This pipeline calculates clusters based on consensus hierarchical clustering with agglomerative average linkage[1],[2]. This pipeline has the following features:
-
Classify samples into consensus clusters.
-
Determine differentially expressed marker genes for each subtype.
The 1500 most variable genes were selected. Consensus average linkage hierarchical clustering of 1601 samples and 1500 genes identified 5 subtypes with the stability of the clustering increasing for k = 2 to k = 8 and the average silhouette width calculation for selecting the robust clusters.
Figure 1. Get High-res Image Silhouette width was calculated and the average silhouette width for all samples within one cluster was shown below according to different clusters (left panel). The robust cluster was pointed out by blue symbol (left panel) and the silhouette width of each sample in robust cluster was shown on right panel.
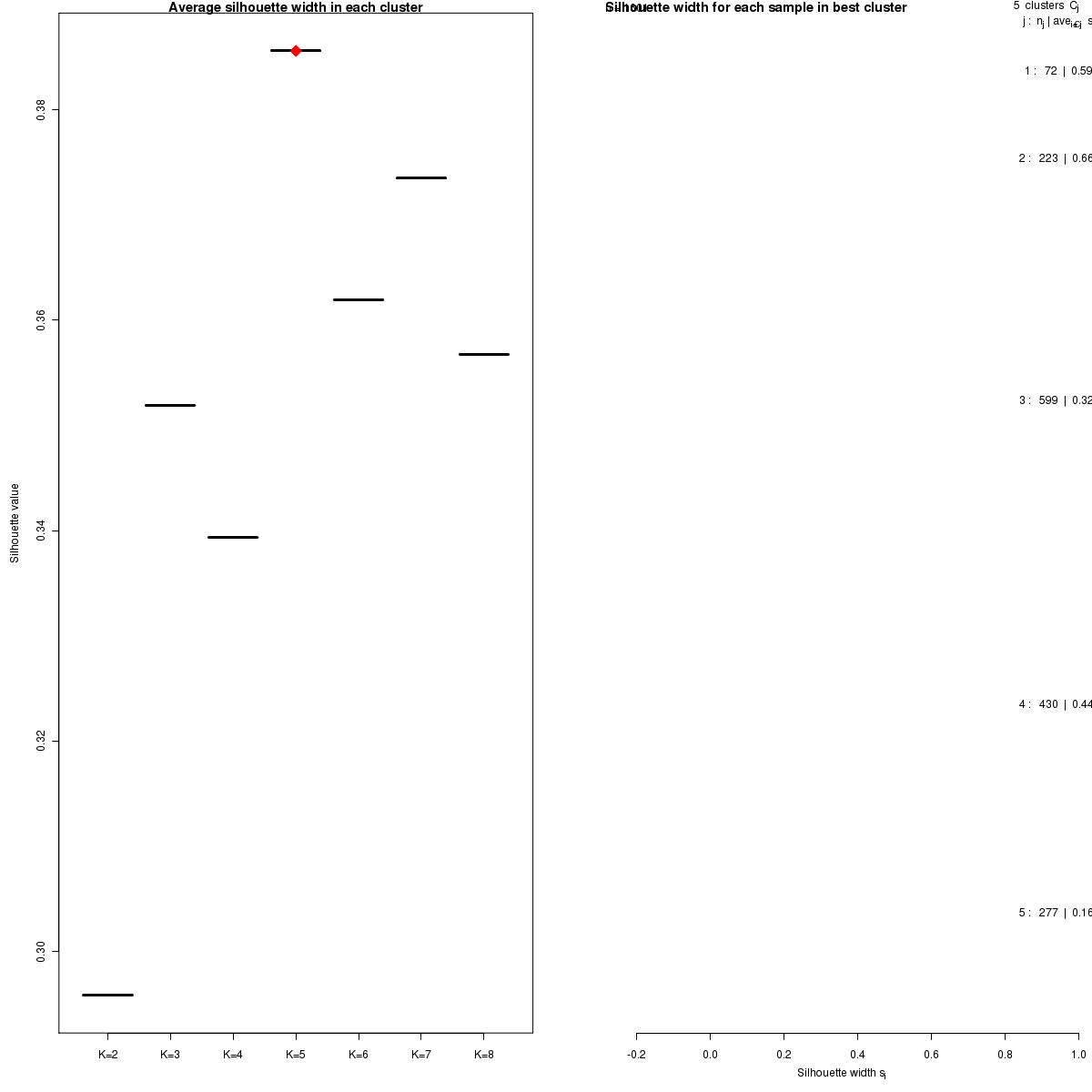
Figure 2. Get High-res Image The gene expression heatmap with a standard hierarchical clustering for 1601 samples and 1500 most variable genes.
