This report serves to describe the mutational landscape and properties of a given individual set, as well as rank genes and genesets according to mutational significance. MutSig v2.0 was used to generate the results found in this report.
-
Working with individual set: KIRP-TP
-
Number of patients in set: 282
The input for this pipeline is a set of individuals with the following files associated for each:
-
An annotated .maf file describing the mutations called for the respective individual, and their properties.
-
A .wig file that contains information about the coverage of the sample.
-
MAF used for this analysis:KIRP-TP.final_analysis_set.maf
-
Blacklist used for this analysis: pancan_mutation_blacklist.v14.hg19.txt
-
Significantly mutated genes (q ≤ 0.1): 30
-
Mutations seen in COSMIC: 82
-
Significantly mutated genes in COSMIC territory: 11
-
Significantly mutated genesets: 1
-
Significantly mutated genesets: (excluding sig. mutated genes):0
-
Read 282 MAFs of type "maf1"
-
Total number of mutations in input MAFs: 18668
-
After removing 123 mutations outside chr1-24: 18545
-
After removing 146 blacklisted mutations: 18399
-
After removing 388 noncoding mutations: 18011
-
After collapsing adjacent/redundant mutations: 17948
-
Number of mutations before filtering: 17948
-
After removing 984 mutations outside gene set: 16964
-
After removing 64 mutations outside category set: 16900
-
After removing 9 "impossible" mutations in
-
gene-patient-category bins of zero coverage: 15843
Table 1. Get Full Table Table representing breakdown of mutations by type.
| type | count |
|---|---|
| De_novo_Start_OutOfFrame | 3 |
| Frame_Shift_Del | 1334 |
| Frame_Shift_Ins | 448 |
| In_Frame_Del | 269 |
| In_Frame_Ins | 61 |
| Missense_Mutation | 9786 |
| Nonsense_Mutation | 562 |
| Nonstop_Mutation | 21 |
| Silent | 3675 |
| Splice_Site | 710 |
| Start_Codon_Del | 5 |
| Start_Codon_SNP | 20 |
| Stop_Codon_Del | 5 |
| Stop_Codon_Ins | 1 |
| Total | 16900 |
Table 2. Get Full Table A breakdown of mutation rates per category discovered for this individual set.
| category | n | N | rate | rate_per_mb | relative_rate | exp_ns_s_ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *CpG->T | 871 | 495087687 | 1.8e-06 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 2.1 |
| *Cp(A/C/T)->T | 1659 | 3948225432 | 4.2e-07 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 1.7 |
| A->G | 1858 | 4224865722 | 4.4e-07 | 0.44 | 0.29 | 2.3 |
| transver | 5414 | 8668178841 | 6.2e-07 | 0.62 | 0.41 | 5 |
| indel+null | 3358 | 8668178841 | 3.9e-07 | 0.39 | 0.25 | NaN |
| double_null | 58 | 8668178841 | 6.7e-09 | 0.0067 | 0.0044 | NaN |
| Total | 13218 | 8668178841 | 1.5e-06 | 1.5 | 1 | 3.5 |
The x axis represents the samples. The y axis represents the exons, one row per exon, and they are sorted by average coverage across samples. For exons with exactly the same average coverage, they are sorted next by the %GC of the exon. (The secondary sort is especially useful for the zero-coverage exons at the bottom). If the figure is unpopulated, then full coverage is assumed (e.g. MutSig CV doesn't use WIGs and assumes full coverage).
Figure 1.
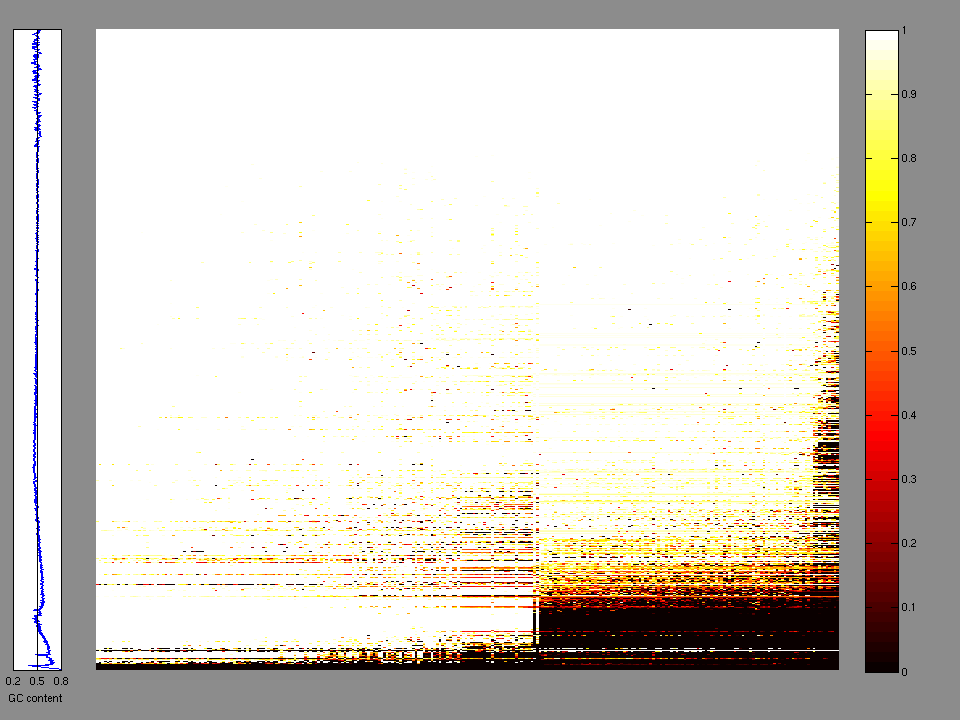
Figure 2. Patients counts and rates file used to generate this plot: KIRP-TP.patients.counts_and_rates.txt

The mutation spectrum is depicted in the lego plots below in which the 96 possible mutation types are subdivided into six large blocks, color-coded to reflect the base substitution type. Each large block is further subdivided into the 16 possible pairs of 5' and 3' neighbors, as listed in the 4x4 trinucleotide context legend. The height of each block corresponds to the mutation frequency for that kind of mutation (counts of mutations normalized by the base coverage in a given bin). The shape of the spectrum is a signature for dominant mutational mechanisms in different tumor types.
Figure 3. Get High-res Image SNV Mutation rate lego plot for entire set. Each bin is normalized by base coverage for that bin. Colors represent the six SNV types on the upper right. The three-base context for each mutation is labeled in the 4x4 legend on the lower right. The fractional breakdown of SNV counts is shown in the pie chart on the upper left. If this figure is blank, not enough information was provided in the MAF to generate it.
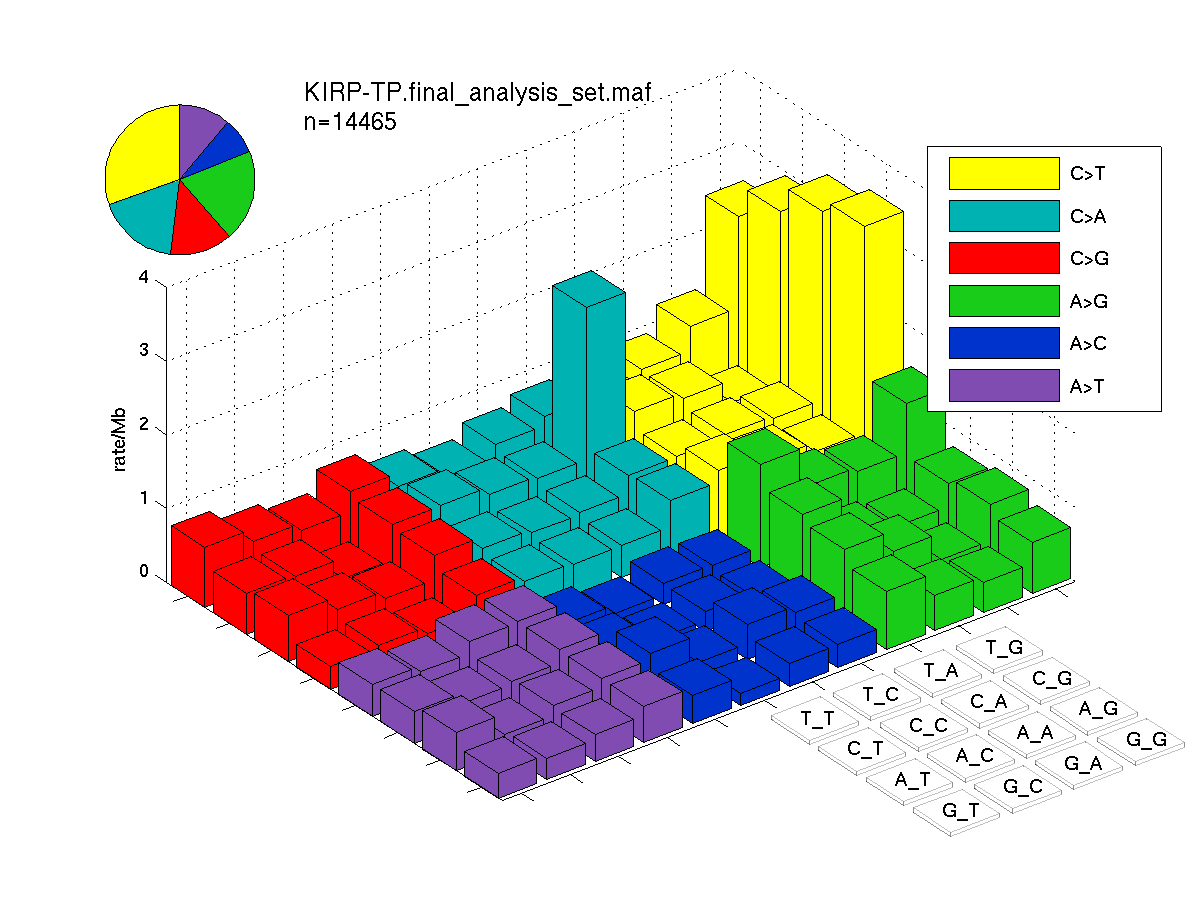
Figure 4. Get High-res Image SNV Mutation rate lego plots for 4 slices of mutation allele fraction (0<=AF<0.1, 0.1<=AF<0.25, 0.25<=AF<0.5, & 0.5<=AF) . The color code and three-base context legends are the same as the previous figure. If this figure is blank, not enough information was provided in the MAF to generate it.

