This pipeline computes the correlation between significantly recurrent gene mutations and selected clinical features.
Testing the association between mutation status of 30 genes and 10 clinical features across 441 patients, 4 significant findings detected with Q value < 0.25.
-
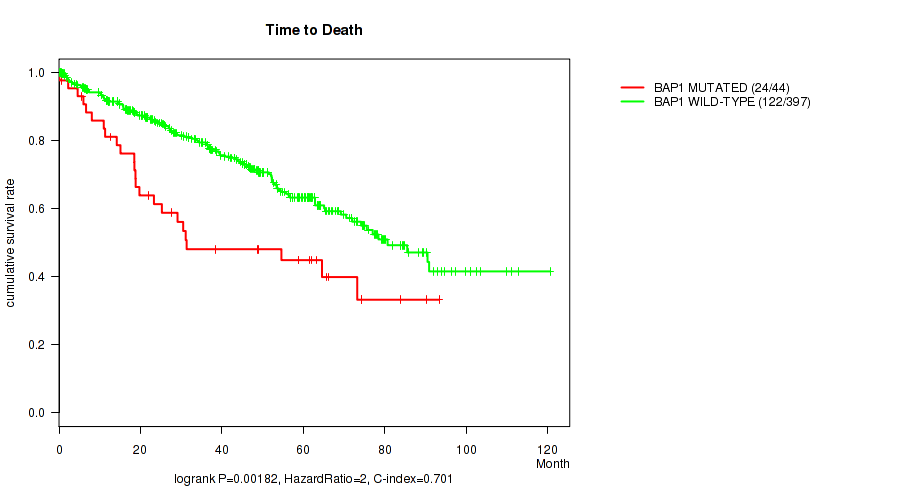
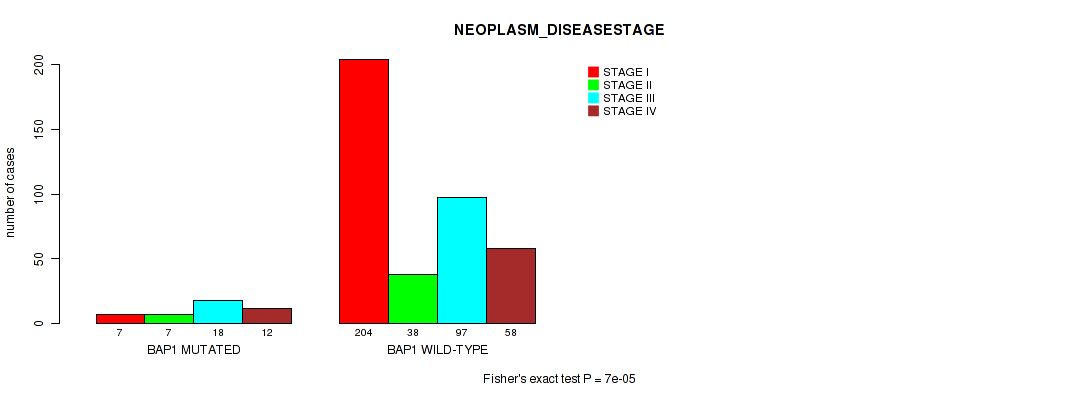
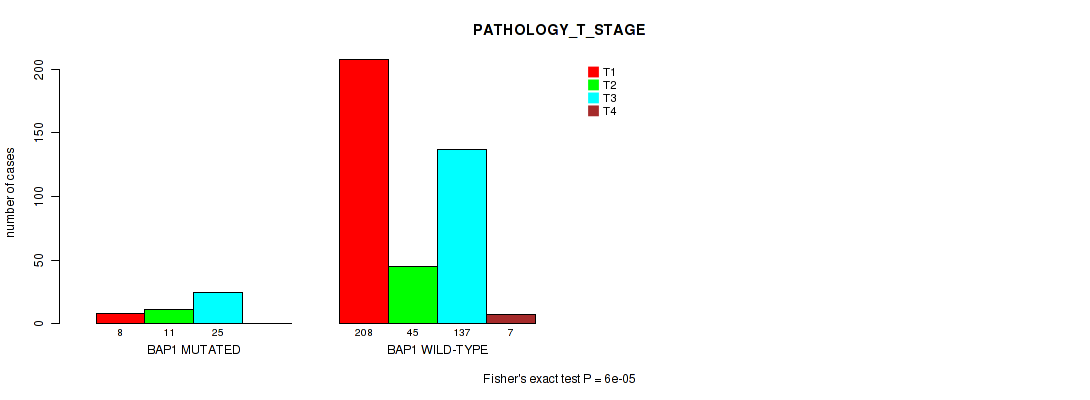
BAP1 mutation correlated to 'Time to Death', 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE', and 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'.