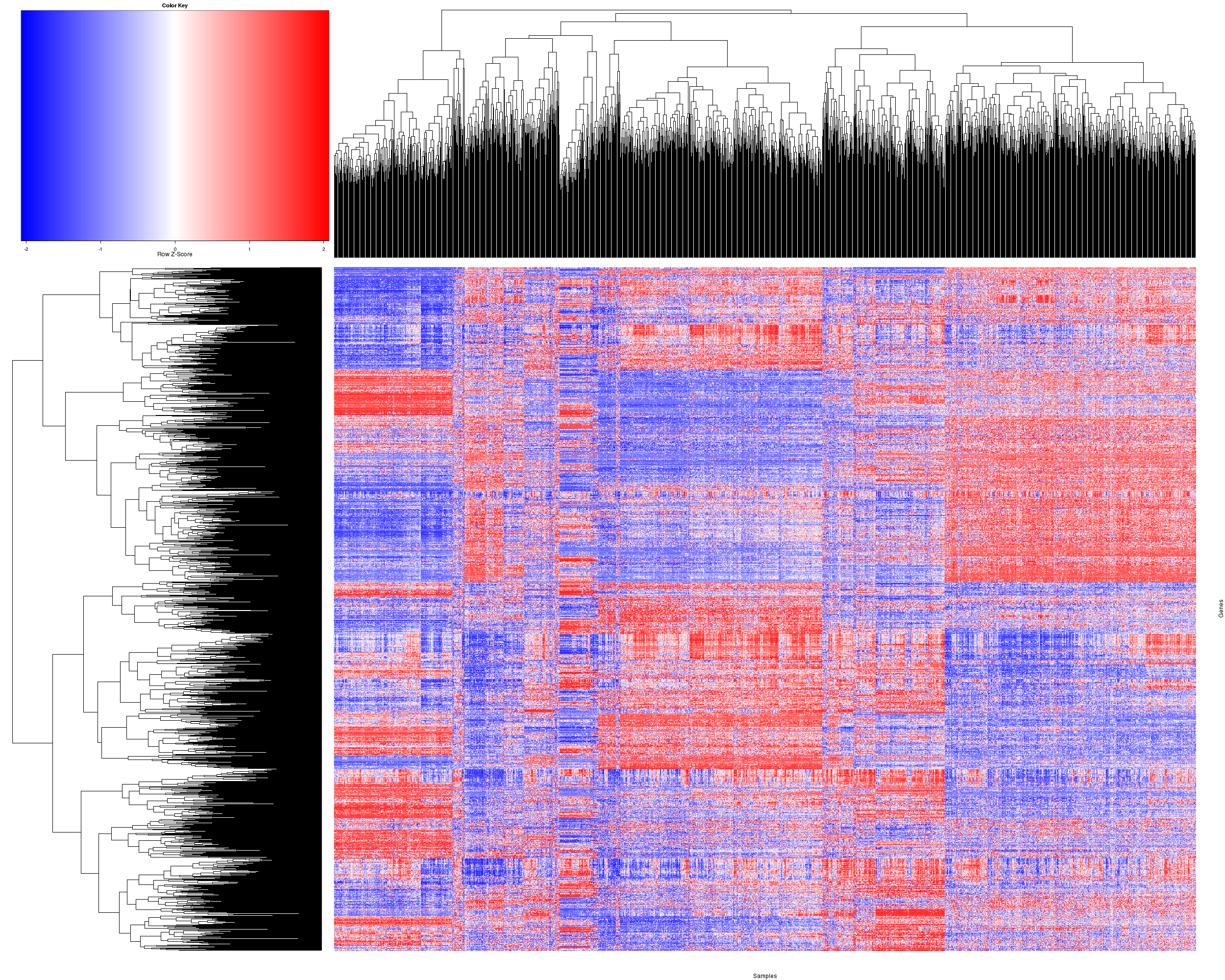
Figure 3. Get High-res Image The consensus matrix after clustering shows 5 robust clusters with limited overlap between clusters.
