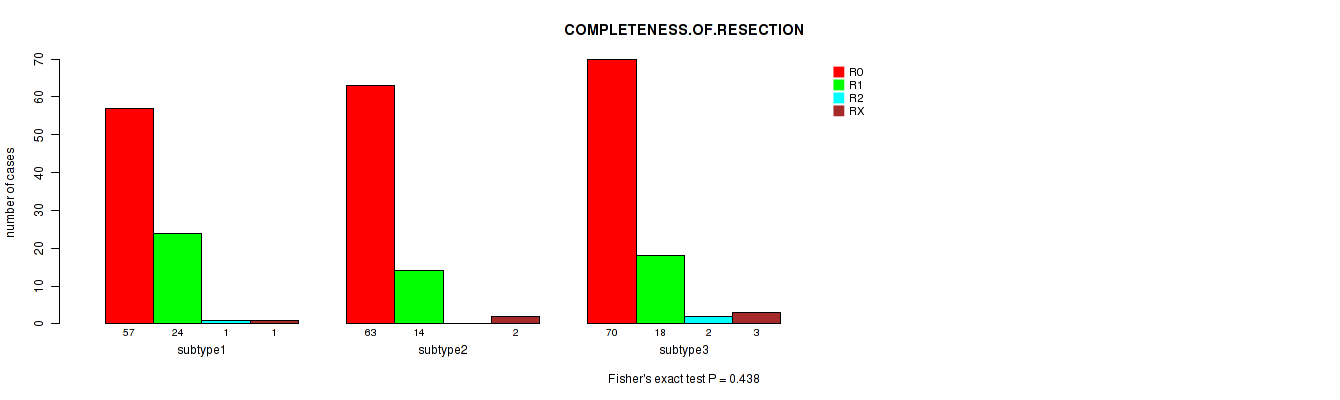
P value = 0.016 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S63. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 220 | 0.2 (1.2) |
| subtype1 | 70 | 0.2 (0.8) |
| subtype2 | 69 | 0.0 (0.2) |
| subtype3 | 81 | 0.5 (1.8) |
Figure S58. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
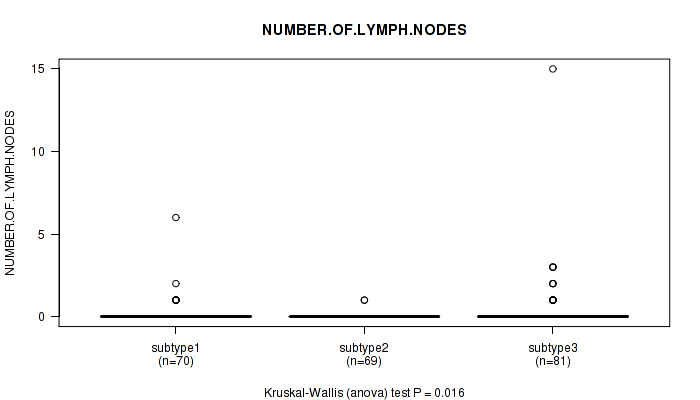
P value = 0.0543 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S64. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 268 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 86 | 7.4 (0.9) |
| subtype2 | 85 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 97 | 7.4 (0.9) |
Figure S59. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
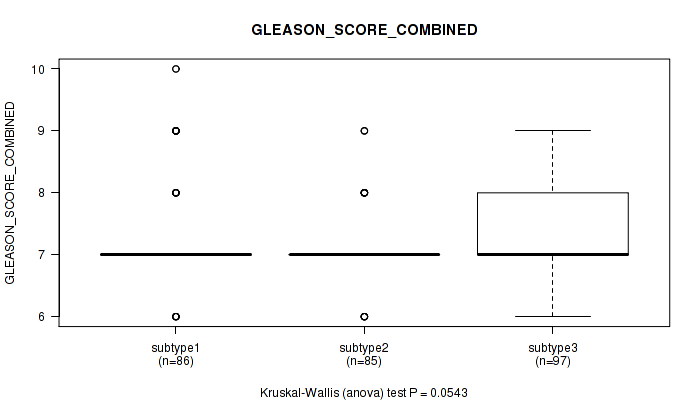
P value = 0.00443 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.43
Table S65. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 268 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 86 | 3.6 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 85 | 3.3 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 97 | 3.6 (0.6) |
Figure S60. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
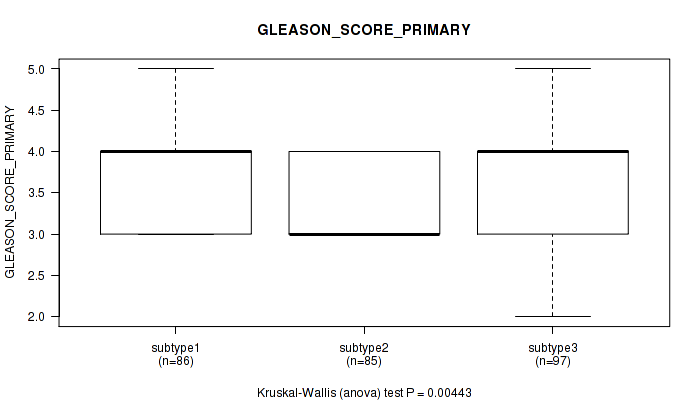
P value = 0.831 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S66. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 268 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 86 | 3.8 (0.7) |
| subtype2 | 85 | 3.8 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 97 | 3.8 (0.6) |
Figure S61. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
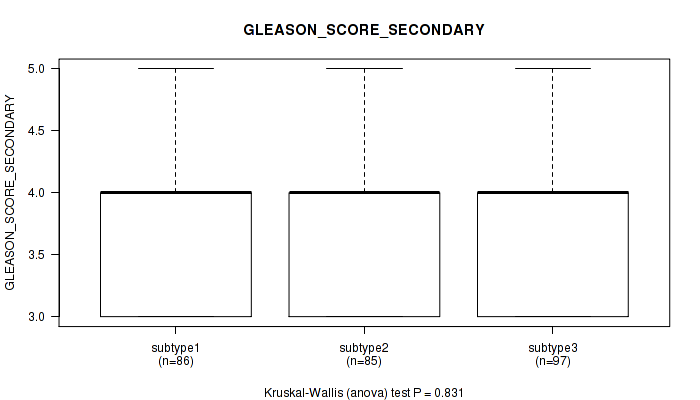
P value = 0.0301 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S67. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 268 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 86 | 7.4 (0.9) |
| subtype2 | 85 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 97 | 7.4 (0.9) |
Figure S62. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
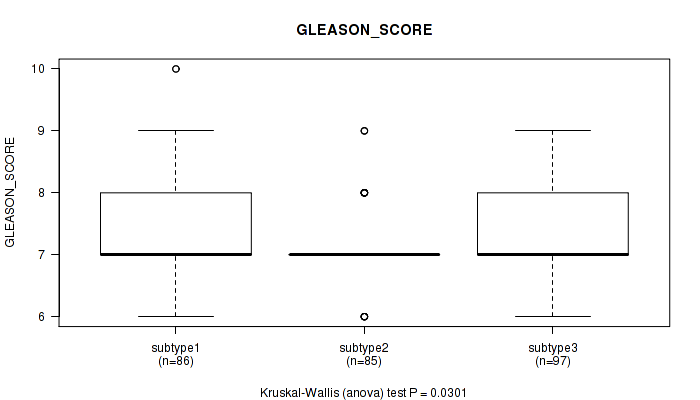
P value = 0.00335 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.34
Table S68. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 266 | 10.1 (10.2) |
| subtype1 | 86 | 13.3 (14.3) |
| subtype2 | 85 | 6.9 (3.5) |
| subtype3 | 95 | 10.0 (8.7) |
Figure S63. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
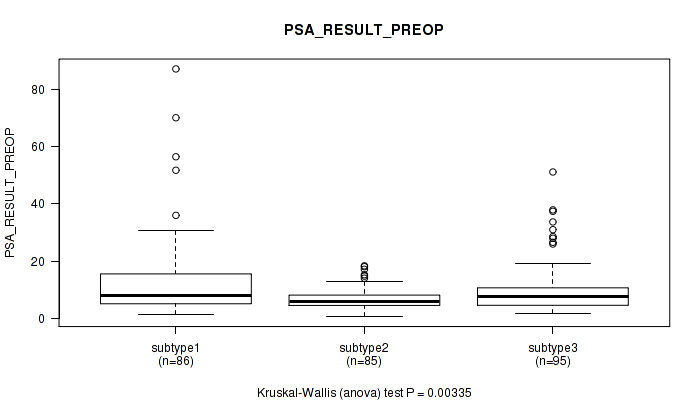
P value = 0.264 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S69. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 224 | 1.1 (3.9) |
| subtype1 | 68 | 0.7 (3.0) |
| subtype2 | 74 | 0.6 (2.2) |
| subtype3 | 82 | 1.8 (5.4) |
Figure S64. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
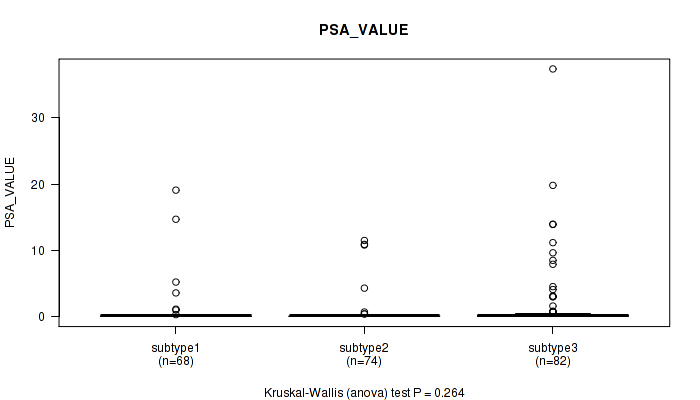
P value = 0.329 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S70. Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 7 | 147 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 3 | 38 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 1 | 52 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 3 | 57 |
Figure S65. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
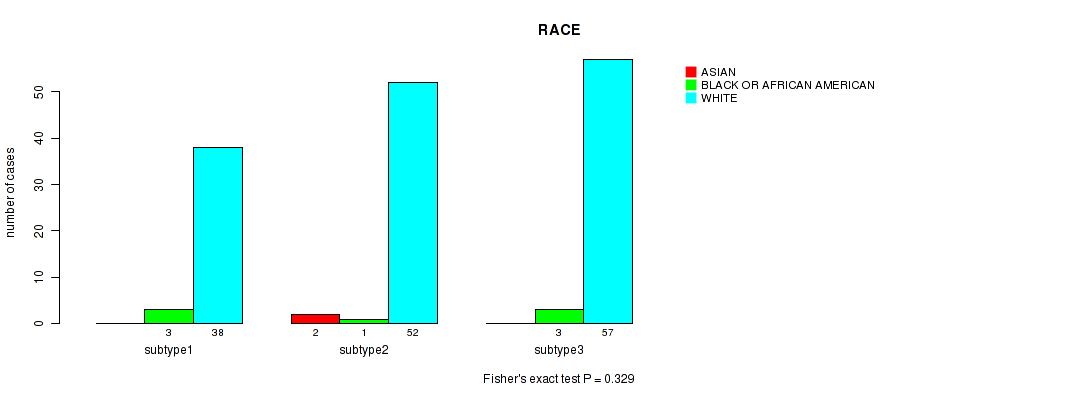
Table S71. Description of clustering approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 97 | 82 | 89 |
P value = 0.57 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
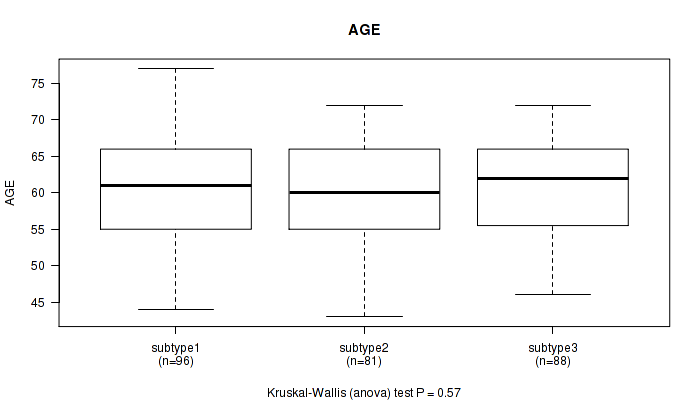
Table S72. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 265 | 60.2 (7.0) |
| subtype1 | 96 | 60.4 (7.2) |
| subtype2 | 81 | 59.5 (6.9) |
| subtype3 | 88 | 60.6 (6.8) |
Figure S66. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
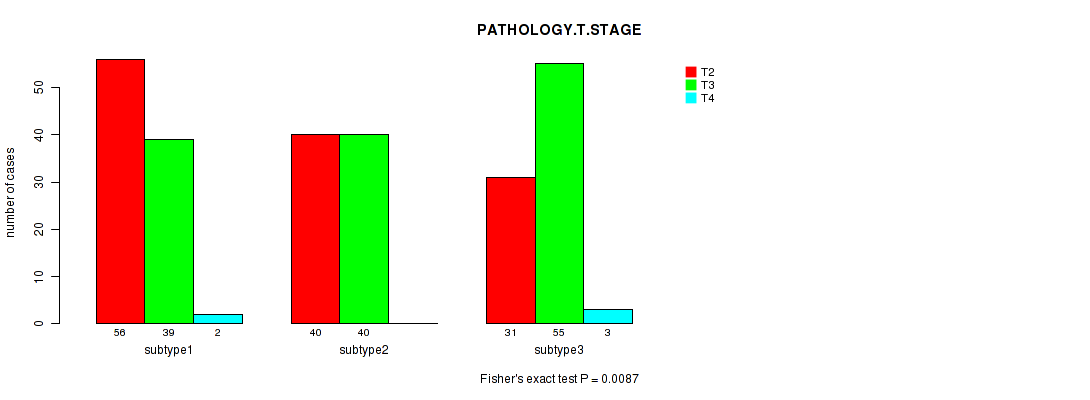
P value = 0.0087 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.78
Table S73. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 127 | 134 | 5 |
| subtype1 | 56 | 39 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 40 | 40 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 31 | 55 | 3 |