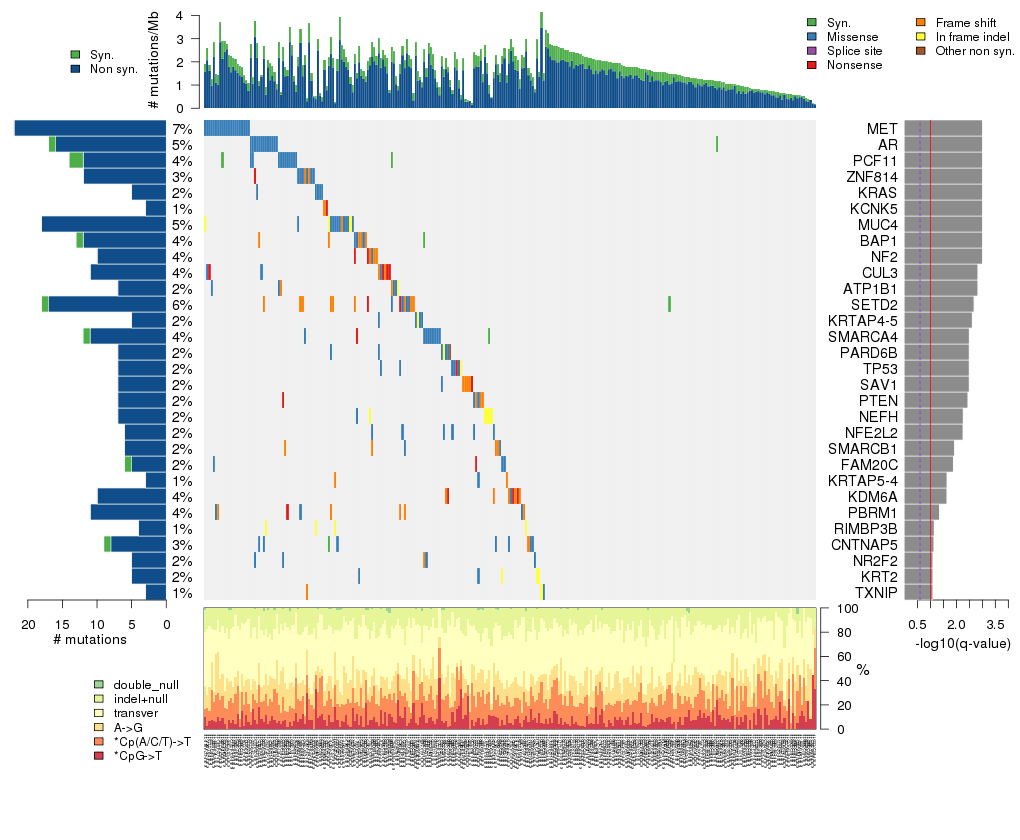
Figure 5. Get High-res Image The matrix in the center of the figure represents individual mutations in patient samples, color-coded by type of mutation, for the significantly mutated genes. The rate of synonymous and non-synonymous mutations is displayed at the top of the matrix. The barplot on the left of the matrix shows the number of mutations in each gene. The percentages represent the fraction of tumors with at least one mutation in the specified gene. The barplot to the right of the matrix displays the q-values for the most significantly mutated genes. The purple boxplots below the matrix (only displayed if required columns are present in the provided MAF) represent the distributions of allelic fractions observed in each sample. The plot at the bottom represents the base substitution distribution of individual samples, using the same categories that were used to calculate significance.
Column Descriptions:
-
N = number of sequenced bases in this gene across the individual set
-
n = number of (nonsilent) mutations in this gene across the individual set
-
npat = number of patients (individuals) with at least one nonsilent mutation
-
nsite = number of unique sites having a non-silent mutation
-
nsil = number of silent mutations in this gene across the individual set
-
n1 = number of nonsilent mutations of type: *CpG->T
-
n2 = number of nonsilent mutations of type: *Cp(A/C/T)->T
-
n3 = number of nonsilent mutations of type: A->G
-
n4 = number of nonsilent mutations of type: transver
-
n5 = number of nonsilent mutations of type: indel+null
-
n6 = number of nonsilent mutations of type: double_null
-
p_classic = p-value for the observed amount of nonsilent mutations being elevated in this gene
-
p_ns_s = p-value for the observed nonsilent/silent ratio being elevated in this gene
-
p_cons = p-value for enrichment of mutations at evolutionarily most-conserved sites in gene
-
p_joint = p-value for clustering + conservation
-
p = p-value (overall)
-
q = q-value, False Discovery Rate (Benjamini-Hochberg procedure)
Table 3. Get Full Table A Ranked List of Significantly Mutated Genes. Number of significant genes found: 30. Number of genes displayed: 35. Click on a gene name to display its stick figure depicting the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the chosen gene (this feature may not be available for all significant genes).
| rank | gene | description | N | n | npat | nsite | nsil | n1 | n2 | n3 | n4 | n5 | n6 | p_classic | p_ns_s | p_clust | p_cons | p_joint | p | q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MET | met proto-oncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) | 1189739 | 22 | 21 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 9.2e-15 | 0.001 | 0 | 0.000082 | 0 | <1.00e-15 | <3.12e-12 |
| 2 | AR | androgen receptor (dihydrotestosterone receptor; testicular feminization; spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy; Kennedy disease) | 630521 | 16 | 13 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 1e-10 | 0.086 | 0 | 1 | 0 | <1.00e-15 | <3.12e-12 |
| 3 | PCF11 | PCF11, cleavage and polyadenylation factor subunit, homolog (S. cerevisiae) | 1206056 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0.00015 | 0.088 | 0 | 0.98 | 0 | <1.00e-15 | <3.12e-12 |
| 4 | ZNF814 | zinc finger protein 814 | 432631 | 12 | 9 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 3.2e-08 | 0.064 | 0 | 0.61 | 0 | <1.00e-15 | <3.12e-12 |
| 5 | KRAS | v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog | 193814 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 7.4e-07 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.023 | 0 | <1.00e-15 | <3.12e-12 |
| 6 | KCNK5 | potassium channel, subfamily K, member 5 | 408980 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0.006 | 0.33 | 0.055 | 0 | 0 | <1.00e-15 | <3.12e-12 |
| 7 | MUC4 | mucin 4, cell surface associated | 944051 | 18 | 14 | 18 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 9.8e-11 | 0.016 | 0.18 | 0.5 | 0.42 | 1.03e-09 | 2.75e-06 |
| 8 | BAP1 | BRCA1 associated protein-1 (ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase) | 595128 | 12 | 10 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 0 | 1.2e-08 | 0.46 | 0.0032 | 0.7 | 0.0079 | 2.25e-09 | 5.26e-06 |
| 9 | NF2 | neurofibromin 2 (merlin) | 483605 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 5.1e-09 | 0.18 | 0.012 | 0.38 | 0.024 | 2.88e-09 | 5.98e-06 |
| 10 | CUL3 | cullin 3 | 650974 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 3.2e-08 | 0.12 | 0.3 | 0.98 | 0.45 | 2.76e-07 | 0.000513 |
| 11 | ATP1B1 | ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, beta 1 polypeptide | 259259 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2.4e-08 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 0.3 | 0.65 | 3.01e-07 | 0.000513 |