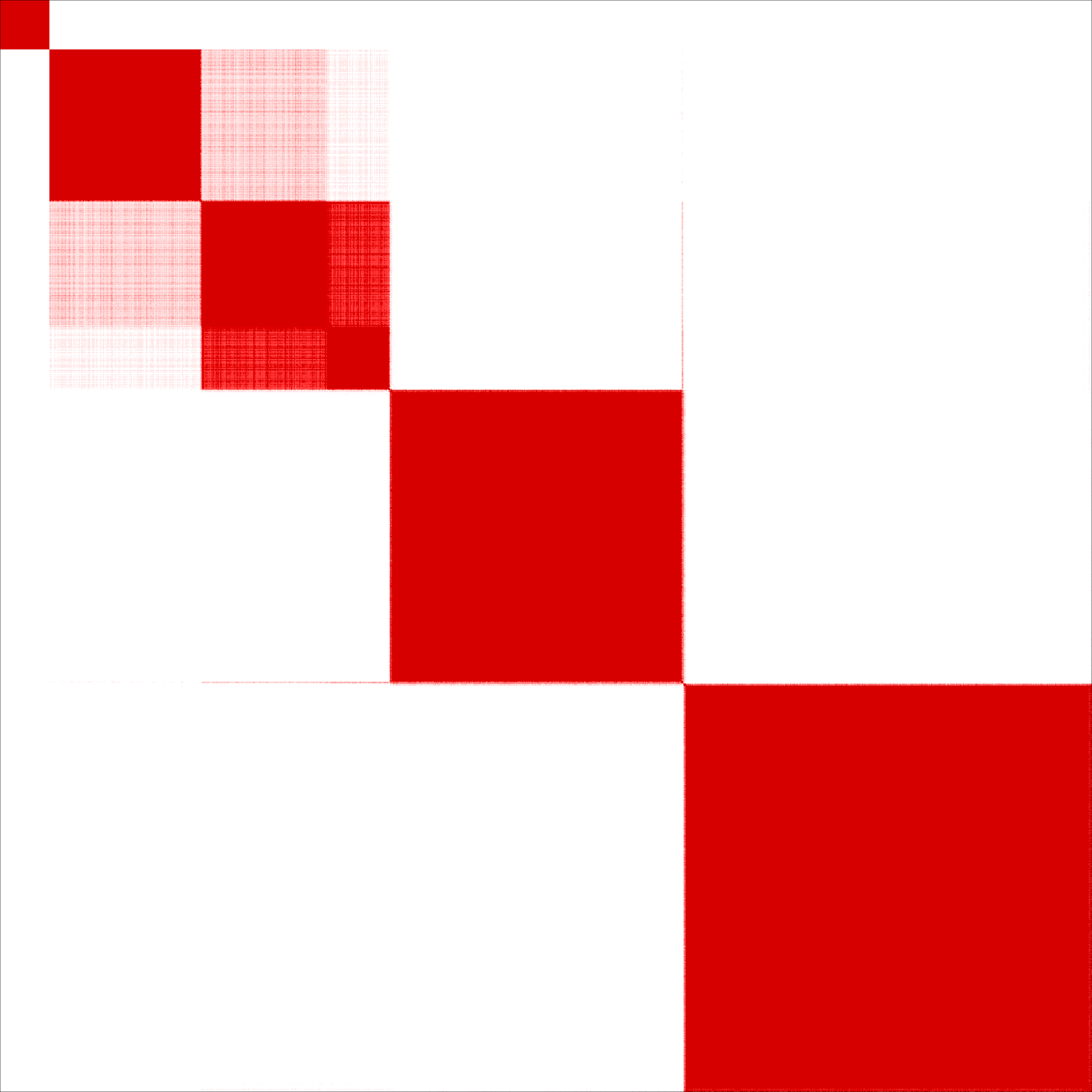
Figure 4. Get High-res Image The correlation matrix also shows 5 robust clusters.