Figure S67. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
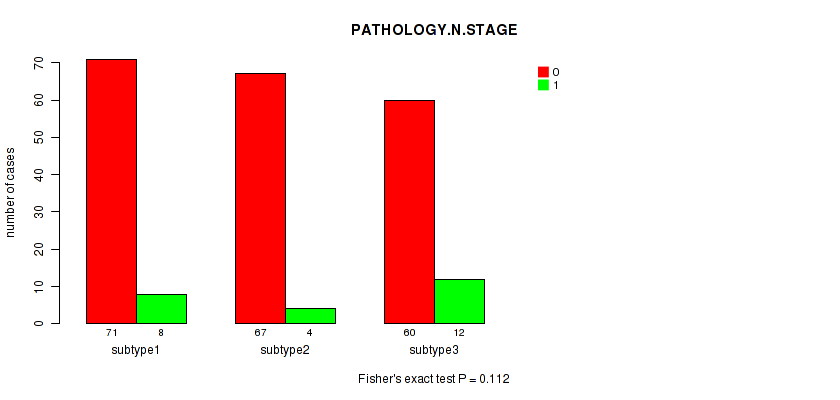
P value = 0.112 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S74. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 198 | 24 |
| subtype1 | 71 | 8 |
| subtype2 | 67 | 4 |
| subtype3 | 60 | 12 |
Figure S68. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
P value = 0.33 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S75. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 5 | 263 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 95 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 82 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 86 |
Figure S69. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
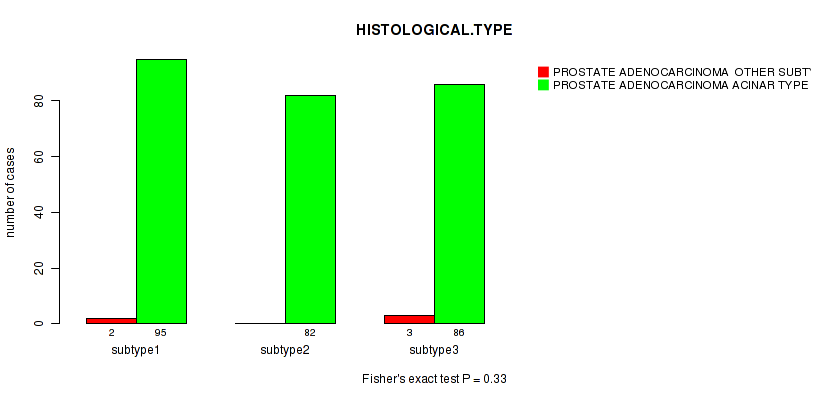
P value = 0.251 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S76. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 190 | 56 | 3 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 67 | 24 | 1 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 64 | 11 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 59 | 21 | 2 | 3 |
Figure S70. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
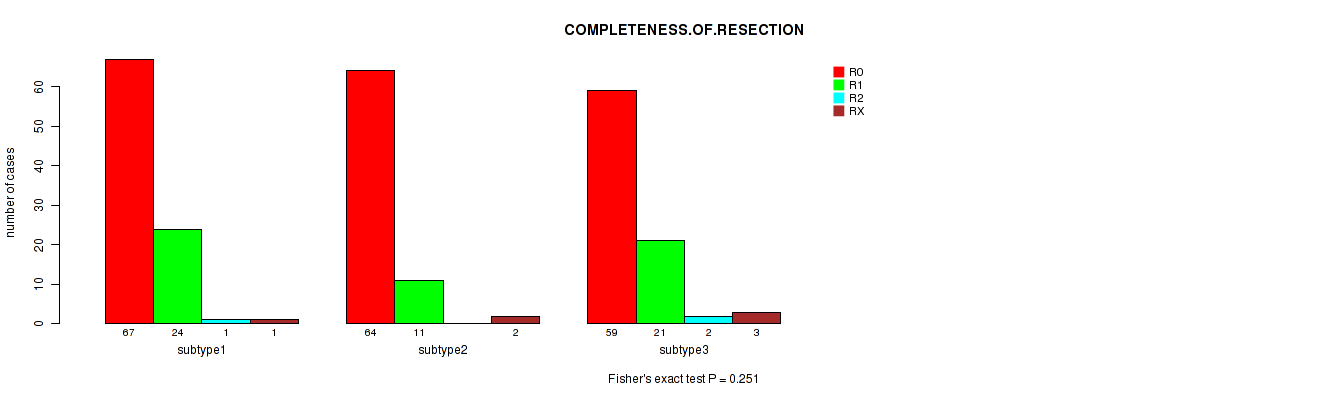
P value = 0.0887 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S77. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 220 | 0.2 (1.2) |
| subtype1 | 79 | 0.2 (0.7) |
| subtype2 | 69 | 0.1 (0.2) |
| subtype3 | 72 | 0.5 (1.9) |
Figure S71. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
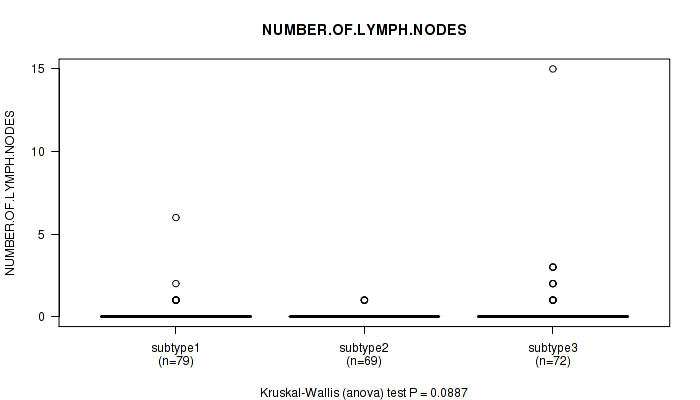
P value = 0.0062 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.58
Table S78. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 268 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 97 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype2 | 82 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 89 | 7.5 (0.9) |
Figure S72. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
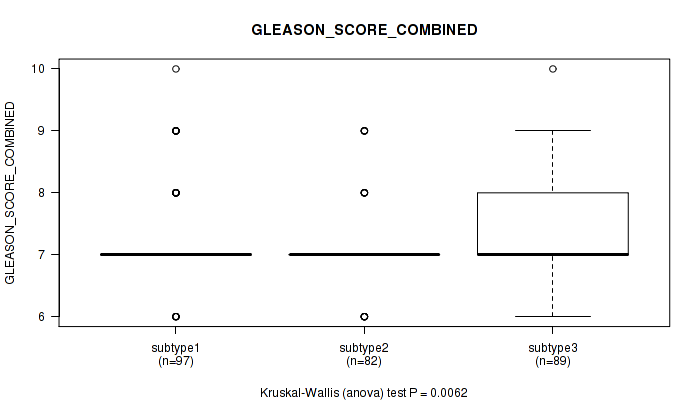
P value = 0.000183 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.021
Table S79. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 268 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 97 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 82 | 3.3 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 89 | 3.7 (0.6) |
Figure S73. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
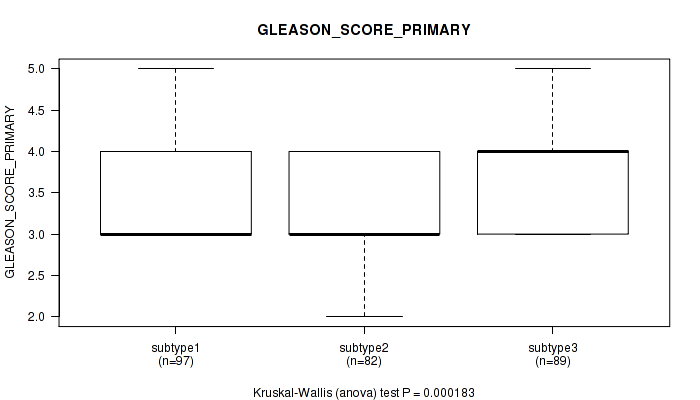
P value = 0.45 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S80. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 268 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 97 | 3.7 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 82 | 3.8 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 89 | 3.9 (0.7) |
Figure S74. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
P value = 0.0124 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S81. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 268 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 97 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype2 | 82 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 89 | 7.5 (1.0) |
Figure S75. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
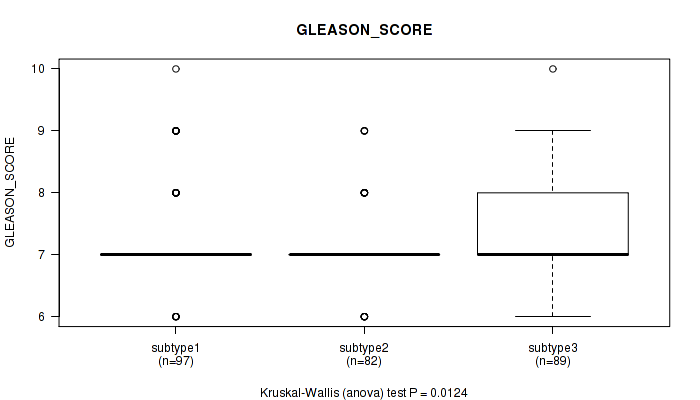
P value = 0.02 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S82. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 266 | 10.1 (10.2) |
| subtype1 | 97 | 12.2 (12.4) |
| subtype2 | 82 | 7.5 (4.4) |
| subtype3 | 87 | 10.3 (10.9) |
Figure S76. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
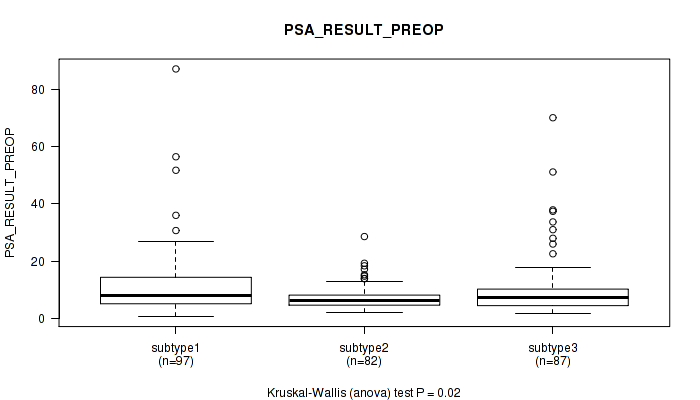
P value = 0.845 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S83. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 224 | 1.1 (3.9) |
| subtype1 | 77 | 0.8 (3.0) |
| subtype2 | 74 | 0.8 (2.9) |
| subtype3 | 73 | 1.7 (5.3) |