| 12 | SETD2 | SET domain containing 2 | 1991508 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 11 | 1 | 6.8e-08 | 0.41 | 0.82 | 0.22 | 0.59 | 7.20e-07 | 0.00112 |
| 13 | KRTAP4-5 | keratin associated protein 4-5 | 140695 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1.2e-06 | 0.61 | 0.014 | 0.87 | 0.048 | 1.03e-06 | 0.00148 |
| 14 | SMARCA4 | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4 | 1304135 | 11 | 10 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0.000056 | 0.32 | 0.0015 | 0.21 | 0.0017 | 1.66e-06 | 0.00222 |
| 15 | PARD6B | par-6 partitioning defective 6 homolog beta (C. elegans) | 298180 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1.4e-07 | 0.088 | 0.89 | 0.4 | 0.75 | 1.85e-06 | 0.00224 |
| 16 | TP53 | tumor protein p53 | 357058 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 7.2e-07 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 2.03e-06 | 0.00224 |
| 17 | SAV1 | salvador homolog 1 (Drosophila) | 323407 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 5.2e-07 | 0.59 | 0.12 | 0.99 | 0.23 | 2.04e-06 | 0.00224 |
| 18 | PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog (mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1) | 343679 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 2.5e-07 | 0.32 | 0.49 | 0.91 | 0.63 | 2.62e-06 | 0.00272 |
| 19 | NEFH | neurofilament, heavy polypeptide 200kDa | 590820 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0.00014 | 0.84 | 0.00054 | 0.74 | 0.002 | 4.59e-06 | 0.00452 |
| 20 | NFE2L2 | nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 | 505966 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0.29 | 0.014 | 0.03 | 0.0031 | 4.96e-06 | 0.00464 |
| 21 | SMARCB1 | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily b, member 1 | 328224 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4.1e-06 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.88 | 0.2 | 1.22e-05 | 0.0109 |
| 22 | FAM20C | family with sequence similarity 20, member C | 132140 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1.9e-06 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.51 | 1.44e-05 | 0.0122 |
| 23 | KRTAP5-4 | keratin associated protein 5-4 | 115571 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0.000076 | 0.74 | 0.27 | 0.018 | 0.026 | 2.74e-05 | 0.0223 |
| 24 | KDM6A | lysine (K)-specific demethylase 6A | 1088765 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 2.1e-06 | 0.32 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 1 | 2.94e-05 | 0.0229 |
| 25 | PBRM1 | polybromo 1 | 1394577 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 4.4e-06 | 0.19 | 0.82 | 0.73 | 1 | 5.93e-05 | 0.0444 |
| 26 | RIMBP3B | RIMS binding protein 3B | 1292036 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0.072 | 1 | 1e-06 | 0.65 | 0.00011 | 9.90e-05 | 0.0712 |
| 27 | CNTNAP5 | contactin associated protein-like 5 | 1022046 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0.00011 | 0.38 | 0.043 | 0.55 | 0.078 | 0.000106 | 0.0735 |
| 28 | NR2F2 | nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group F, member 2 | 305604 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 7e-05 | 0.46 | 0.11 | 0.39 | 0.14 | 0.000126 | 0.0815 |
| 29 | KRT2 | keratin 2 (epidermal ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens) | 525430 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0.0014 | 0.67 | 0.054 | 0.015 | 0.0075 | 0.000128 | 0.0815 |
| 30 | TXNIP | thioredoxin interacting protein | 340061 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0.0026 | 0.63 | 0.0035 | 0.29 | 0.0041 | 0.000131 | 0.0815 |
| 31 | IL32 | interleukin 32 | 159460 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0.000039 | 0.44 | 0.23 | 0.51 | 0.38 | 0.000180 | 0.108 |
| 32 | SHANK3 | SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains 3 | 786253 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.0013 | 0.1 | 0.0097 | 0.54 | 0.017 | 0.000266 | 0.156 |
| 33 | KRT10 | keratin 10 (epidermolytic hyperkeratosis; keratosis palmaris et plantaris) | 434029 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.041 | 0.28 | 0.00011 | 1 | 0.00096 | 0.000439 | 0.249 |
| 34 | GXYLT1 | glucoside xylosyltransferase 1 | 315252 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.00017 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.64 | 0.24 | 0.000453 | 0.250 |
| 35 | RTKN | rhotekin | 501559 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.008 | 0.75 | 0.068 | 0.0034 | 0.0055 | 0.000486 | 0.260 |
Figure S1. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the MET significant gene.
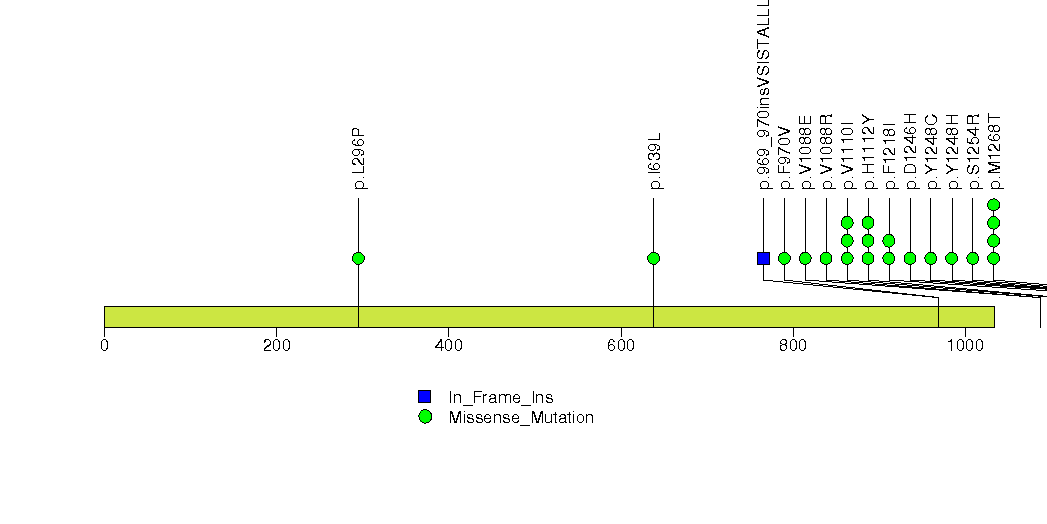
Figure S2. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the AR significant gene.
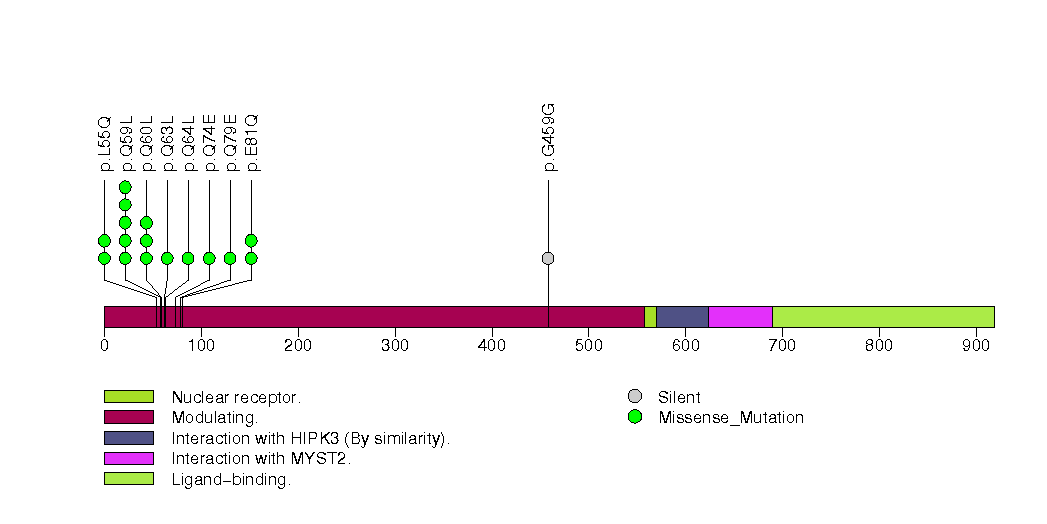
Figure S3. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the PCF11 significant gene.
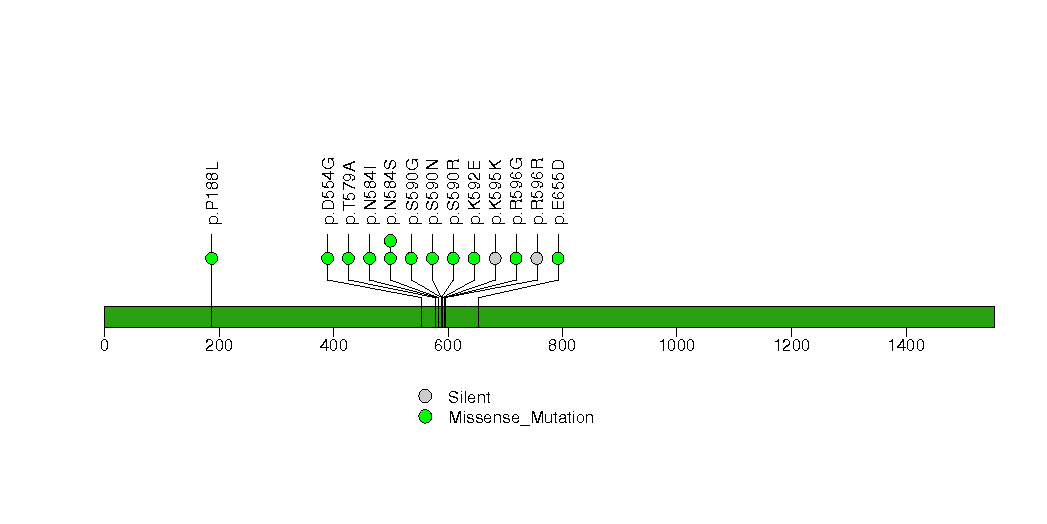
Figure S4. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the ZNF814 significant gene.