-
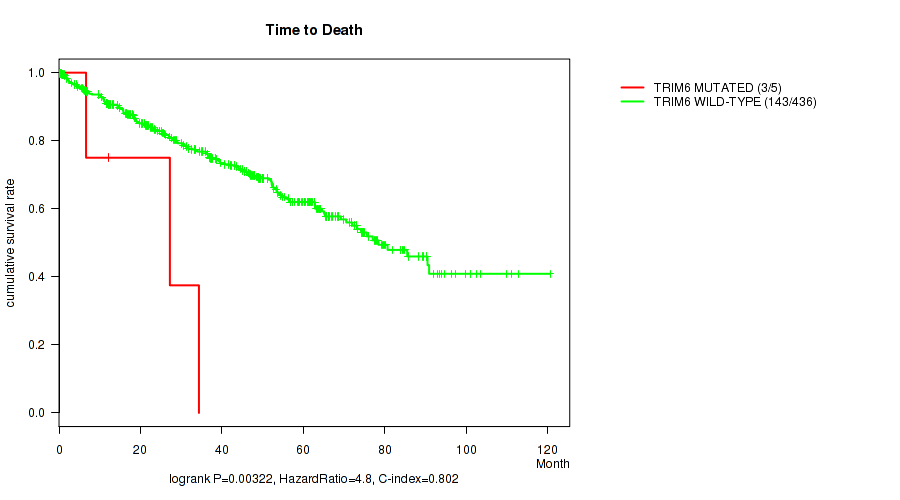
TRIM6 mutation correlated to 'Time to Death'.
Table 1. Get Full Table Overview of the association between mutation status of 30 genes and 10 clinical features. Shown in the table are P values (Q values). Thresholded by Q value < 0.25, 4 significant findings detected.
|
Clinical Features |
Time to Death |
YEARS TO BIRTH |
NEOPLASM DISEASESTAGE |
PATHOLOGY T STAGE |
PATHOLOGY N STAGE |
PATHOLOGY M STAGE |
GENDER |
KARNOFSKY PERFORMANCE SCORE |
RACE | ETHNICITY | ||
| nMutated (%) | nWild-Type | logrank test | Wilcoxon-test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | Wilcoxon-test | Fisher's exact test | Fisher's exact test | |
| BAP1 | 44 (10%) | 397 |
0.00182 (0.182) |
0.916 (1.00) |
7e-05 (0.0105) |
6e-05 (0.0105) |
0.245 (1.00) |
0.0152 (0.364) |
0.00713 (0.267) |
1 (1.00) |
0.724 (1.00) |
|
| TRIM6 | 5 (1%) | 436 |
0.00322 (0.242) |
0.196 (0.944) |
0.634 (1.00) |
0.599 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| SETD2 | 46 (10%) | 395 |
0.1 (0.916) |
0.241 (1.00) |
0.299 (1.00) |
0.191 (0.944) |
0.379 (1.00) |
0.285 (1.00) |
0.332 (1.00) |
0.732 (1.00) |
0.71 (1.00) |
|
| PBRM1 | 139 (32%) | 302 |
0.505 (1.00) |
0.185 (0.944) |
0.986 (1.00) |
0.186 (0.944) |
0.163 (0.944) |
0.781 (1.00) |
0.592 (1.00) |
0.547 (1.00) |
0.255 (1.00) |
0.234 (1.00) |
| KDM5C | 27 (6%) | 414 |
0.0591 (0.771) |
0.0331 (0.584) |
0.98 (1.00) |
0.975 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.00615 (0.267) |
1 (1.00) |
0.379 (1.00) |
|
| VHL | 171 (39%) | 270 |
0.898 (1.00) |
0.726 (1.00) |
0.137 (0.916) |
0.111 (0.916) |
0.791 (1.00) |
0.287 (1.00) |
0.474 (1.00) |
0.278 (1.00) |
0.0156 (0.364) |
0.821 (1.00) |
| PTEN | 17 (4%) | 424 |
0.855 (1.00) |
0.575 (1.00) |
0.0871 (0.916) |
0.328 (1.00) |
0.158 (0.944) |
0.494 (1.00) |
0.0405 (0.675) |
0.427 (1.00) |
0.658 (1.00) |
0.61 (1.00) |
| MTOR | 28 (6%) | 413 |
0.138 (0.916) |
0.12 (0.916) |
0.276 (1.00) |
0.378 (1.00) |
0.356 (1.00) |
0.182 (0.944) |
0.103 (0.916) |
0.0256 (0.511) |
0.179 (0.944) |
1 (1.00) |
| TP53 | 12 (3%) | 429 |
0.00989 (0.33) |
0.875 (1.00) |
0.507 (1.00) |
0.262 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.416 (1.00) |
0.76 (1.00) |
0.529 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| FAM200A | 5 (1%) | 436 |
0.495 (1.00) |
0.685 (1.00) |
0.759 (1.00) |
0.486 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.0538 (0.74) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| NEFH | 5 (1%) | 436 |
0.669 (1.00) |
0.543 (1.00) |
0.128 (0.916) |
0.197 (0.944) |
1 (1.00) |
0.58 (1.00) |
0.661 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| PTCH1 | 7 (2%) | 434 |
0.0543 (0.74) |
0.245 (1.00) |
0.366 (1.00) |
0.0758 (0.843) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.701 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| NF2 | 6 (1%) | 435 |
0.139 (0.916) |
0.322 (1.00) |
0.457 (1.00) |
0.471 (1.00) |
0.0143 (0.364) |