Figure S77. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
P value = 0.0104 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.92
Table S84. Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 7 | 147 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 5 | 37 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 0 | 63 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 2 | 47 |
Figure S78. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
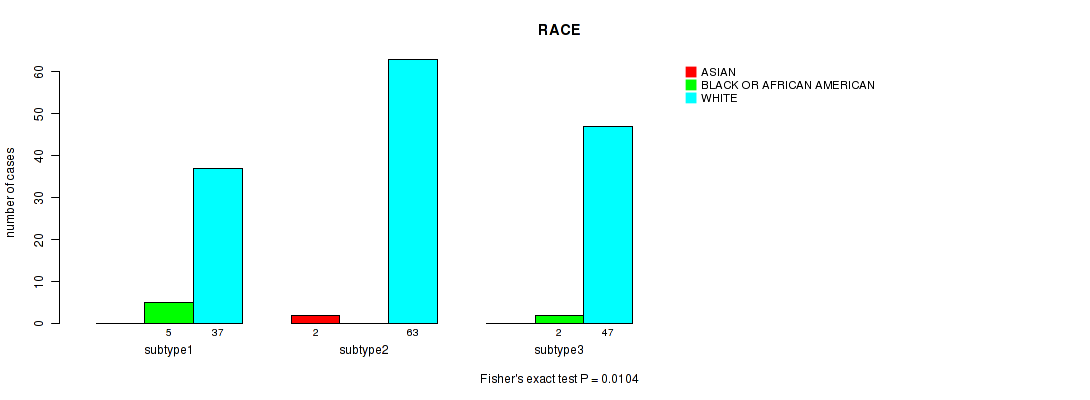
Table S85. Description of clustering approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 50 | 23 | 58 | 60 | 81 |
P value = 0.379 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S86. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 269 | 60.4 (7.0) |
| subtype1 | 50 | 59.0 (7.2) |
| subtype2 | 23 | 60.0 (7.3) |
| subtype3 | 58 | 60.9 (7.1) |
| subtype4 | 60 | 61.6 (6.5) |
| subtype5 | 78 | 59.9 (7.1) |
Figure S79. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
P value = 0.0124 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S87. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 127 | 139 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 23 | 25 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 16 | 6 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 22 | 36 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 23 | 34 | 3 |
| subtype5 | 43 | 38 | 0 |
Figure S80. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
P value = 0.193 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S88. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 203 | 23 |
| subtype1 | 39 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 17 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 42 | 6 |
| subtype4 | 46 | 10 |
| subtype5 | 59 | 4 |
Figure S81. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
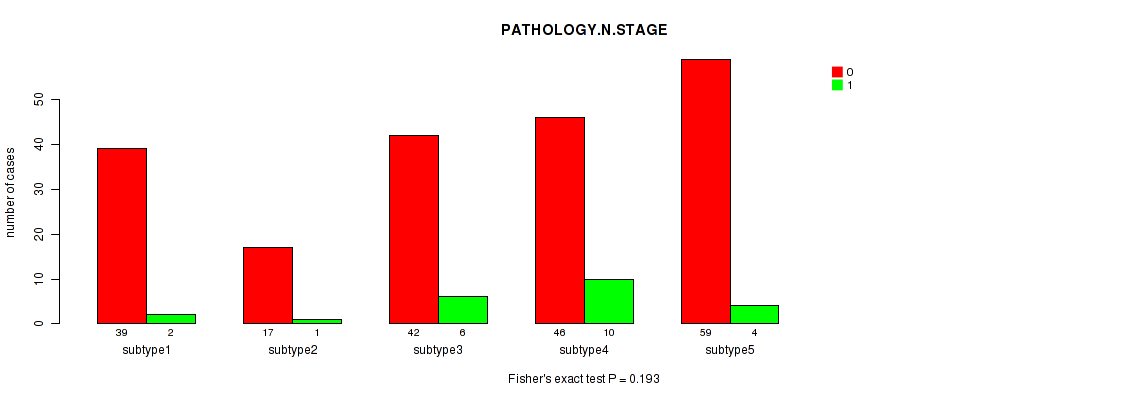
P value = 0.00064 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.069
Table S89. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 266 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 50 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 23 |
| subtype3 | 6 | 52 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 60 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 81 |
Figure S82. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
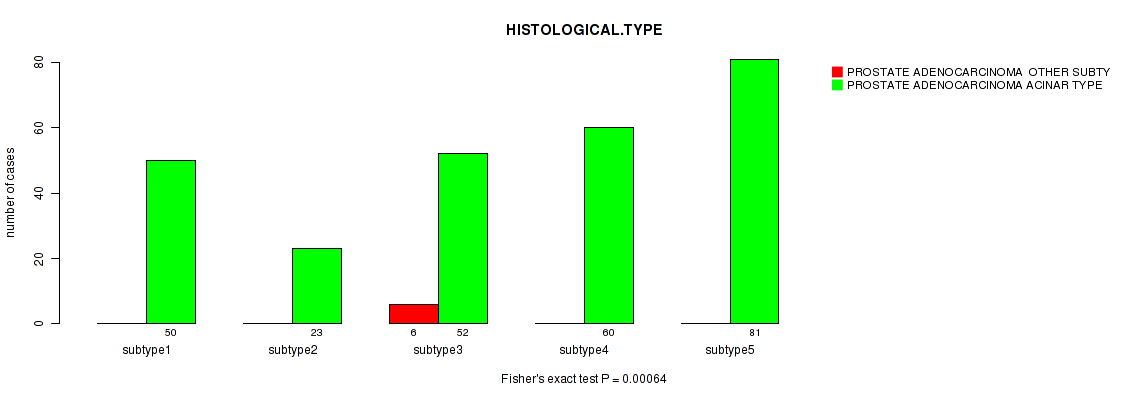
P value = 0.0301 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S90. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 193 | 57 | 3 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 35 | 9 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 6 | 1 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 35 | 19 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype4 | 45 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 63 | 8 | 2 | 2 |
Figure S83. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
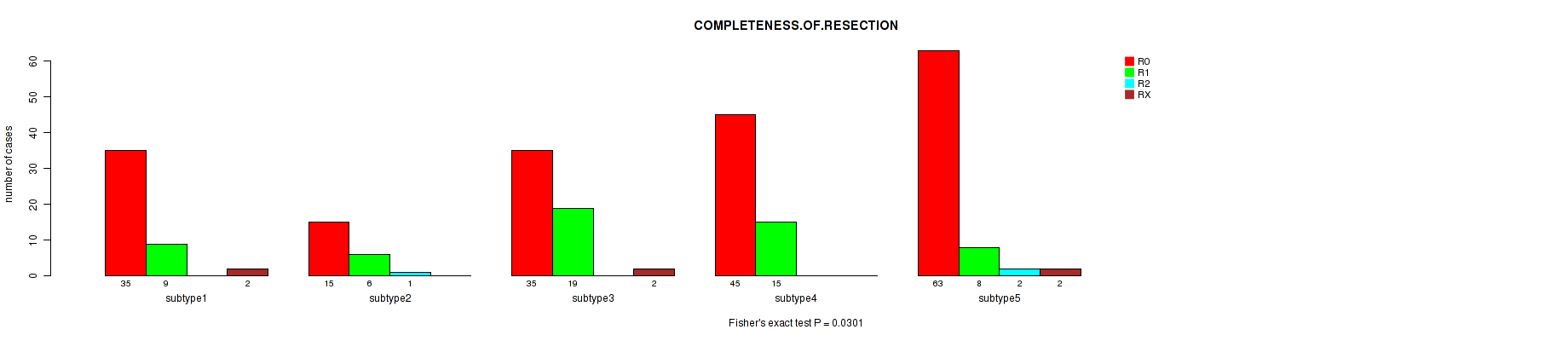
P value = 0.148 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S91. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 224 | 0.2 (1.2) |
| subtype1 | 39 | 0.1 (0.2) |
| subtype2 | 18 | 0.1 (0.2) |
| subtype3 | 48 | 0.5 (2.2) |
| subtype4 | 56 | 0.4 (1.1) |
| subtype5 | 63 | 0.1 (0.3) |
Figure S84. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
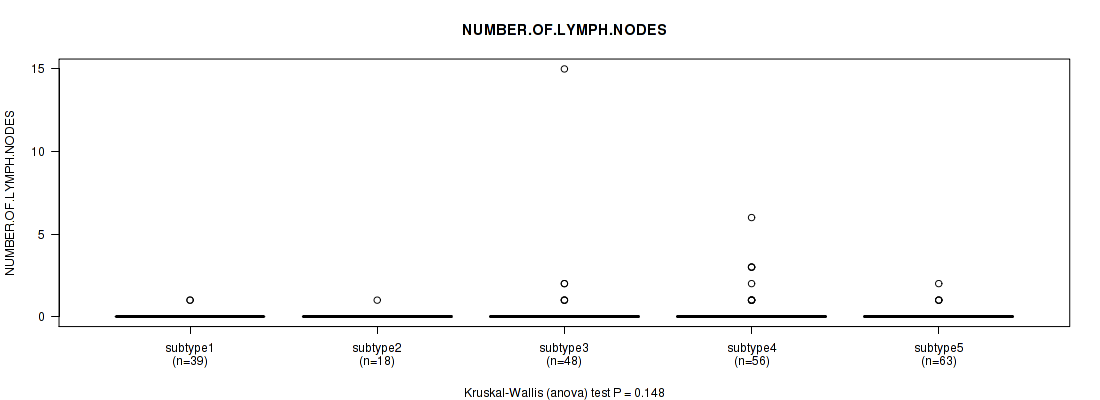
P value = 0.0301 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S92. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 50 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 23 | 7.2 (1.0) |
| subtype3 | 58 | 7.5 (1.0) |
| subtype4 | 60 | 7.4 (0.8) |
| subtype5 | 81 | 7.1 (0.7) |
Figure S85. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
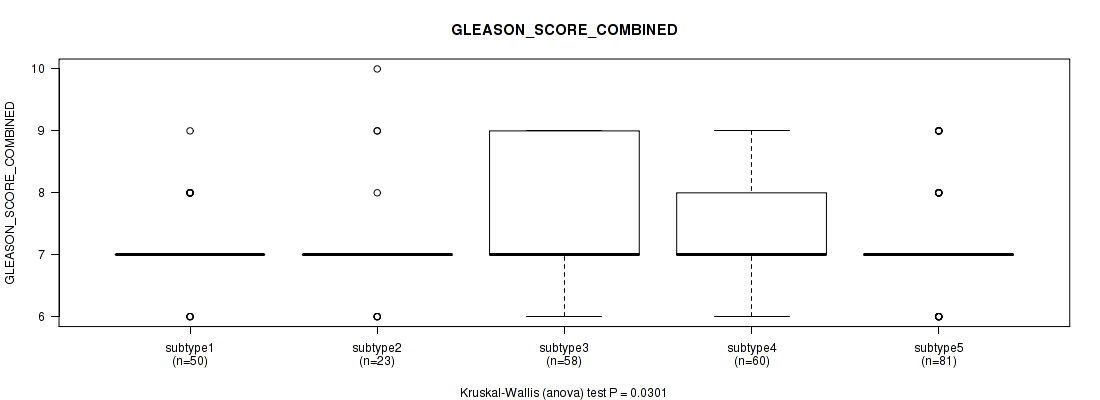
P value = 0.000358 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.039
Table S93. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 50 | 3.3 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 23 | 3.3 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 58 | 3.6 (0.6) |