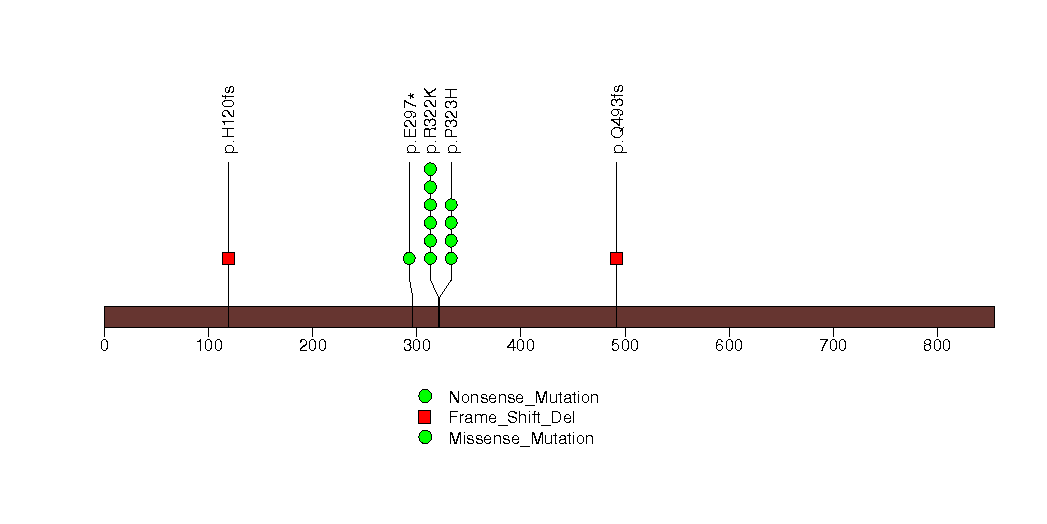
Figure S5. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the KRAS significant gene.

Figure S6. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the KCNK5 significant gene.
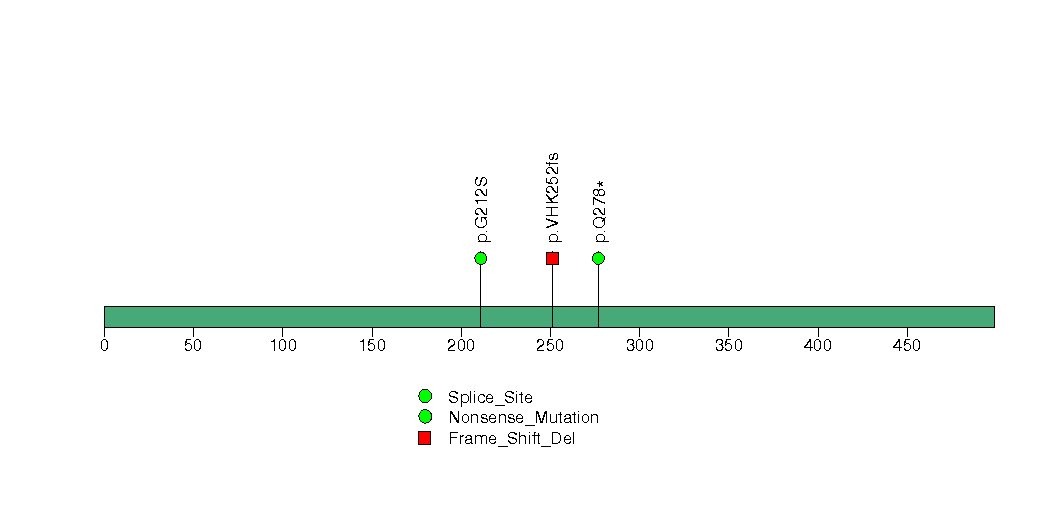
Figure S7. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the MUC4 significant gene.
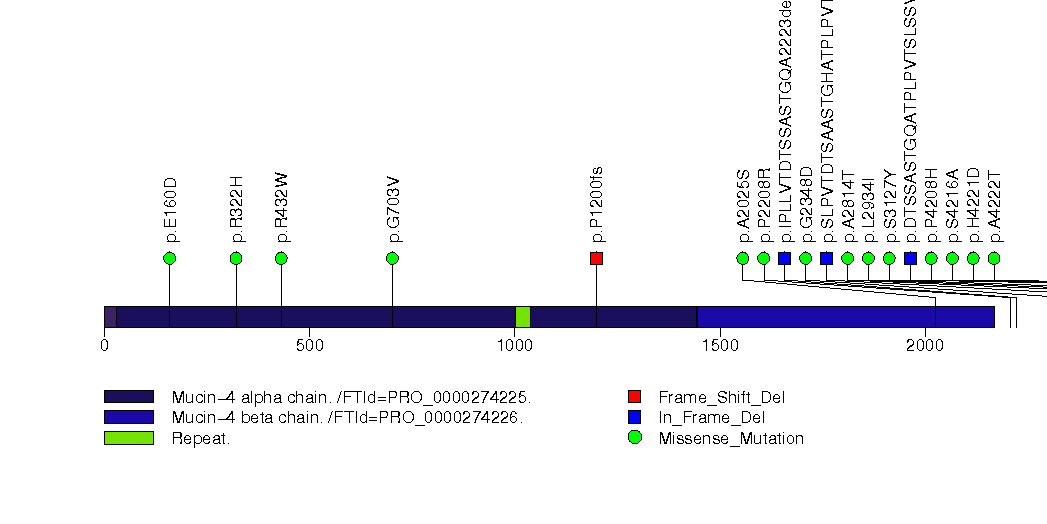
Figure S8. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the BAP1 significant gene.
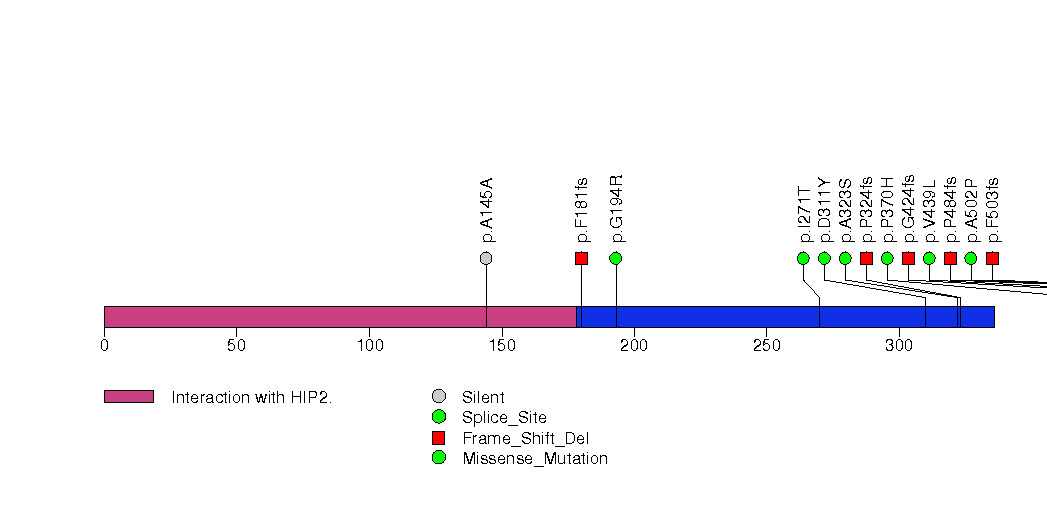
Figure S9. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the NF2 significant gene.
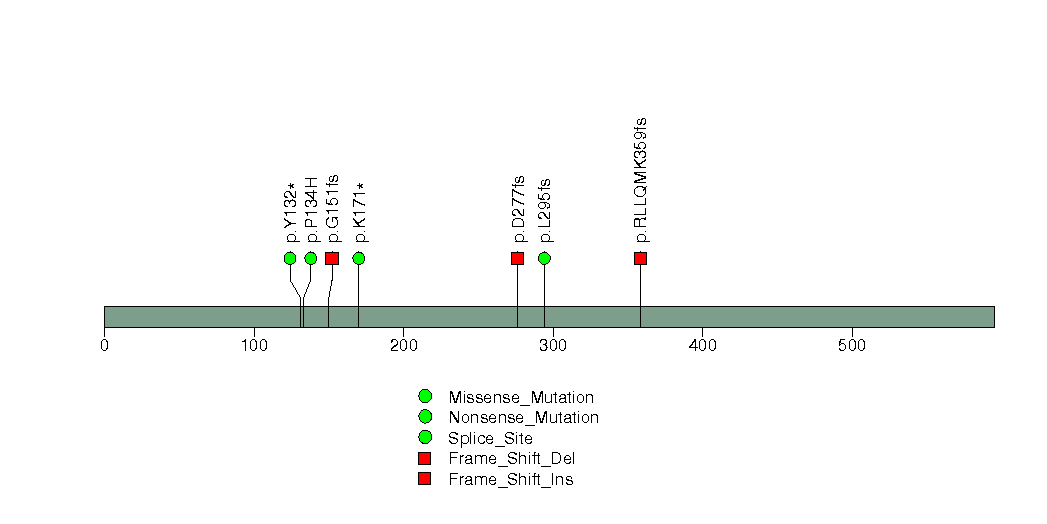
Figure S10. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the CUL3 significant gene.
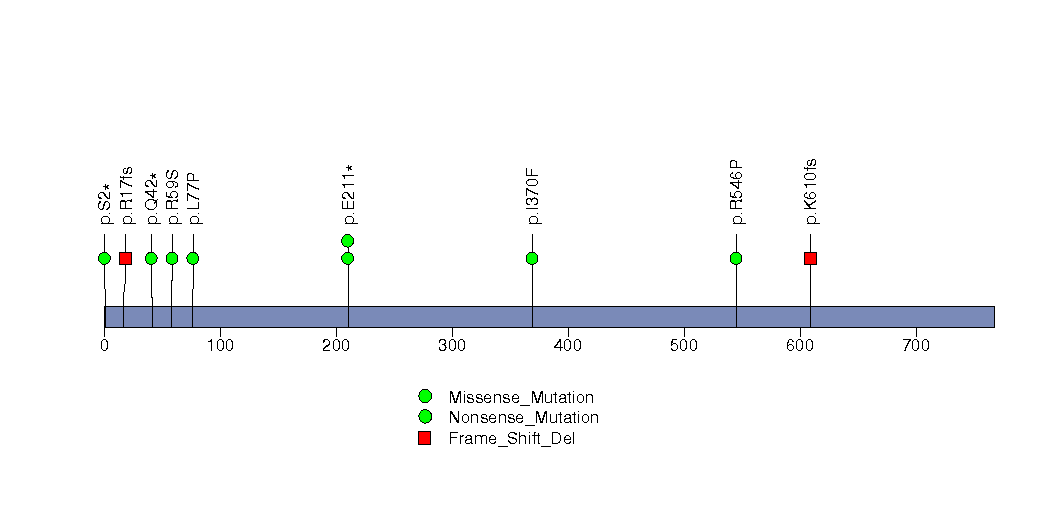
Figure S11. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the ATP1B1 significant gene.
