This pipeline calculates clusters based on a consensus non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) clustering method , . This pipeline has the following features:
-
Convert input data set to a non-negitive matrix by column rank normalization.
-
Classify samples into consensus clusters.
-
Determine differentially expressed focal events for each subtype.
The most robust consensus NMF clustering of 441 samples using the 88 copy number focal regions was identified for k = 4 clusters. We computed the clustering for k = 2 to k = 8 and used the cophenetic correlation coefficient to determine the best solution.
Figure 1. Get High-res Image Samples were separated into 4 clusters. Shown are 441 samples and 145 marker focal events. The color bar of the row indicates the marker focal events for the corresponding cluster.
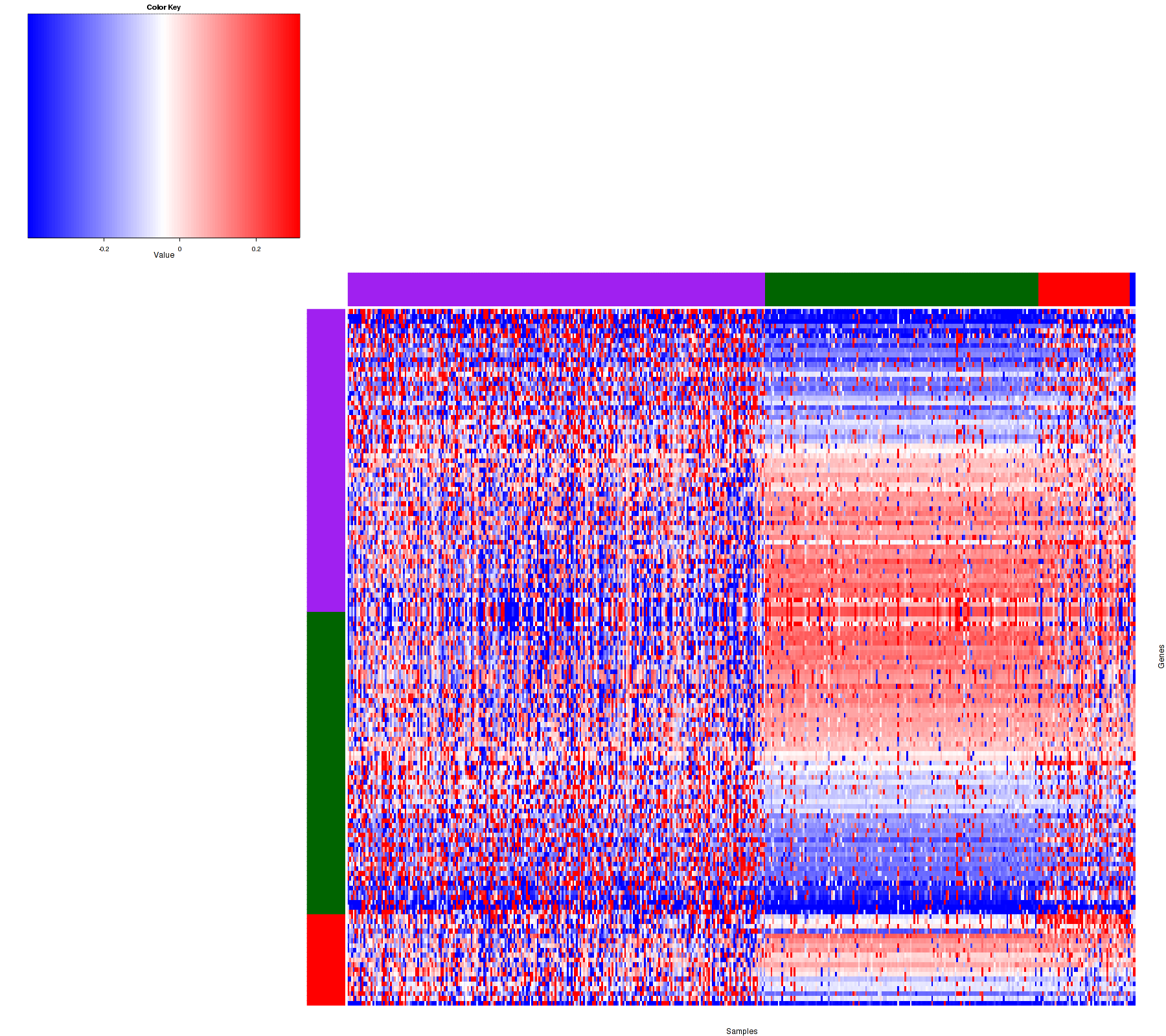
Figure 2. Get High-res Image Heatmap with a standard hierarchical clustering for 441 samples and the 88 focal events.
Figure 3. Get High-res Image The silhouette width was calculated for each sample and each value of k. The left panel shows the average silhouette width across all samples for each tested k (left panel). The right panels shows assignments of clusters to samples and the silhouette width of each sample for the most robust clustering.