| subtype4 | 60 | 3.7 (0.6) |
| subtype5 | 81 | 3.4 (0.5) |
Figure S86. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
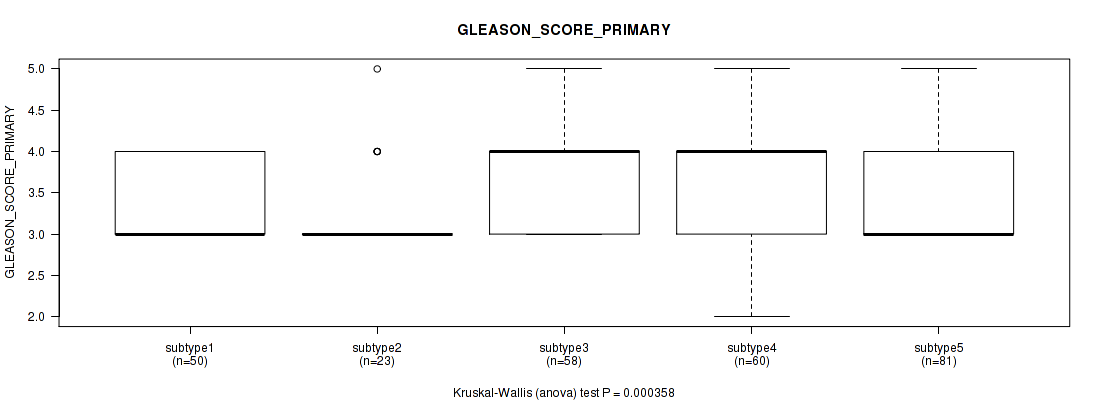
P value = 0.25 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S94. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 50 | 3.8 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 23 | 3.9 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 58 | 3.9 (0.7) |
| subtype4 | 60 | 3.8 (0.7) |
| subtype5 | 81 | 3.7 (0.6) |
Figure S87. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
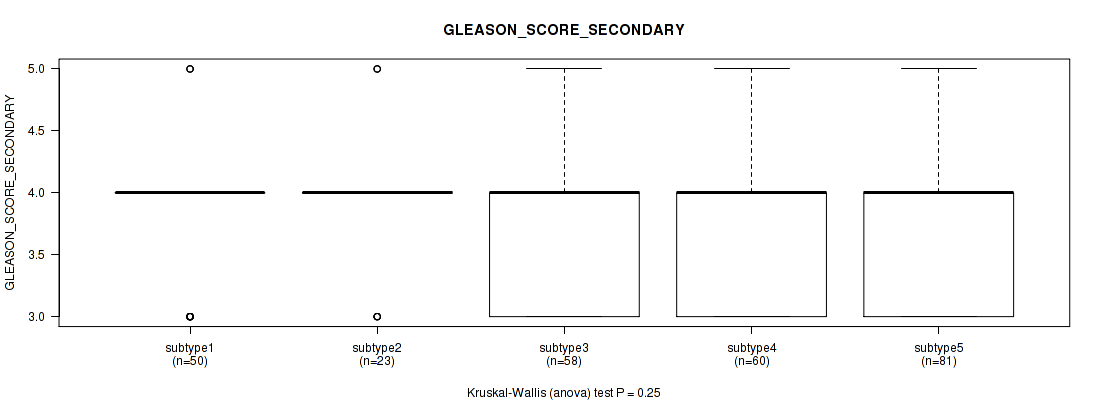
P value = 0.034 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S95. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 50 | 7.2 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 23 | 7.2 (1.1) |
| subtype3 | 58 | 7.6 (1.0) |
| subtype4 | 60 | 7.5 (0.8) |
| subtype5 | 81 | 7.2 (0.7) |
Figure S88. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
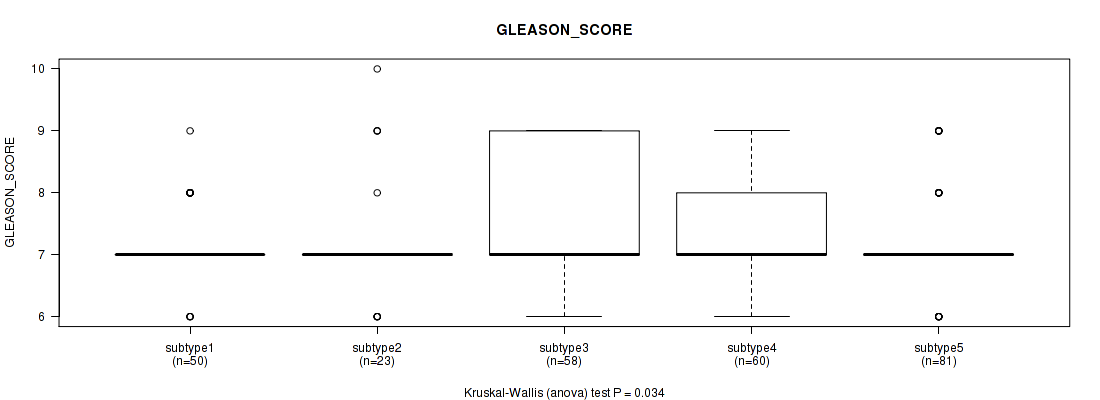
P value = 0.0118 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S96. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 270 | 10.5 (11.2) |
| subtype1 | 50 | 7.2 (3.7) |
| subtype2 | 23 | 11.6 (16.3) |
| subtype3 | 58 | 11.7 (14.0) |
| subtype4 | 58 | 13.9 (14.1) |
| subtype5 | 81 | 8.8 (6.3) |
Figure S89. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
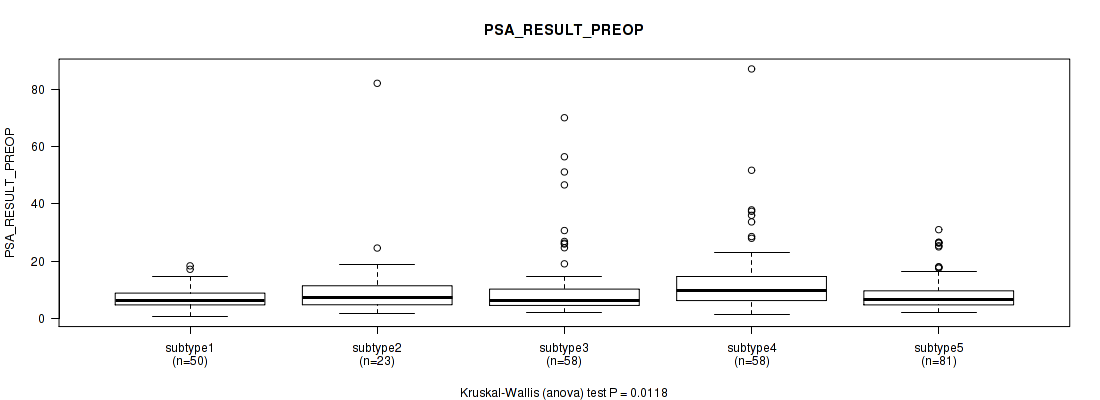
P value = 0.131 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S97. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 228 | 1.1 (3.9) |
| subtype1 | 44 | 0.7 (2.6) |
| subtype2 | 22 | 0.4 (1.7) |
| subtype3 | 42 | 1.1 (4.2) |
| subtype4 | 54 | 2.4 (6.1) |
| subtype5 | 66 | 0.5 (1.8) |
Figure S90. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
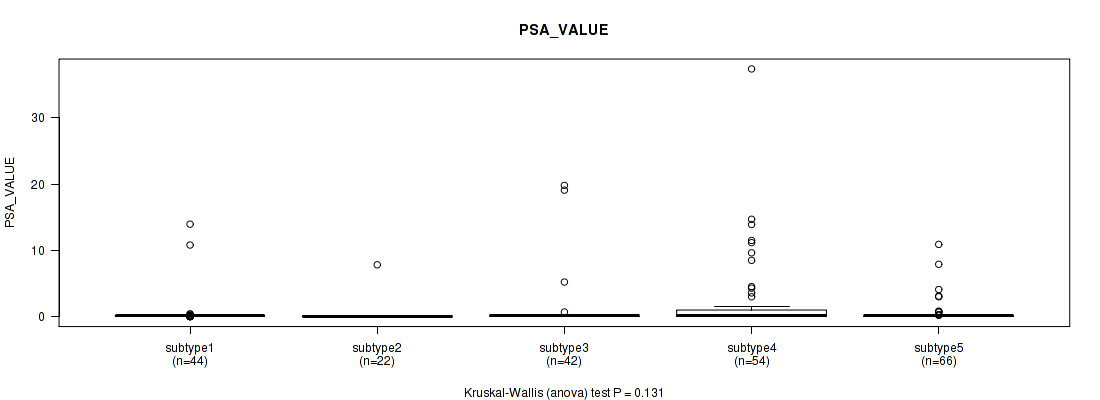
P value = 0.417 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S98. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 7 | 146 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 0 | 25 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 1 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype4 | 1 | 1 | 50 |
| subtype5 | 1 | 5 | 61 |
Figure S91. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
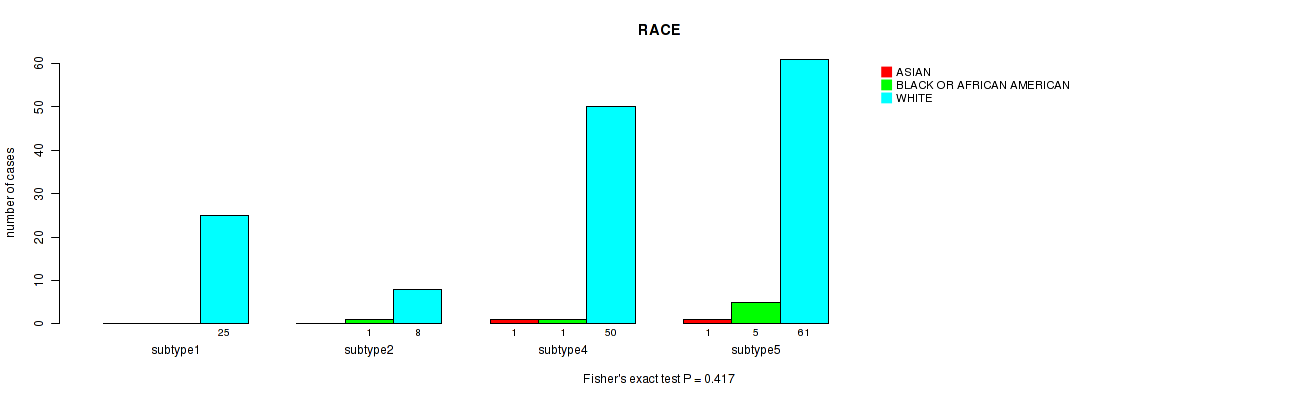
Table S99. Description of clustering approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 94 | 50 | 128 |
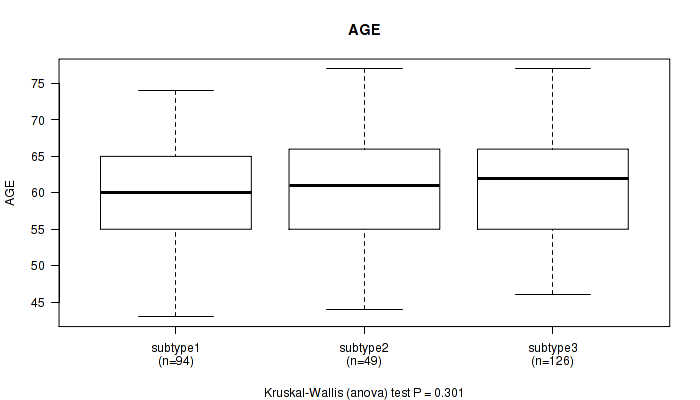
P value = 0.301 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S100. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 269 | 60.4 (7.0) |
| subtype1 | 94 | 59.7 (6.5) |
| subtype2 | 49 | 60.0 (7.2) |
| subtype3 | 126 | 61.0 (7.3) |
Figure S92. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
P value = 0.00014 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.016
Table S101. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 127 | 139 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 44 | 48 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 31 | 15 | 4 |
| subtype3 | 52 | 76 | 0 |
Figure S93. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
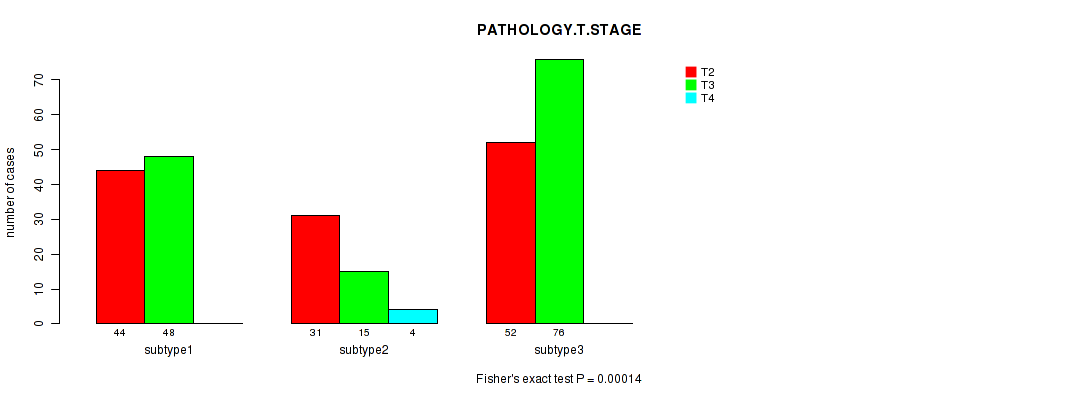
P value = 0.00299 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.3
Table S102. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 203 | 23 |
| subtype1 | 77 | 5 |
| subtype2 | 37 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 89 | 18 |
Figure S94. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
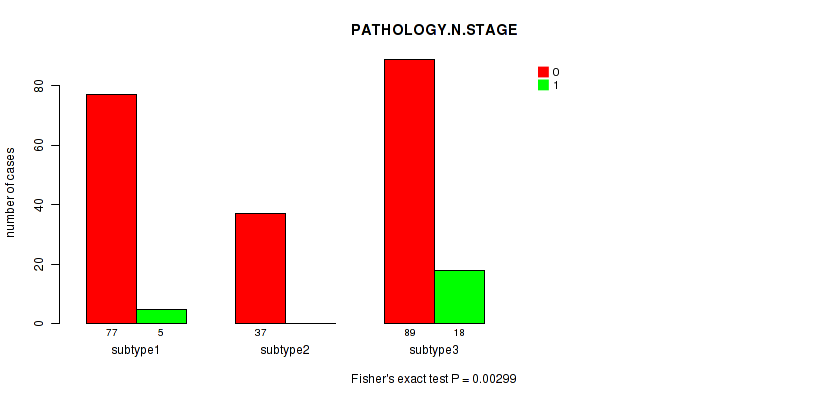
P value = 0.577 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S103. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 266 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 91 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 50 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 125 |