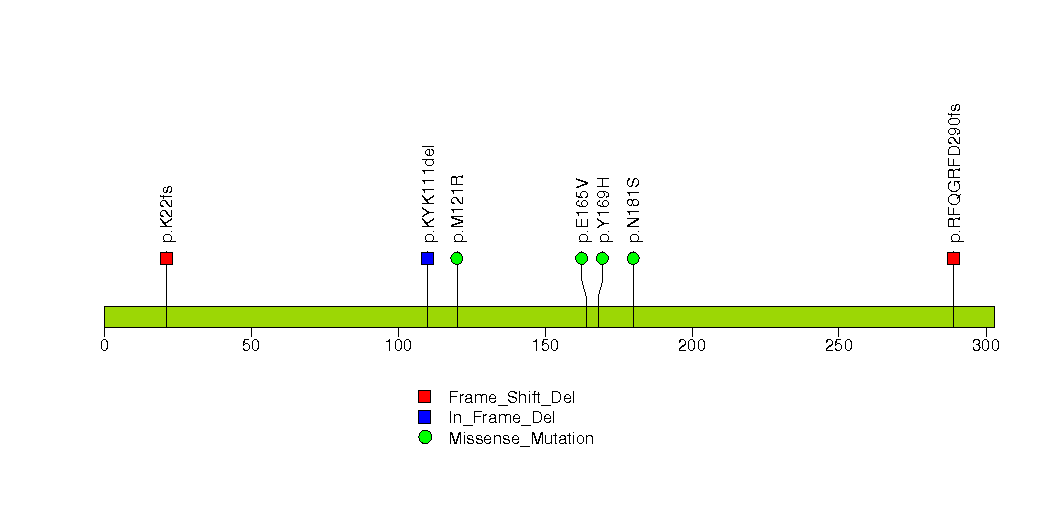
Figure S12. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the SETD2 significant gene.
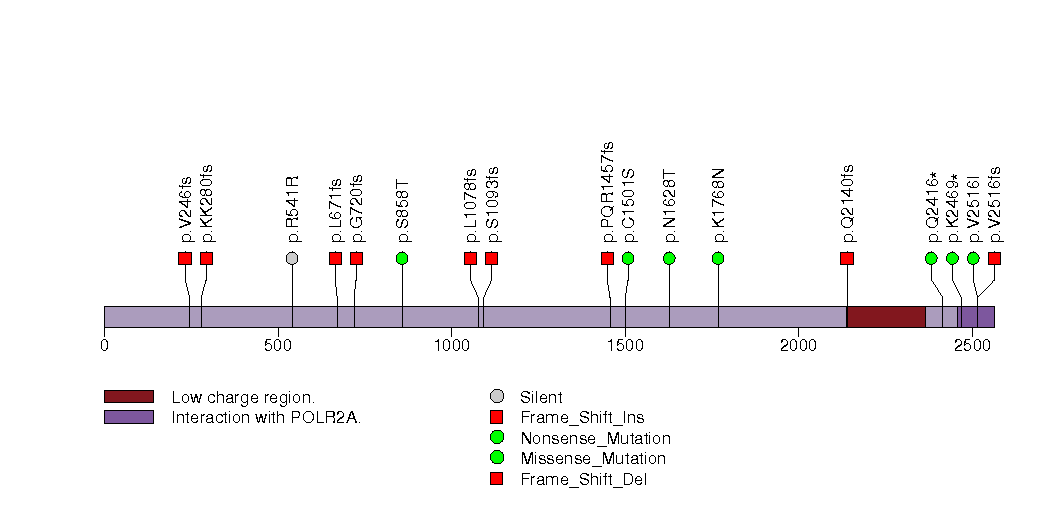
Figure S13. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the KRTAP4-5 significant gene.

Figure S14. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the SMARCA4 significant gene.

Figure S15. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the PARD6B significant gene.
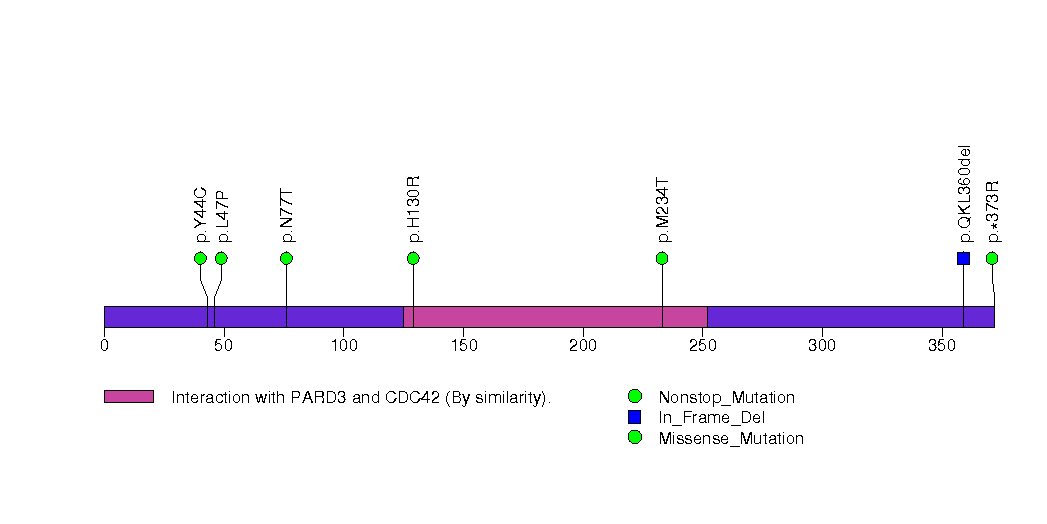
Figure S16. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the TP53 significant gene.
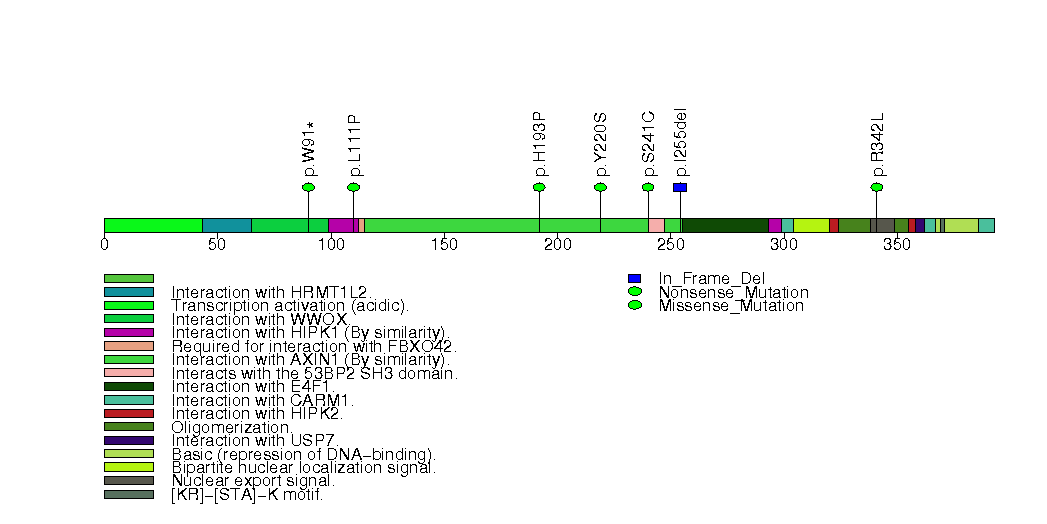
Figure S17. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the SAV1 significant gene.
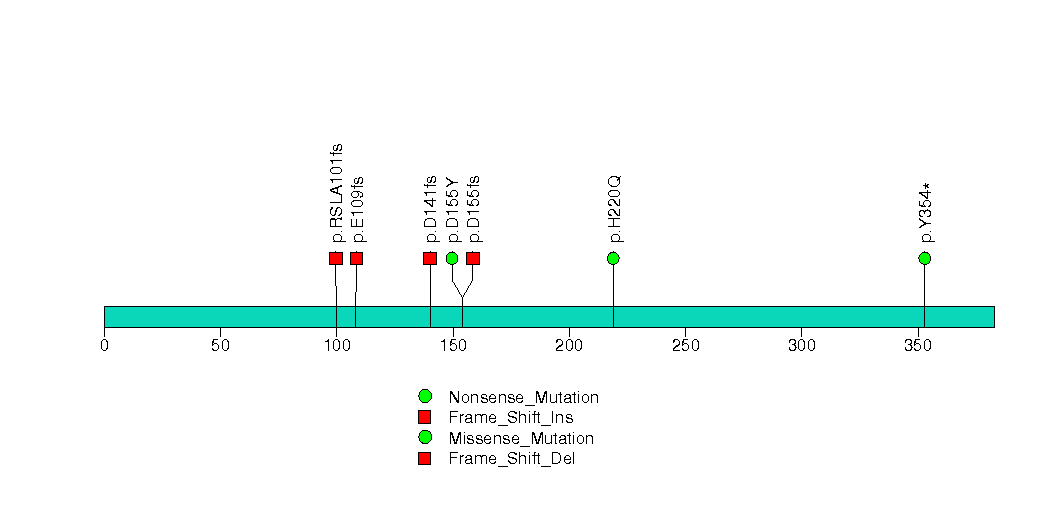
Figure S18. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the PTEN significant gene.