0.244 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.31 (1.00) |
0.358 (1.00) |
|
| CCDC120 | 4 (1%) | 437 |
0.134 (0.916) |
0.856 (1.00) |
0.105 (0.916) |
0.122 (0.916) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.198 (0.944) |
|
| PIK3CA | 12 (3%) | 429 |
0.618 (1.00) |
0.83 (1.00) |
0.57 (1.00) |
0.593 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.0296 (0.556) |
1 (1.00) |
0.56 (1.00) |
|
| ATM | 12 (3%) | 429 |
0.96 (1.00) |
0.332 (1.00) |
0.136 (0.916) |
0.00711 (0.267) |
0.132 (0.916) |
0.416 (1.00) |
0.358 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.405 (1.00) |
|
| KIAA1751 | 6 (1%) | 435 |
0.9 (1.00) |
0.186 (0.944) |
0.497 (1.00) |
0.878 (1.00) |
0.317 (1.00) |
0.596 (1.00) |
0.67 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| GUSB | 4 (1%) | 437 |
0.826 (1.00) |
0.0707 (0.839) |
0.168 (0.944) |
0.396 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| ARID1A | 11 (2%) | 430 |
0.866 (1.00) |
0.735 (1.00) |
0.0518 (0.74) |
0.112 (0.916) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.528 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.127 (0.916) |
|
| GPR50 | 3 (1%) | 438 |
0.272 (1.00) |
0.9 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.283 (1.00) |
0.168 (0.944) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| PCK1 | 5 (1%) | 436 |
0.187 (0.944) |
0.345 (1.00) |
0.18 (0.944) |
0.278 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| DPCR1 | 6 (1%) | 435 |
0.384 (1.00) |
0.517 (1.00) |
0.103 (0.916) |
0.877 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.0536 (0.74) |
1 (1.00) |
0.31 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| NFAT5 | 6 (1%) | 435 |
0.88 (1.00) |
0.628 (1.00) |
0.708 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.596 (1.00) |
0.67 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| EGFR | 7 (2%) | 434 |
0.017 (0.364) |
0.595 (1.00) |
0.0161 (0.364) |
0.00624 (0.267) |
0.262 (1.00) |
0.308 (1.00) |
0.43 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| RBMX | 4 (1%) | 437 |
0.701 (1.00) |
0.217 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.14 (0.916) |
0.5 (1.00) |
0.302 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| GPR172B | 4 (1%) | 437 |
0.576 (1.00) |
0.798 (1.00) |
0.885 (1.00) |
0.805 (1.00) |
0.204 (0.954) |
1 (1.00) |
0.127 (0.916) |
1 (1.00) |
0.0707 (0.839) |
|
| FGFR3 | 4 (1%) | 437 |
0.973 (1.00) |
0.666 (1.00) |
0.283 (1.00) |
0.496 (1.00) |
0.0727 (0.839) |
1 (1.00) |
0.302 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| ARAP3 | 3 (1%) | 438 |
0.733 (1.00) |
0.544 (1.00) |
0.819 (1.00) |
0.735 (1.00) |
0.405 (1.00) |
0.283 (1.00) |
0.169 (0.944) |
1 (1.00) |
||
| OPTC | 4 (1%) | 437 |
0.946 (1.00) |
0.636 (1.00) |
0.884 (1.00) |
0.808 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
0.615 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
|
| GOLGA5 | 5 (1%) | 436 |
0.44 (1.00) |
0.725 (1.00) |
0.181 (0.944) |