Figure S95. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
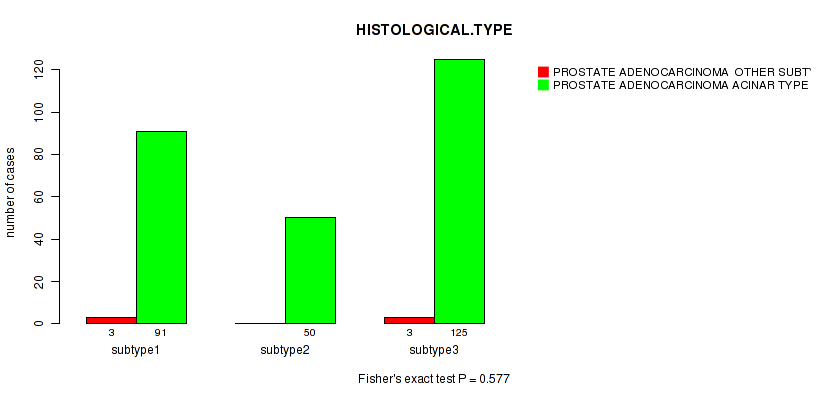
P value = 0.768 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S104. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 193 | 57 | 3 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 70 | 16 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 34 | 12 | 1 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 89 | 29 | 2 | 3 |
Figure S96. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
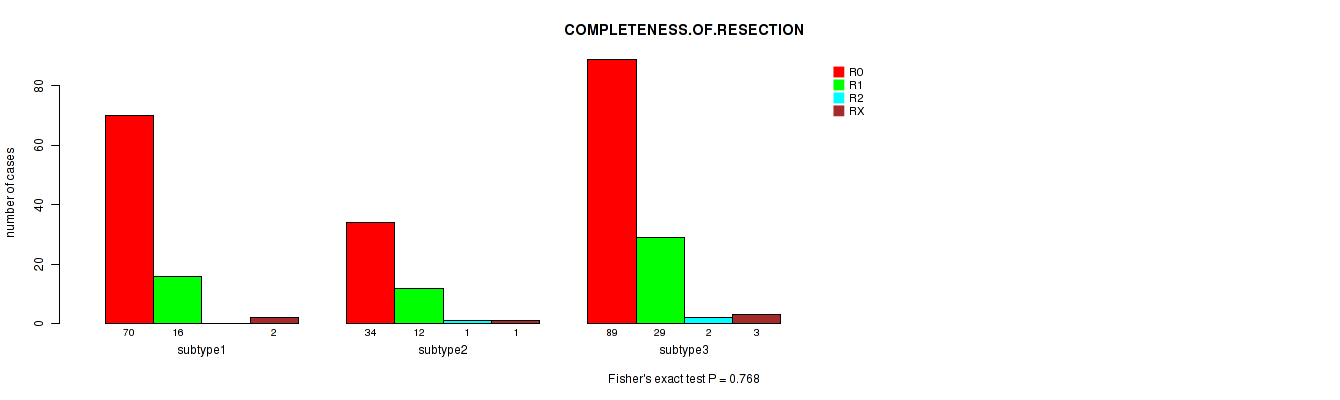
P value = 0.00463 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.44
Table S105. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 224 | 0.2 (1.2) |
| subtype1 | 80 | 0.1 (0.4) |
| subtype2 | 37 | 0.0 (0.0) |
| subtype3 | 107 | 0.4 (1.6) |
Figure S97. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
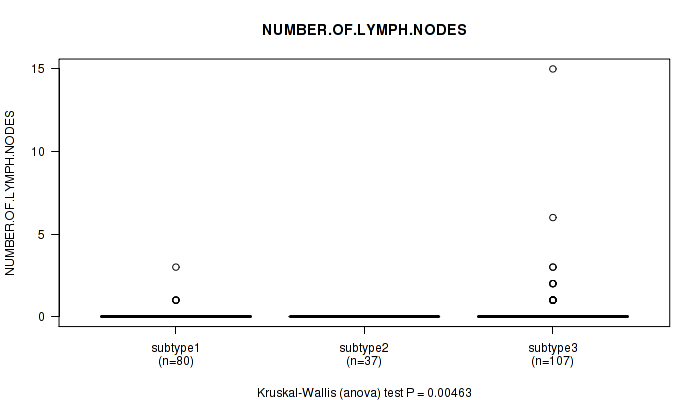
P value = 8.63e-06 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.0011
Table S106. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 94 | 7.1 (0.7) |
| subtype2 | 50 | 7.0 (0.7) |
| subtype3 | 128 | 7.5 (0.9) |
Figure S98. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
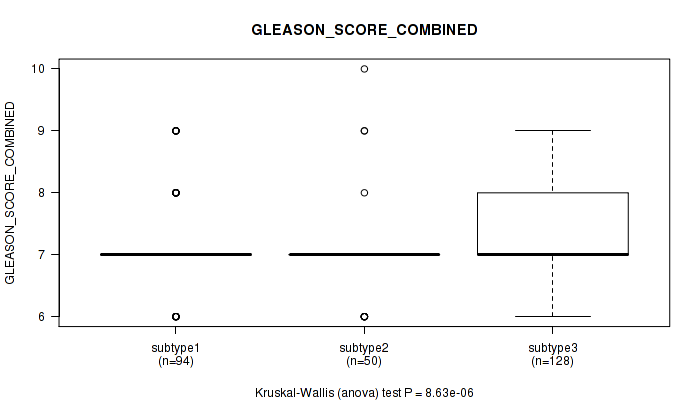
P value = 1.63e-05 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.002
Table S107. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 94 | 3.4 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 50 | 3.3 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 128 | 3.7 (0.6) |
Figure S99. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
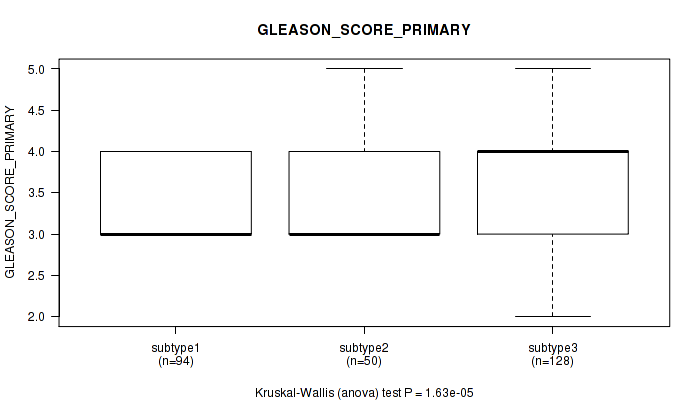
P value = 0.28 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S108. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 94 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 50 | 3.7 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 128 | 3.9 (0.7) |
Figure S100. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
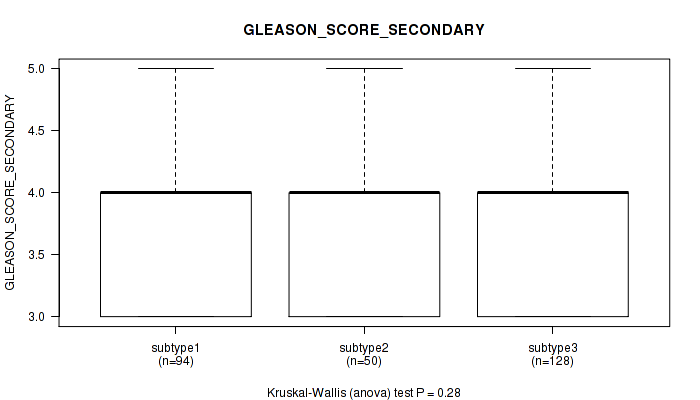
P value = 0.00014 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.016
Table S109. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 94 | 7.1 (0.7) |
| subtype2 | 50 | 7.1 (0.8) |
| subtype3 | 128 | 7.5 (0.9) |
Figure S101. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
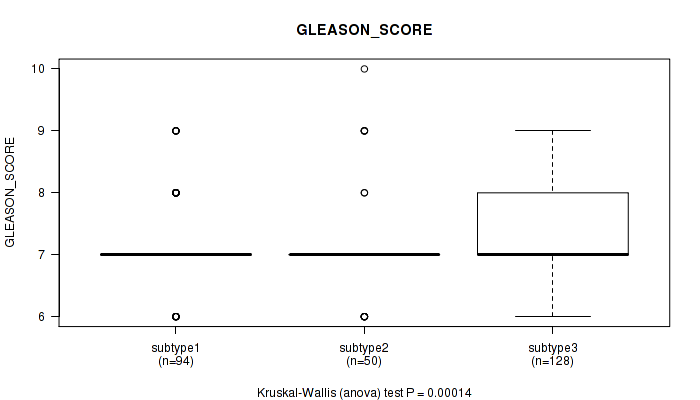
P value = 0.188 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S110. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 270 | 10.5 (11.2) |
| subtype1 | 93 | 9.1 (10.3) |
| subtype2 | 50 | 10.6 (13.2) |
| subtype3 | 127 | 11.4 (11.0) |
Figure S102. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
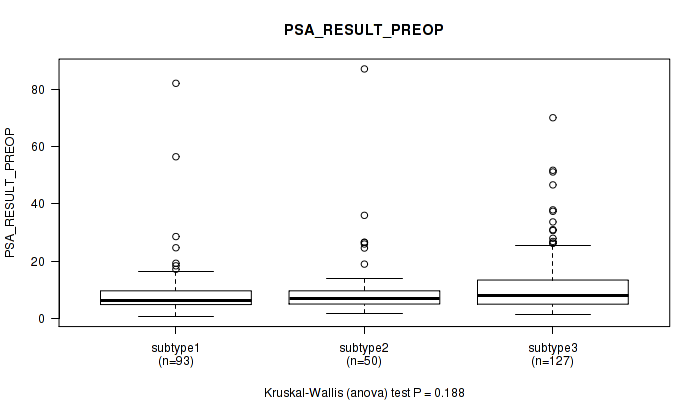
P value = 0.0193 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S111. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 228 | 1.1 (3.9) |
| subtype1 | 85 | 1.0 (3.0) |
| subtype2 | 47 | 0.1 (0.2) |
| subtype3 | 96 | 1.7 (5.2) |
Figure S103. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
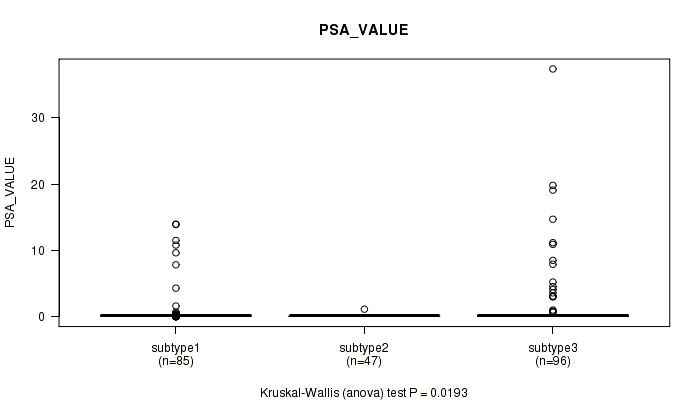
P value = 0.824 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S112. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 7 | 146 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 1 | 50 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 2 | 28 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 4 | 68 |
Figure S104. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
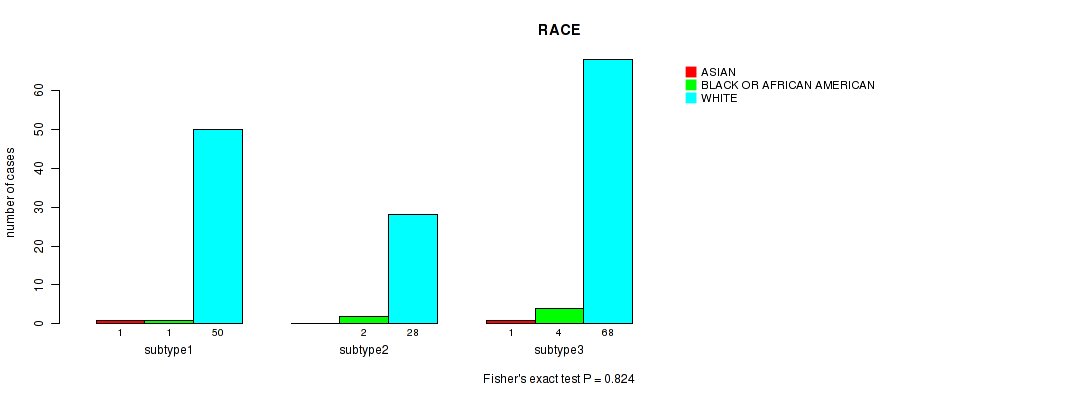
Table S113. Description of clustering approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 73 | 99 | 100 |
P value = 0.0573 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S114. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 269 | 60.4 (7.0) |
| subtype1 | 73 | 62.0 (6.7) |
| subtype2 | 96 | 59.3 (7.1) |
| subtype3 | 100 | 60.2 (7.0) |
Figure S105. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
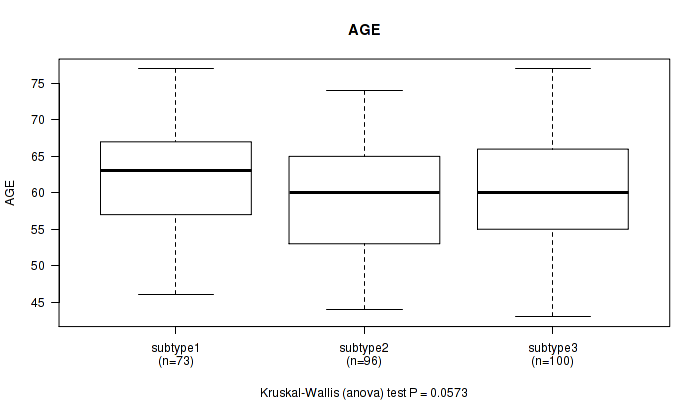