Figure S19. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the NEFH significant gene.
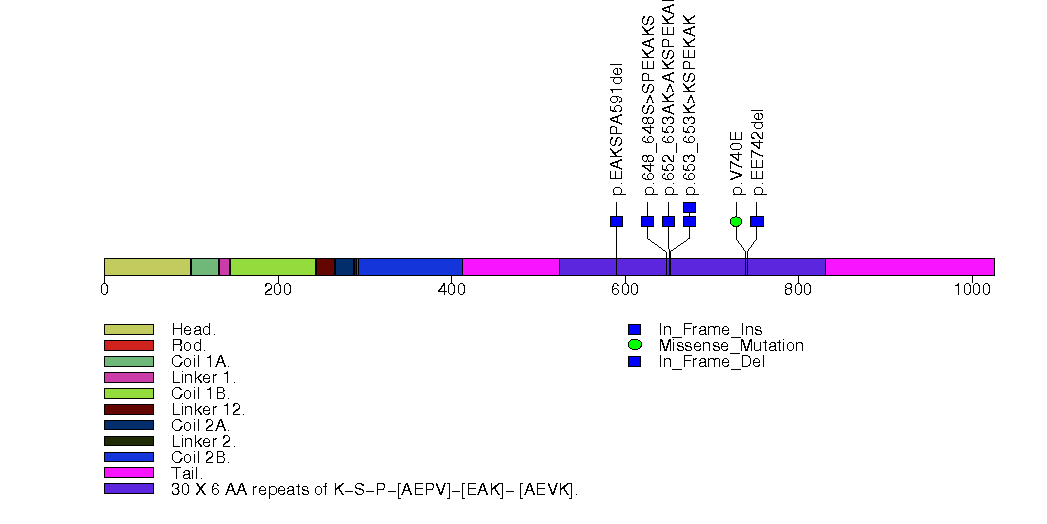
Figure S20. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the NFE2L2 significant gene.
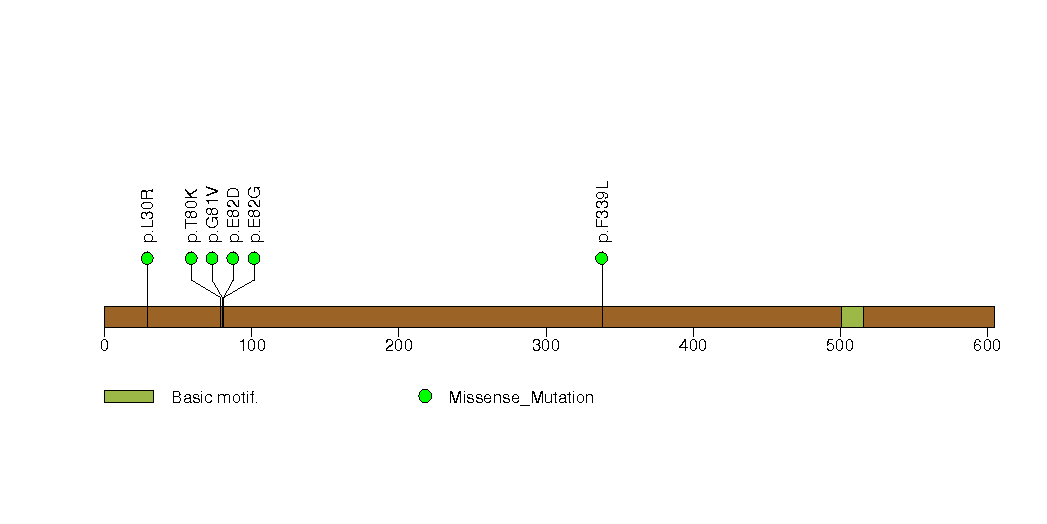
Figure S21. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the SMARCB1 significant gene.

Figure S22. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the FAM20C significant gene.
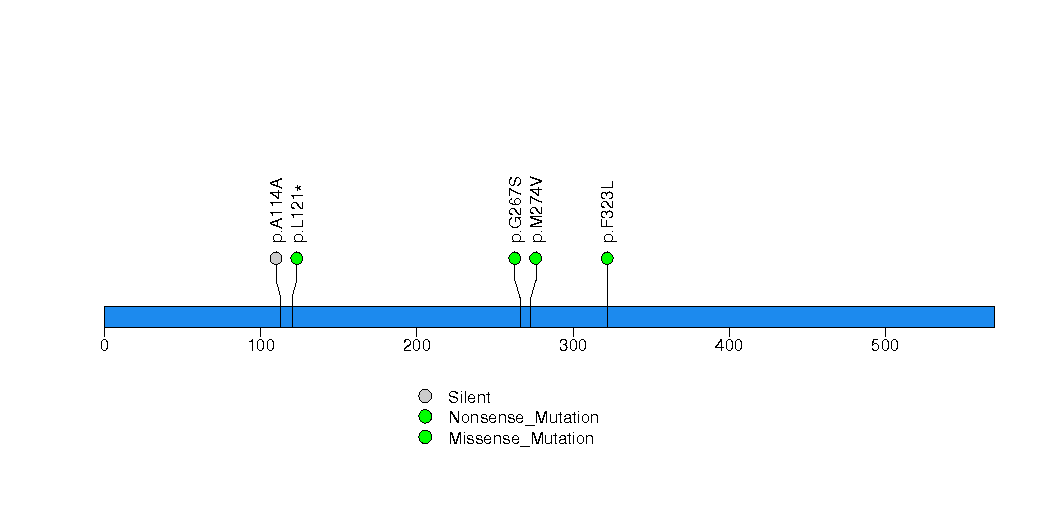
Figure S23. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the KRTAP5-4 significant gene.
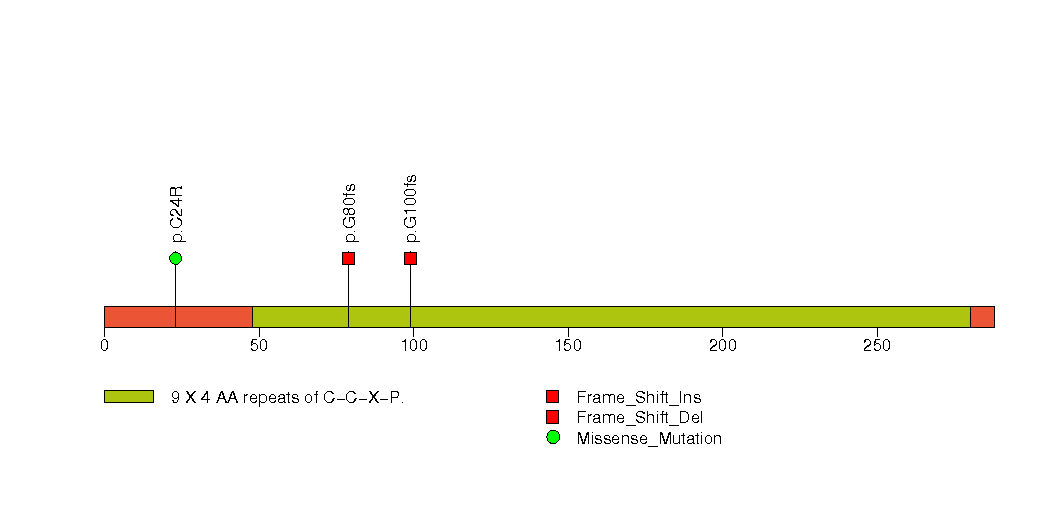
Figure S24. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the KDM6A significant gene.
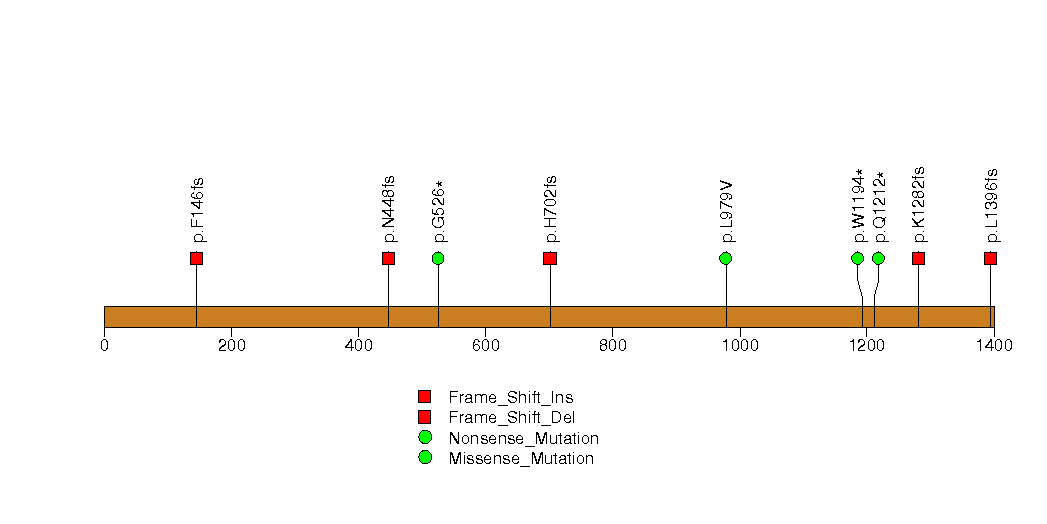
Figure S25. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the PBRM1 significant gene.