0.276 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
P value = 0.00182 (logrank test), Q value = 0.18
Table S1. Gene #2: 'BAP1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 441 | 146 | 0.1 - 120.6 (37.6) |
| BAP1 MUTATED | 44 | 24 | 0.1 - 93.3 (28.3) |
| BAP1 WILD-TYPE | 397 | 122 | 0.2 - 120.6 (39.2) |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image Gene #2: 'BAP1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
P value = 7e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.01
Table S2. Gene #2: 'BAP1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE II | STAGE III | STAGE IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 211 | 45 | 115 | 70 |
| BAP1 MUTATED | 7 | 7 | 18 | 12 |
| BAP1 WILD-TYPE | 204 | 38 | 97 | 58 |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image Gene #2: 'BAP1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
P value = 6e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.01
Table S3. Gene #2: 'BAP1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| nPatients | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 216 | 56 | 162 | 7 |
| BAP1 MUTATED | 8 | 11 | 25 | 0 |
| BAP1 WILD-TYPE | 208 | 45 | 137 | 7 |
Figure S3. Get High-res Image Gene #2: 'BAP1 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
P value = 0.00322 (logrank test), Q value = 0.24
Table S4. Gene #24: 'TRIM6 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 441 | 146 | 0.1 - 120.6 (37.6) |
| TRIM6 MUTATED | 5 | 3 | 0.2 - 34.4 (12.3) |
| TRIM6 WILD-TYPE | 436 | 143 | 0.1 - 120.6 (38.5) |
Figure S4. Get High-res Image Gene #24: 'TRIM6 MUTATION STATUS' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
-
Mutation data file = sample_sig_gene_table.txt from Mutsig_2CV pipeline
-
Processed Mutation data file = /xchip/cga/gdac-prod/tcga-gdac/jobResults/GDAC_Correlate_Genomic_Events_Preprocess/KIRC-TP/15182434/transformed.cor.cli.txt
-
Clinical data file = /xchip/cga/gdac-prod/tcga-gdac/jobResults/Append_Data/KIRC-TP/15081616/KIRC-TP.merged_data.txt
-
Number of patients = 441
-
Number of significantly mutated genes = 30
-
Number of selected clinical features = 10
-
Exclude genes that fewer than K tumors have mutations, K = 3
For survival clinical features, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of tumors with and without gene mutations were plotted and the statistical significance P values were estimated by logrank test (Bland and Altman 2004) using the 'survdiff' function in R
For binary or multi-class clinical features (nominal or ordinal), two-tailed Fisher's exact tests (Fisher 1922) were used to estimate the P values using the 'fisher.test' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.
In addition to the links below, the full results of the analysis summarized in this report can also be downloaded programmatically using firehose_get, or interactively from either the Broad GDAC website or TCGA Data Coordination Center Portal.