P value = 0.419 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S115. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 127 | 139 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 31 | 42 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 51 | 47 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 45 | 50 | 3 |
Figure S106. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
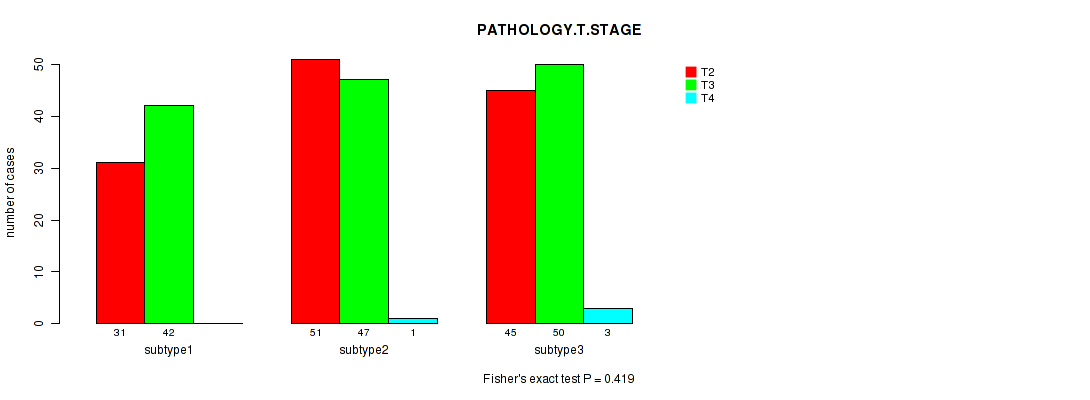
P value = 0.113 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S116. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 203 | 23 |
| subtype1 | 50 | 10 |
| subtype2 | 72 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 81 | 5 |
Figure S107. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
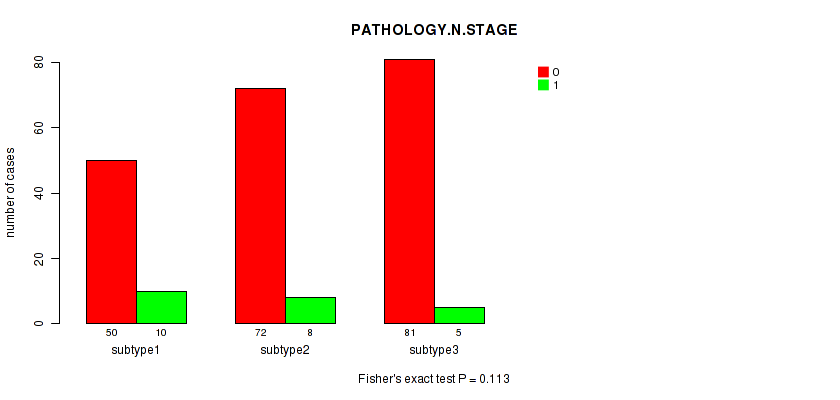
P value = 0.0408 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S117. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 266 |
| subtype1 | 4 | 69 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 99 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 98 |
Figure S108. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
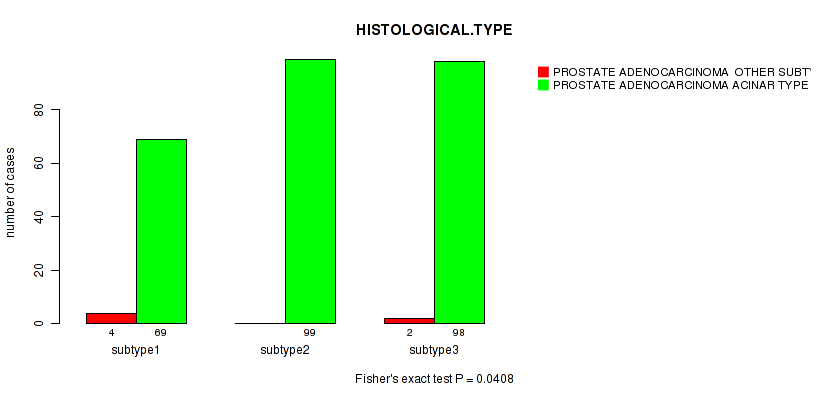
P value = 0.435 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S118. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 193 | 57 | 3 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 48 | 21 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 73 | 15 | 2 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 72 | 21 | 1 | 2 |
Figure S109. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
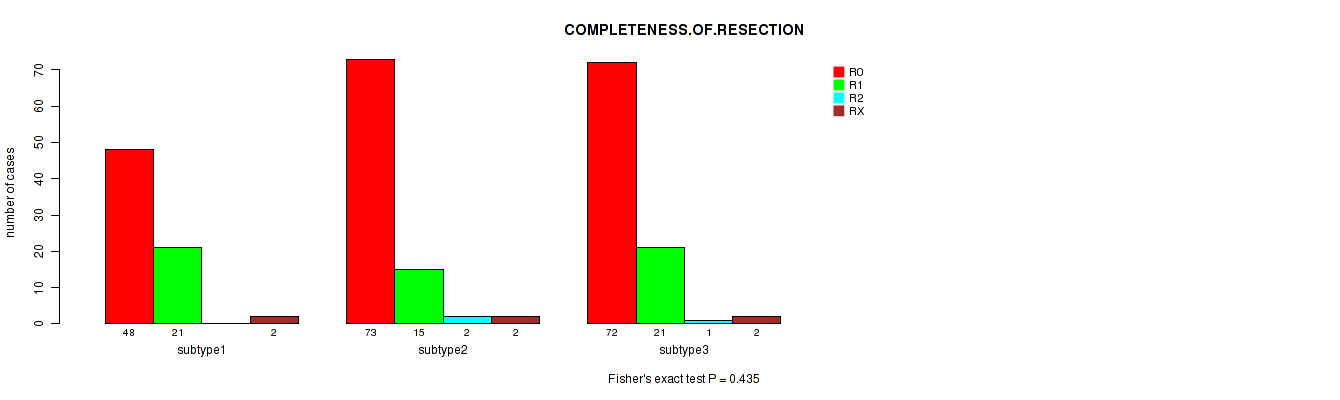
P value = 0.0953 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S119. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 224 | 0.2 (1.2) |
| subtype1 | 60 | 0.4 (1.0) |
| subtype2 | 80 | 0.3 (1.7) |
| subtype3 | 84 | 0.1 (0.4) |
Figure S110. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
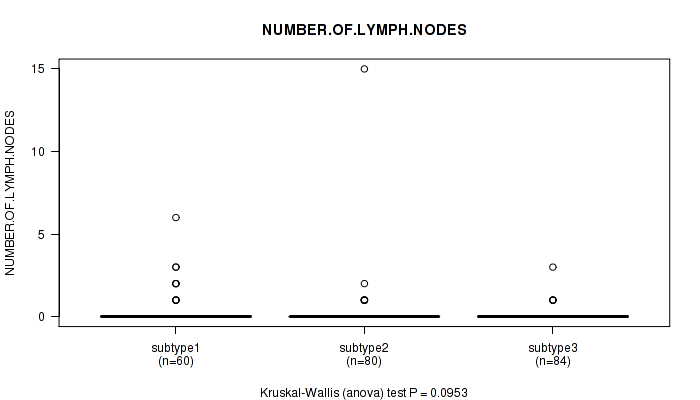
P value = 0.0034 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.34
Table S120. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 73 | 7.6 (0.9) |
| subtype2 | 99 | 7.2 (0.7) |
| subtype3 | 100 | 7.2 (0.7) |
Figure S111. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
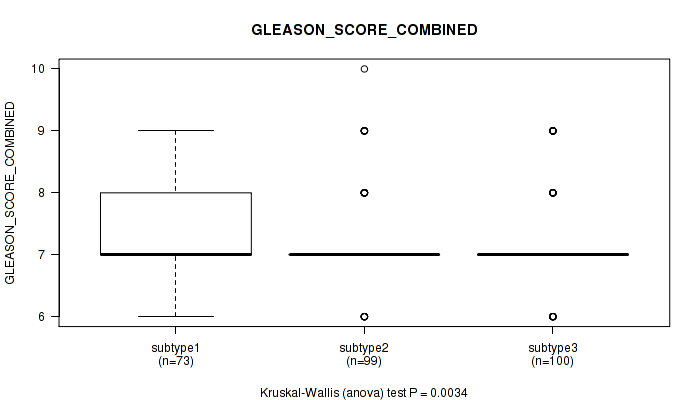
P value = 0.00568 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.54
Table S121. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 73 | 3.7 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 99 | 3.4 (0.5) |
| subtype3 | 100 | 3.4 (0.5) |
Figure S112. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
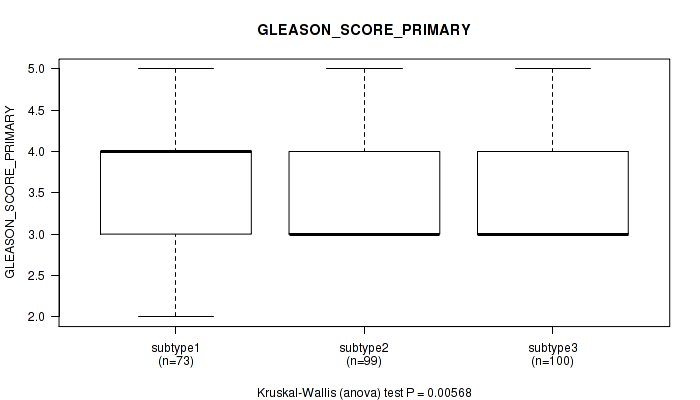
P value = 0.333 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S122. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 73 | 3.9 (0.7) |
| subtype2 | 99 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 100 | 3.8 (0.6) |
Figure S113. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
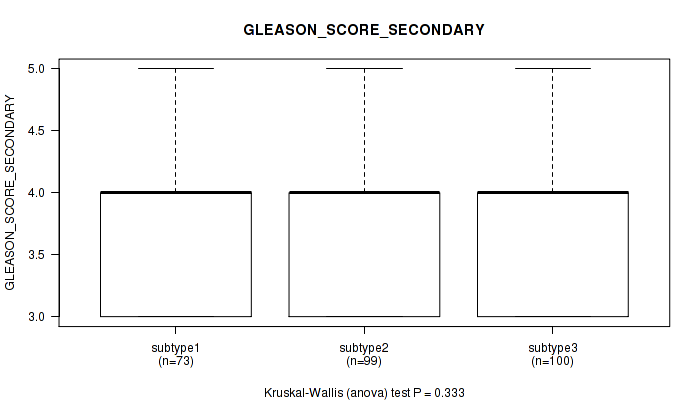
P value = 0.00761 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.7
Table S123. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 73 | 7.6 (1.0) |
| subtype2 | 99 | 7.2 (0.7) |
| subtype3 | 100 | 7.2 (0.8) |
Figure S114. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
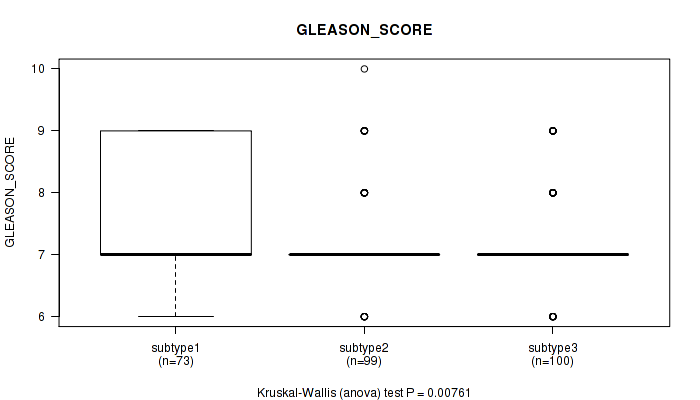
P value = 0.775 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S124. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 270 | 10.5 (11.2) |
| subtype1 | 72 | 12.0 (12.4) |
| subtype2 | 99 | 10.0 (10.7) |
| subtype3 | 99 | 9.9 (10.8) |
Figure S115. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
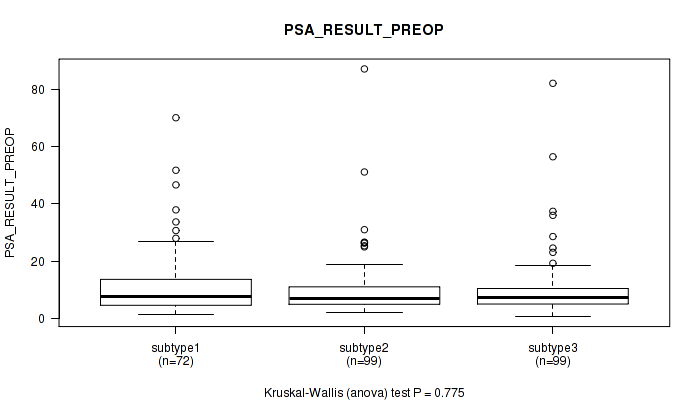
P value = 0.668 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S125. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 228 | 1.1 (3.9) |
| subtype1 | 54 | 1.7 (4.4) |
| subtype2 | 81 | 0.5 (1.6) |
| subtype3 | 93 | 1.3 (4.8) |
Figure S116. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