Figure S26. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the RIMBP3B significant gene.

Figure S27. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the CNTNAP5 significant gene.
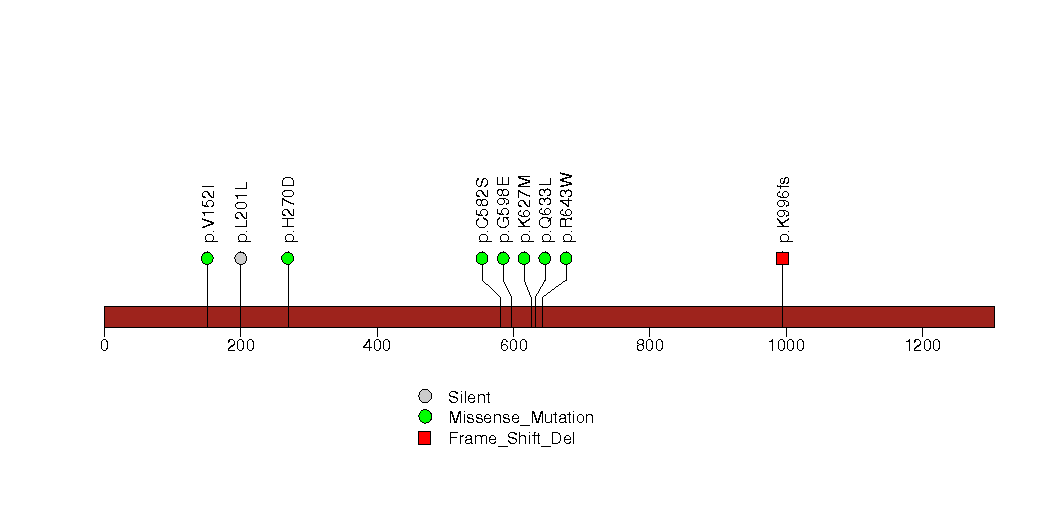
Figure S28. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the NR2F2 significant gene.
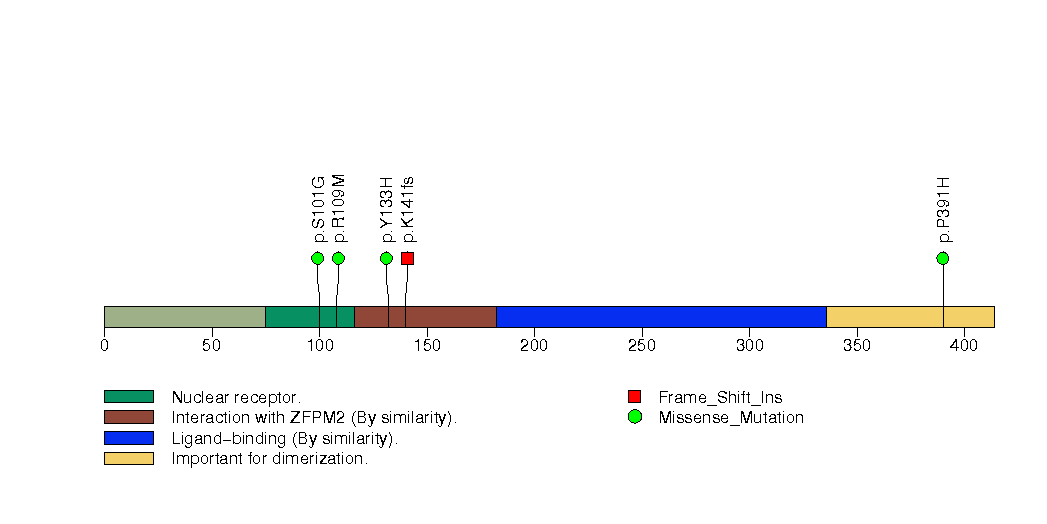
Figure S29. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the KRT2 significant gene.
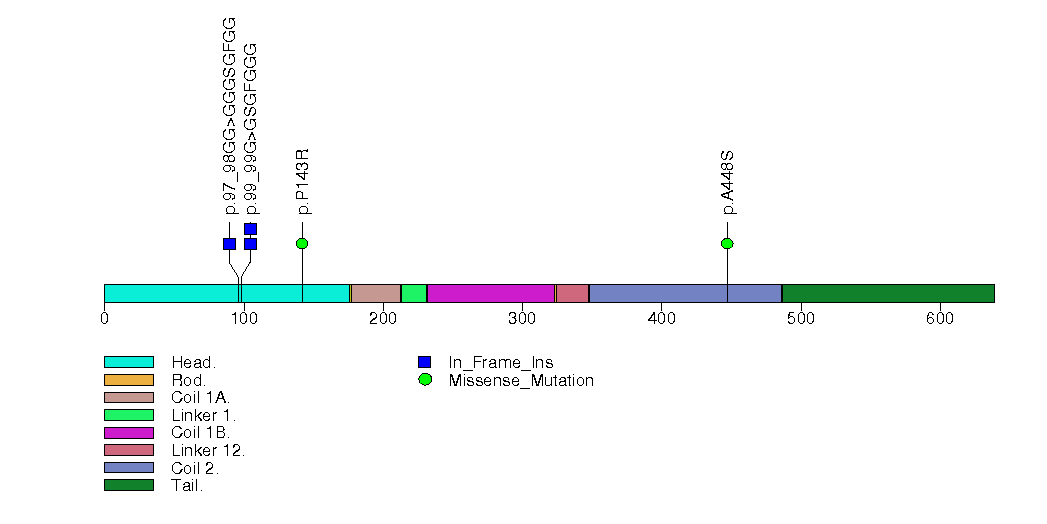
Figure S30. This figure depicts the distribution of mutations and mutation types across the TXNIP significant gene.
In this analysis, COSMIC is used as a filter to increase power by restricting the territory of each gene. Cosmic version: v48.
Table 4. Get Full Table Significantly mutated genes (COSMIC territory only). To access the database please go to: COSMIC. Number of significant genes found: 11. Number of genes displayed: 10
| rank | gene | description | n | cos | n_cos | N_cos | cos_ev | p | q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MET | met proto-oncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) | 22 | 34 | 10 | 9588 | 48 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | KRAS | v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog | 5 | 52 | 5 | 14664 | 73020 | 4.5e-11 | 1e-07 |
| 3 | TP53 | tumor protein p53 | 7 | 356 | 6 | 100392 | 483 | 1.6e-08 | 0.000023 |
| 4 | FGFR3 | fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (achondroplasia, thanatophoric dwarfism) | 6 | 62 | 4 | 17484 | 1811 | 2.1e-08 | 0.000023 |
| 5 | PIK3CA | phosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, alpha polypeptide | 6 | 220 | 5 | 62040 | 1661 | 5.8e-08 | 0.000048 |
| 6 | PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog (mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1) | 7 | 767 | 7 | 216294 | 75 | 6.3e-08 | 0.000048 |
| 7 | SMARCB1 | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily b, member 1 | 6 | 129 | 4 | 36378 | 12 | 3.8e-07 | 0.00024 |
| 8 | NF2 | neurofibromin 2 (merlin) | 10 | 550 | 5 | 155100 | 21 | 5.1e-06 | 0.0029 |
| 9 | BRAF | v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 | 4 | 89 | 3 | 25098 | 28754 | 9.1e-06 | 0.0046 |
| 10 | SMARCA4 | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4 | 11 | 30 | 2 | 8460 | 3 | 0.000082 | 0.037 |
Note:
n - number of (nonsilent) mutations in this gene across the individual set.
cos = number of unique mutated sites in this gene in COSMIC
n_cos = overlap between n and cos.