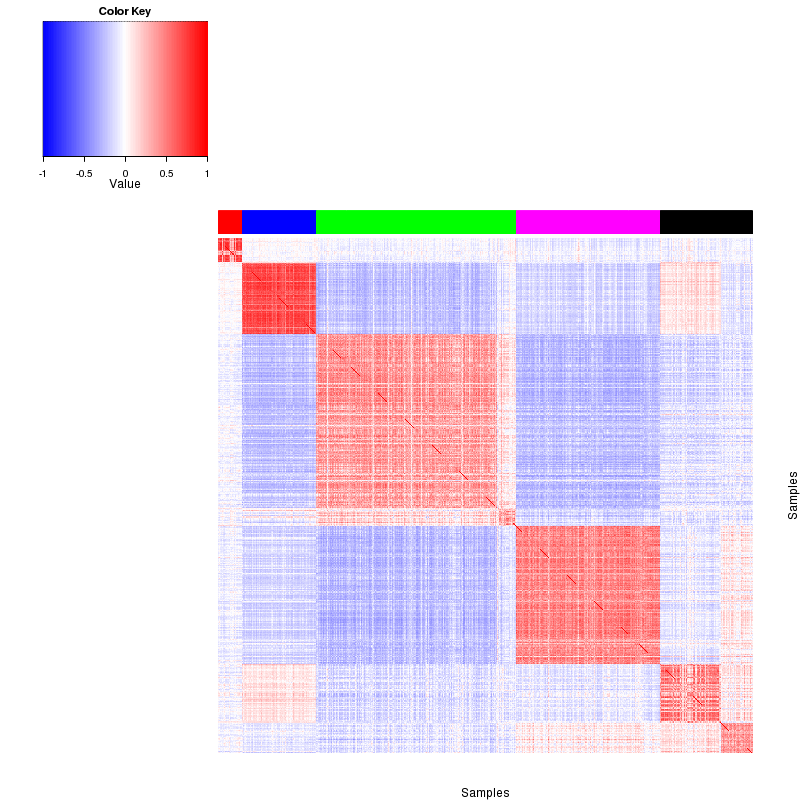
Table 1. Get Full Table List of samples with 5 subtypes and silhouette width.
| SampleName | cluster | silhouetteValue |
|---|---|---|
| TCGA-A3-3306-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.64 |
| TCGA-A3-3307-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.7 |
| TCGA-A3-3308-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.64 |
| TCGA-A3-3311-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.68 |
| TCGA-A3-3313-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.56 |
| TCGA-A3-3316-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.6 |
| TCGA-A3-3317-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.63 |
| TCGA-A3-3319-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.51 |
| TCGA-A3-3320-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.69 |
| TCGA-A3-3322-01A-01R-0864-07 | 1 | 0.69 |
Table 2. Get Full Table List of samples belonging to each cluster in different k clusters.
| TCGA_ID | K.2 | K.3 | K.4 | K.5 | K.6 | K.7 | K.8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCGA-04-1331-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| TCGA-04-1332-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| TCGA-04-1335-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| TCGA-04-1336-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| TCGA-04-1337-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| TCGA-04-1338-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| TCGA-04-1341-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| TCGA-04-1342-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| TCGA-04-1343-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| TCGA-04-1346-01A-01R-0436-07 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
Samples most representative of the clusters, hereby called core samples were identified based on positive silhouette width, indicating higher similarity to their own class than to any other class member. Core samples were used to select differentially expressed marker genes for each subtype by comparing the subclass versus the other subclasses, using Student's t-test.
Table 3. Get Full Table List of marker genes with p<= 0.05 (The positive value of column difference means gene is upregulated in this subtype and vice versa).
| Composite.Element.REF | p | difference | q | subclass |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACSM2B | 6.4e-32 | 7.2 | 1.4e-30 | 1 |
| NAT8 | 2.1e-33 | 6.8 | 5.3e-32 | 1 |
| C14ORF105 | 1.5e-59 | 6.3 | 5.2e-57 | 1 |
| BHMT | 2e-34 | 6.1 | 5.8e-33 | 1 |
| GBA3 | 6.2e-28 | 6 | 9.1e-27 | 1 |
| CDH16 | 6.1e-116 | 6 | 2.7e-112 | 1 |
| FXYD2 | 1.1e-73 | 6 | 7.7e-71 | 1 |
| NR1H4 | 3.2e-39 | 6 | 1.5e-37 | 1 |
| TMEM27 | 1.6e-35 | 6 | 5.2e-34 | 1 |
| SLC17A3 | 2.3e-30 | 5.8 | 4.3e-29 | 1 |
Consensus Hierarchical clustering is a resampling-based clustering. It provides for a method to represent the consensus across multiple runs of a clustering algorithm and to assess the stability of the discovered clusters. To this end, perturbations of the original data are simulated by resampling techniques [1],[2].
Silhouette width is defined as the ratio of average distance of each sample to samples in the same cluster to the smallest distance to samples not in the same cluster. If silhouette width is close to 1, it means that sample is well clustered. If silhouette width is close to -1, it means that sample is misclassified [3].
In addition to the links below, the full results of the analysis summarized in this report can also be downloaded programmatically using firehose_get, or interactively from either the Broad GDAC website or TCGA Data Coordination Center Portal.