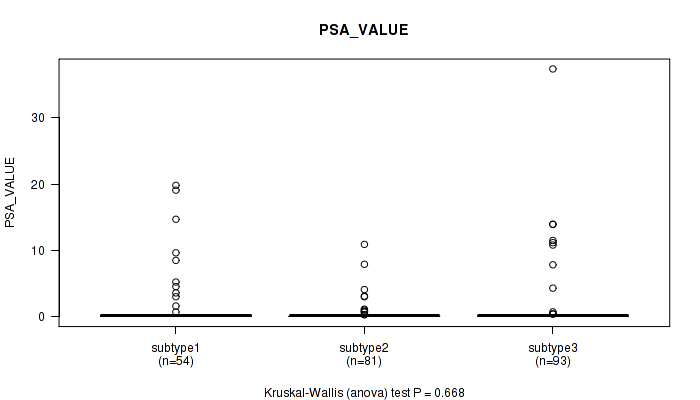
P value = 0.828 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S126. Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 7 | 146 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 0 | 19 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 5 | 69 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 2 | 58 |
Figure S117. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #9: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
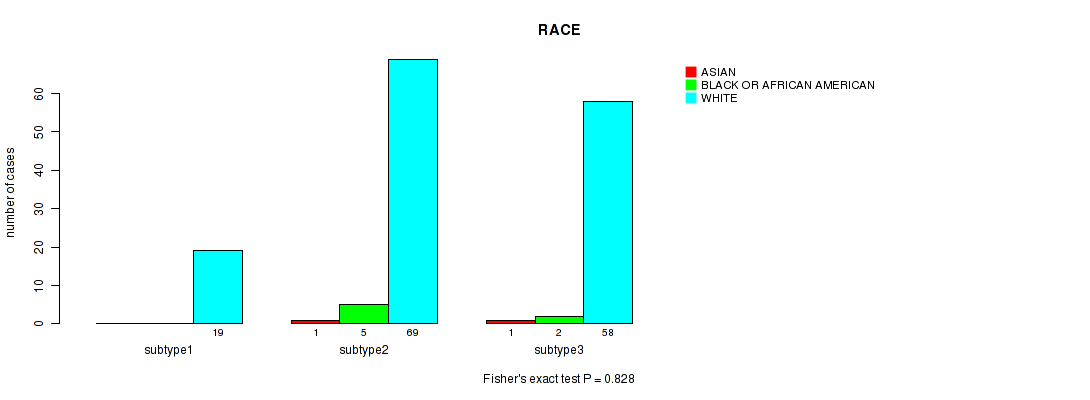
Table S127. Description of clustering approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 44 | 25 | 55 | 62 | 86 |
P value = 0.636 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S128. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 269 | 60.4 (7.0) |
| subtype1 | 44 | 60.6 (6.6) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 59.4 (7.8) |
| subtype3 | 55 | 61.4 (7.0) |
| subtype4 | 62 | 60.7 (7.0) |
| subtype5 | 83 | 59.7 (7.1) |
Figure S118. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'AGE'
P value = 8e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0095
Table S129. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
| nPatients | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 127 | 139 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 25 | 18 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 14 | 7 | 4 |
| subtype3 | 20 | 35 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 22 | 39 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 46 | 40 | 0 |
Figure S119. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'PATHOLOGY.T.STAGE'
P value = 0.0916 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S130. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 203 | 23 |
| subtype1 | 33 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 19 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 40 | 7 |
| subtype4 | 50 | 9 |
| subtype5 | 61 | 6 |
Figure S120. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'PATHOLOGY.N.STAGE'
P value = 0.014 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S131. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
| nPatients | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA OTHER SUBTYPE | PROSTATE ADENOCARCINOMA ACINAR TYPE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 266 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 41 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 25 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 52 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 62 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 86 |
Figure S121. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'HISTOLOGICAL.TYPE'
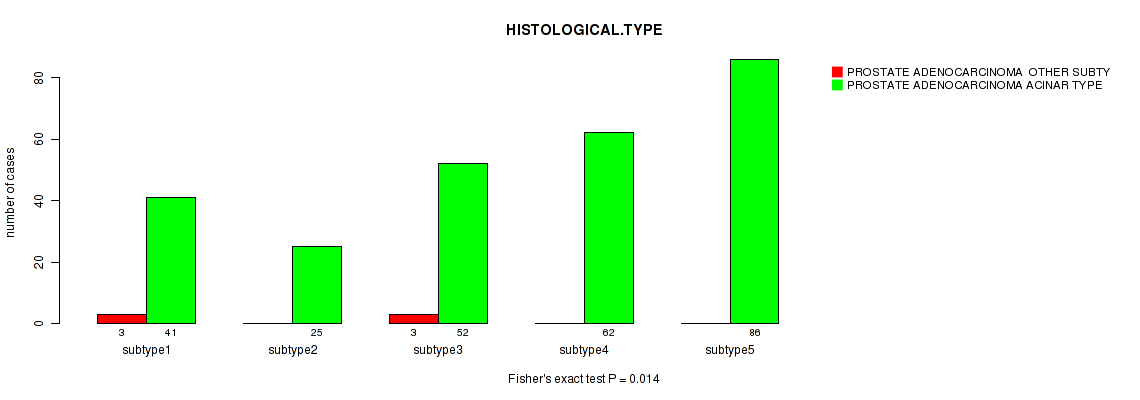
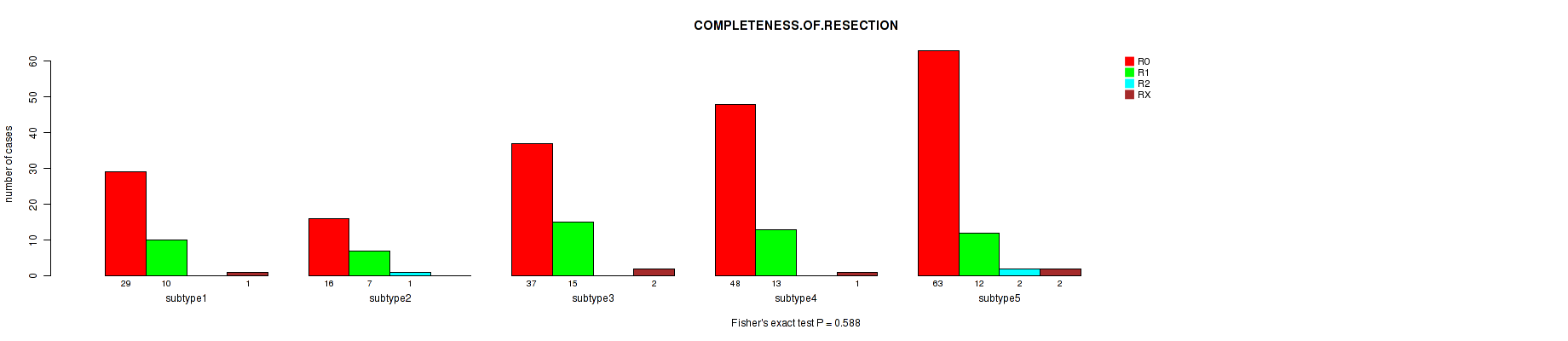
P value = 0.588 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S132. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 193 | 57 | 3 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 29 | 10 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 16 | 7 | 1 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 37 | 15 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype4 | 48 | 13 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype5 | 63 | 12 | 2 | 2 |
Figure S122. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'COMPLETENESS.OF.RESECTION'
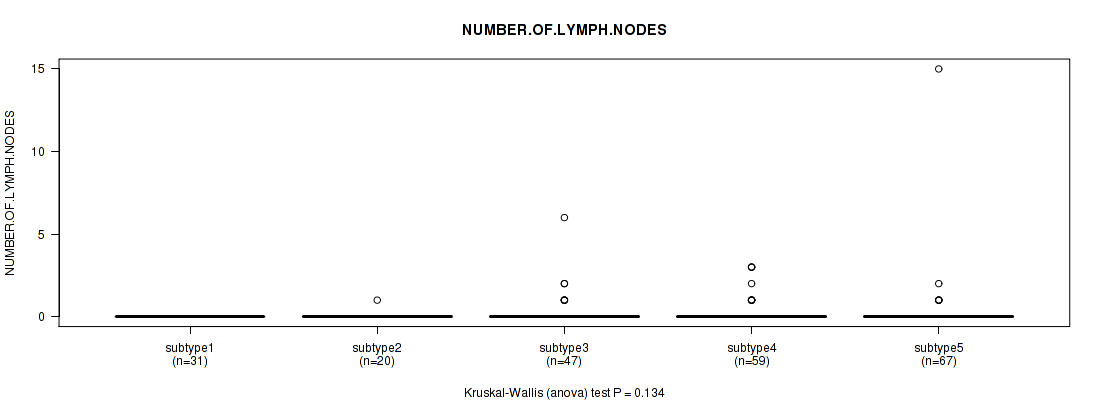
P value = 0.134 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S133. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 224 | 0.2 (1.2) |
| subtype1 | 31 | 0.0 (0.0) |
| subtype2 | 20 | 0.1 (0.2) |
| subtype3 | 47 | 0.3 (1.0) |
| subtype4 | 59 | 0.3 (0.7) |
| subtype5 | 67 | 0.3 (1.9) |
Figure S123. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'NUMBER.OF.LYMPH.NODES'
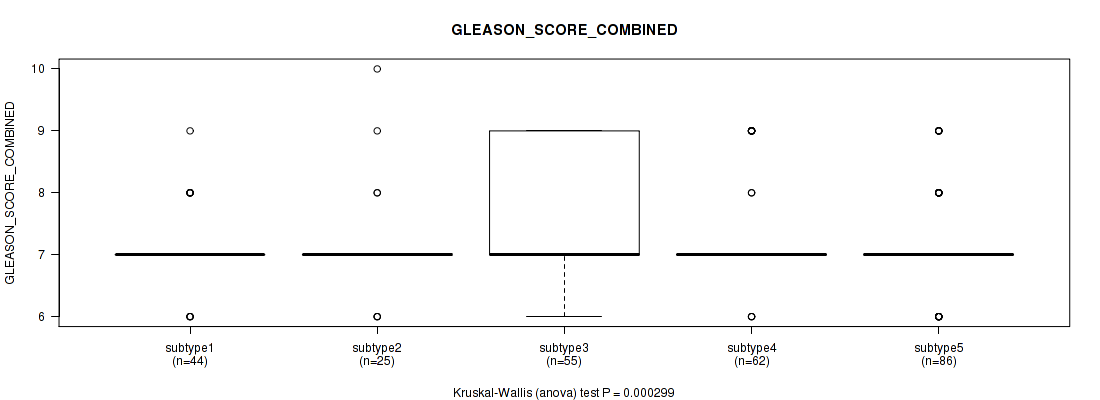
P value = 0.000299 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.033