N_cos = number of individuals times cos.
cos_ev = total evidence: number of reports in COSMIC for mutations seen in this gene.
p = p-value for seeing the observed amount of overlap in this gene)
q = q-value, False Discovery Rate (Benjamini-Hochberg procedure)
Table 5. Get Full Table A Ranked List of Significantly Mutated Genesets. (Source: MSigDB GSEA Cannonical Pathway Set).Number of significant genesets found: 1. Number of genesets displayed: 10
| rank | geneset | description | genes | N_genes | mut_tally | N | n | npat | nsite | nsil | n1 | n2 | n3 | n4 | n5 | n6 | p_ns_s | p | q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CBLPATHWAY | Activated EGF receptors undergo endocytosis into clathrin-coated vesicles, where they are recycled to the membrane or ubiquitinated by Cbl. | CBL, CSF1R, EGF, EGFR, GRB2, MET, PDGFRA, PRKCA, PRKCB1, SH3GLB1, SH3GLB2, SH3KBP1, SRC | 12 | CSF1R(3), EGF(1), EGFR(1), GRB2(1), MET(22), PDGFRA(1), PRKCA(1), SH3KBP1(2) | 8180436 | 32 | 28 | 24 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 11 | 3 | 0 | 0.0041 | 0.000047 | 0.029 |
| 2 | ARGININECPATHWAY | Related catabolic pathways process arginine, histidine, glutamine, and proline through glutamate to alpha-ketoglutamate, which feeds into the citric acid cycle. | ALDH4A1, ARG1, GLS, GLUD1, OAT, PRODH | 6 | ALDH4A1(1), ARG1(1), GLS(5), GLUD1(1), OAT(2) | 2436277 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0.098 | 0.0025 | 0.5 |
| 3 | HSA00627_1,4_DICHLOROBENZENE_DEGRADATION | Genes involved in 1,4-dichlorobenzene degradation | CMBL | 1 | CMBL(3) | 213542 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.86 | 0.0031 | 0.5 |
| 4 | ERBB4PATHWAY | ErbB4 (aka HER4) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that binds neuregulins as well as members of the EGF family, which also target EGF receptors. | ADAM17, ERBB4, NRG2, NRG3, PRKCA, PRKCB1, PSEN1 | 6 | ADAM17(3), ERBB4(4), NRG2(1), NRG3(3), PRKCA(1), PSEN1(1) | 3787830 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0.17 | 0.0033 | 0.5 |
| 5 | HSA00550_PEPTIDOGLYCAN_BIOSYNTHESIS | Genes involved in peptidoglycan biosynthesis | GLUL, PGLYRP2 | 2 | GLUL(2), PGLYRP2(3) | 757351 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0.72 | 0.0044 | 0.54 |
| 6 | PARKINPATHWAY | In Parkinson's disease, dopaminergic neurons contain Lewy bodies consisting of alpha-synuclein and parkin, an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets glycosylated alpha-synuclein. | GPR37, PARK2, PNUTL1, SNCA, SNCAIP, UBE2E2, UBE2F, UBE2G1, UBE2G2, UBE2L3, UBE2L6, UBL1 | 10 | GPR37(4), PARK2(2), SNCAIP(3), UBE2L3(1) | 2673213 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.0075 | 0.77 |
| 7 | SA_PTEN_PATHWAY | PTEN is a tumor suppressor that dephosphorylates the lipid messenger phosphatidylinositol triphosphate. | AKT1, AKT2, AKT3, BPNT1, GRB2, ILK, MAPK1, MAPK3, PDK1, PIK3CA, PIK3CD, PIP3-E, PTEN, PTK2B, RBL2, SHC1, SOS1 | 16 | AKT2(1), AKT3(1), BPNT1(3), GRB2(1), MAPK1(1), PIK3CA(6), PIK3CD(1), PTEN(7), PTK2B(1), SOS1(2) | 8543628 | 24 | 21 | 22 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 0.031 | 0.0088 | 0.78 |
| 8 | ARENRF2PATHWAY | Nrf1 and nrf2 are transcription factors that bind to antioxidant response elements (AREs), promoters of genes involved in oxidative damage control. | CREB1, FOS, FXYD2, JUN, KEAP1, MAFF, MAFG, MAFK, MAPK1, MAPK14, MAPK8, NFE2L2, PRKCA, PRKCB1 | 13 | CREB1(1), KEAP1(2), MAPK1(1), MAPK14(1), NFE2L2(6), PRKCA(1) | 3800165 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 0.23 | 0.019 | 1 |
| 9 | GLUTAMATE_METABOLISM | ABAT, ALDH4A1, ALDH5A1, CAD, CPS1, EPRS, GAD1, GAD2, GCLC, GCLM, GFPT1, GLS, GLS2, GLUD1, GLUL, GMPS, GOT1, GOT2, GPT, GPT2, GSS, NADSYN1, PPAT, QARS | 24 | ABAT(1), ALDH4A1(1), CAD(4), CPS1(1), EPRS(1), GAD1(2), GAD2(2), GCLC(3), GCLM(1), GFPT1(2), GLS(5), GLUD1(1), GLUL(2), GMPS(1), GOT2(1), GPT(2), PPAT(1), QARS(3) | 14031798 | 34 | 32 | 34 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 15 | 9 | 0 | 0.014 | 0.023 | 1 | |
| 10 | ACE_INHIBITOR_PATHWAY_PHARMGKB | ACE, AGT, AGTR1, AGTR2, BDKRB2, KNG1, NOS3, REN | 8 | ACE(4), AGT(3), AGTR2(1), KNG1(3), NOS3(1) | 4215483 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0.053 | 0.025 | 1 |
Table 6. Get Full Table A Ranked List of Significantly Mutated Genesets (Excluding Significantly Mutated Genes). Number of significant genesets found: 0. Number of genesets displayed: 10
| rank | geneset | description | genes | N_genes | mut_tally | N | n | npat | nsite | nsil | n1 | n2 | n3 | n4 | n5 | n6 | p_ns_s | p | q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ARGININECPATHWAY | Related catabolic pathways process arginine, histidine, glutamine, and proline through glutamate to alpha-ketoglutamate, which feeds into the citric acid cycle. | ALDH4A1, ARG1, GLS, GLUD1, OAT, PRODH | 6 | ALDH4A1(1), ARG1(1), GLS(5), GLUD1(1), OAT(2) | 2436277 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0.098 | 0.0025 | 0.67 |
| 2 | HSA00627_1,4_DICHLOROBENZENE_DEGRADATION | Genes involved in 1,4-dichlorobenzene degradation | CMBL | 1 | CMBL(3) | 213542 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.86 | 0.0031 | 0.67 |
| 3 | ERBB4PATHWAY | ErbB4 (aka HER4) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that binds neuregulins as well as members of the EGF family, which also target EGF receptors. | ADAM17, ERBB4, NRG2, NRG3, PRKCA, PRKCB1, PSEN1 | 6 | ADAM17(3), ERBB4(4), NRG2(1), NRG3(3), PRKCA(1), PSEN1(1) | 3787830 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0.17 | 0.0033 | 0.67 |
| 4 | HSA00550_PEPTIDOGLYCAN_BIOSYNTHESIS | Genes involved in peptidoglycan biosynthesis | GLUL, PGLYRP2 | 2 | GLUL(2), PGLYRP2(3) | 757351 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0.72 | 0.0044 | 0.67 |
| 5 | PARKINPATHWAY | In Parkinson's disease, dopaminergic neurons contain Lewy bodies consisting of alpha-synuclein and parkin, an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets glycosylated alpha-synuclein. | GPR37, PARK2, PNUTL1, SNCA, SNCAIP, UBE2E2, UBE2F, UBE2G1, UBE2G2, UBE2L3, UBE2L6, UBL1 | 10 | GPR37(4), PARK2(2), SNCAIP(3), UBE2L3(1) | 2673213 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.0075 | 0.92 |
| 6 | GLUTAMATE_METABOLISM | ABAT, ALDH4A1, ALDH5A1, CAD, CPS1, EPRS, GAD1, GAD2, GCLC, GCLM, GFPT1, GLS, GLS2, GLUD1, GLUL, GMPS, GOT1, GOT2, GPT, GPT2, GSS, NADSYN1, PPAT, QARS | 24 | ABAT(1), ALDH4A1(1), CAD(4), CPS1(1), EPRS(1), GAD1(2), GAD2(2), GCLC(3), GCLM(1), GFPT1(2), GLS(5), GLUD1(1), GLUL(2), GMPS(1), GOT2(1), GPT(2), PPAT(1), QARS(3) | 14031798 | 34 | 32 | 34 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 15 | 9 | 0 | 0.014 | 0.023 | 1 | |
| 7 | ACE_INHIBITOR_PATHWAY_PHARMGKB | ACE, AGT, AGTR1, AGTR2, BDKRB2, KNG1, NOS3, REN | 8 | ACE(4), AGT(3), AGTR2(1), KNG1(3), NOS3(1) | 4215483 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0.053 | 0.025 | 1 | |
| 8 | MTA3PATHWAY | The estrogen receptor regulates proliferation in mammary epithelia via MTA3 activation; loss of either protein is implicated in breast cancer. | ALDOA, CTSD, ESR1, GAPD, GREB1, HSPB1, HSPB2, MTA1, MTA3, PDZK1, TUBA1, TUBA2, TUBA3, TUBA4, TUBA6, TUBA8 | 10 | CTSD(1), GREB1(6), HSPB2(1), MTA1(4), MTA3(2), PDZK1(1), TUBA8(1) | 4765391 | 16 | 14 | 16 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.029 | 1 |
| 9 | BETAOXIDATIONPATHWAY | Beta-Oxidation of Fatty Acids | ACADL, ACADM, ACADS, ACAT1, ECHS1, HADHA | 6 | ACADL(3), ACADM(2), HADHA(2) | 2302526 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0.12 | 0.039 | 1 |
| 10 | CYANOAMINO_ACID_METABOLISM | ATP6V0C, SHMT1, GBA3, GGT1, SHMT1, SHMT2 | 5 | GGT1(1), SHMT1(2), SHMT2(3) | 1788627 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0.19 | 0.039 | 1 |
In brief, we tabulate the number of mutations and the number of covered bases for each gene. The counts are broken down by mutation context category: four context categories that are discovered by MutSig, and one for indel and 'null' mutations, which include indels, nonsense mutations, splice-site mutations, and non-stop (read-through) mutations. For each gene, we calculate the probability of seeing the observed constellation of mutations, i.e. the product P1 x P2 x ... x Pm, or a more extreme one, given the background mutation rates calculated across the dataset. [1]
In addition to the links below, the full results of the analysis summarized in this report can also be downloaded programmatically using firehose_get, or interactively from either the Broad GDAC website or TCGA Data Coordination Center Portal.