Table S134. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 44 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 7.2 (0.9) |
| subtype3 | 55 | 7.7 (1.0) |
| subtype4 | 62 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype5 | 86 | 7.2 (0.7) |
Figure S124. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GLEASON_SCORE_COMBINED'
P value = 0.00148 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.15
Table S135. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 44 | 3.4 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 3.5 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 55 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype4 | 62 | 3.4 (0.6) |
| subtype5 | 86 | 3.4 (0.5) |
Figure S125. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'GLEASON_SCORE_PRIMARY'
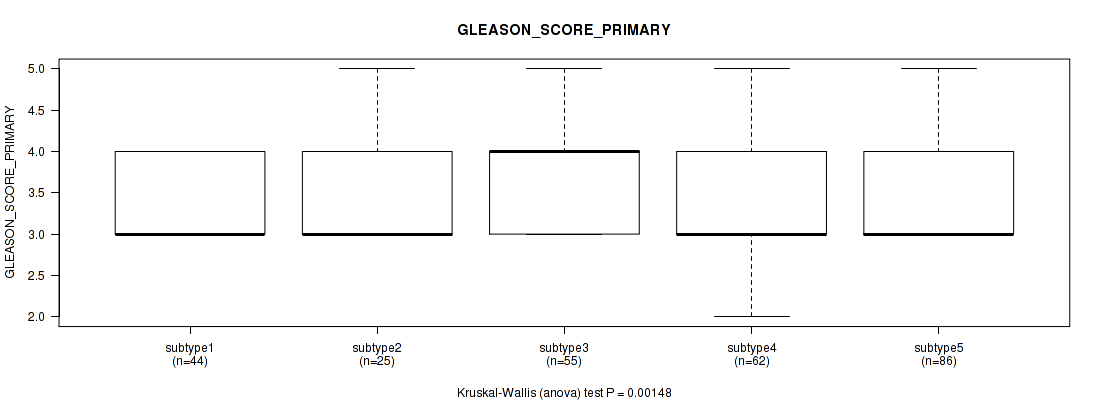
P value = 0.264 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S136. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype1 | 44 | 3.7 (0.5) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 3.7 (0.6) |
| subtype3 | 55 | 4.0 (0.7) |
| subtype4 | 62 | 3.8 (0.6) |
| subtype5 | 86 | 3.7 (0.6) |
Figure S126. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'GLEASON_SCORE_SECONDARY'
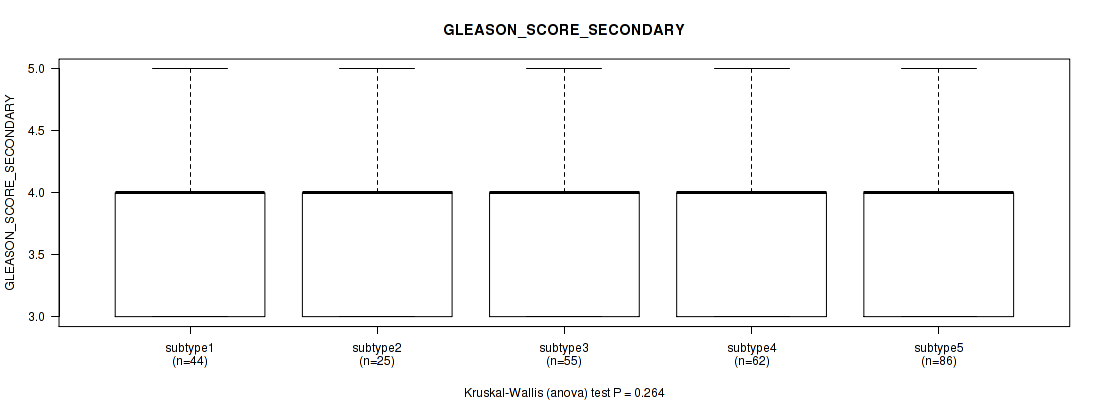
P value = 0.00113 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.12
Table S137. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 272 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype1 | 44 | 7.1 (0.6) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 7.4 (1.0) |
| subtype3 | 55 | 7.7 (1.0) |
| subtype4 | 62 | 7.3 (0.8) |
| subtype5 | 86 | 7.2 (0.7) |
Figure S127. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GLEASON_SCORE'
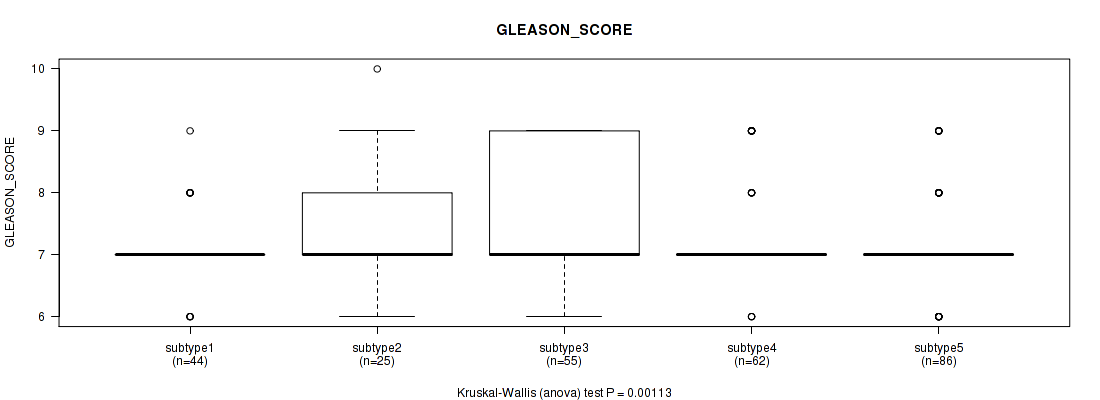
P value = 0.0185 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S138. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 270 | 10.5 (11.2) |
| subtype1 | 44 | 9.1 (13.8) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 13.3 (17.2) |
| subtype3 | 55 | 12.6 (12.8) |
| subtype4 | 60 | 10.8 (8.3) |
| subtype5 | 86 | 8.9 (7.5) |
Figure S128. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'PSA_RESULT_PREOP'
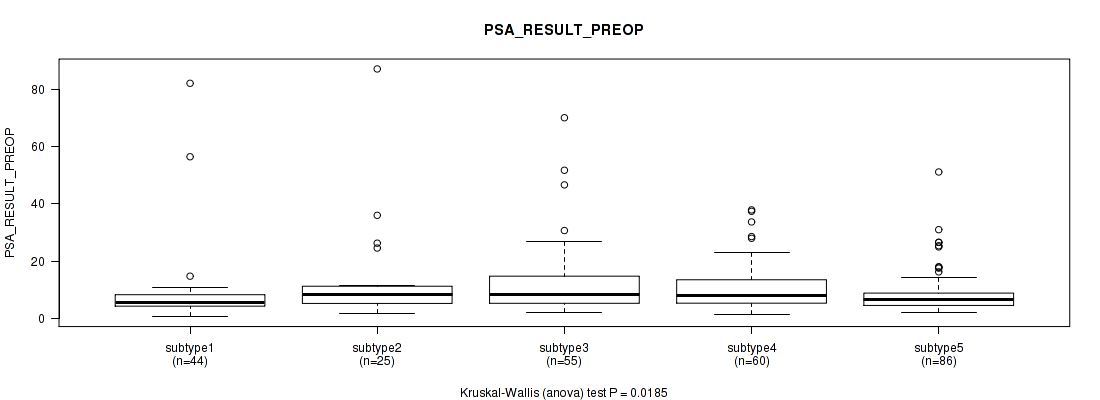
P value = 0.149 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S139. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 228 | 1.1 (3.9) |
| subtype1 | 37 | 0.6 (2.1) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 0.1 (0.2) |
| subtype3 | 36 | 1.7 (4.7) |
| subtype4 | 60 | 2.1 (6.0) |
| subtype5 | 70 | 0.5 (1.7) |
Figure S129. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'PSA_VALUE'
P value = 0.139 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S140. Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 7 | 146 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 2 | 11 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 1 | 9 |
| subtype4 | 1 | 0 | 61 |
| subtype5 | 1 | 4 | 61 |
Figure S130. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #10: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
-
Cluster data file = PRAD-TP.mergedcluster.txt
-
Clinical data file = PRAD-TP.merged_data.txt
-
Number of patients = 274
-
Number of clustering approaches = 10
-
Number of selected clinical features = 13
-
Exclude small clusters that include fewer than K patients, K = 3
consensus non-negative matrix factorization clustering approach (Brunet et al. 2004)
Resampling-based clustering method (Monti et al. 2003)
For binary clinical features, two-tailed Fisher's exact tests (Fisher 1922) were used to estimate the P values using the 'fisher.test' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.
In addition to the links below, the full results of the analysis summarized in this report can also be downloaded programmatically using firehose_get, or interactively from either the Broad GDAC website or TCGA Data Coordination Center Portal.