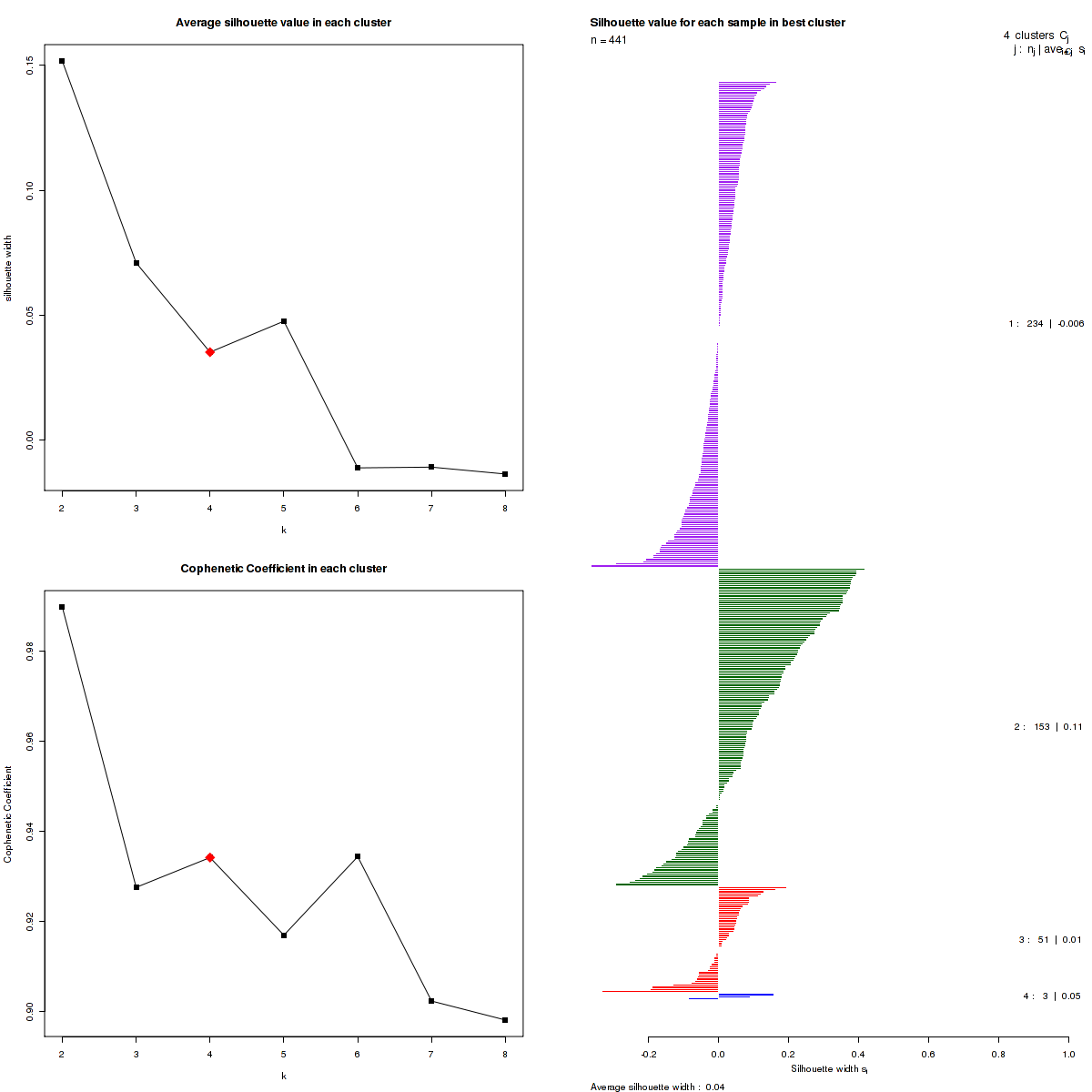
Figure 4. Get High-res Image The consensus matrix after clustering shows 4 clusters with limited overlap between clusters.
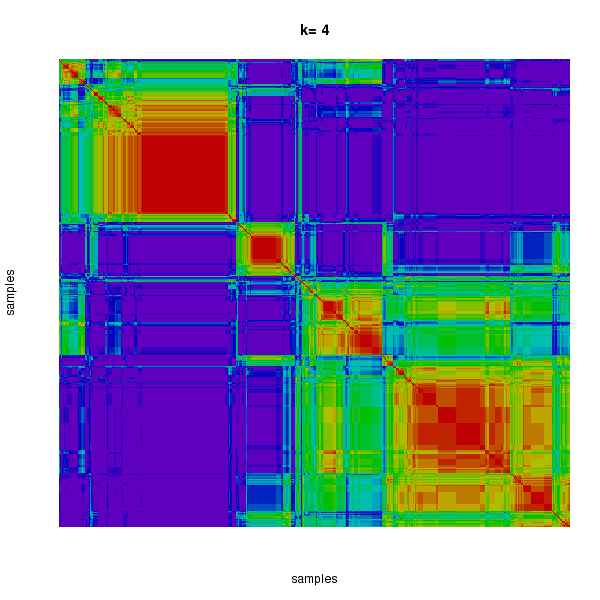
Table 1. Get Full Table List of samples with 4 subtypes and silhouette width.
| SampleName | cluster | silhouetteValue |
|---|---|---|
| TCGA-3M-AB46-01A-11D-A40Z-01 | 1 | 0.067 |
| TCGA-B7-A5TJ-01A-11D-A31K-01 | 1 | 0.22 |
| TCGA-B7-A5TN-01A-21D-A31K-01 | 1 | 0.064 |
| TCGA-BR-4183-01A-02D-1130-01 | 1 | 0.062 |
| TCGA-BR-4191-01A-02D-1130-01 | 1 | 0.054 |
| TCGA-BR-4255-01A-01D-1130-01 | 1 | -0.03 |
| TCGA-BR-4257-01A-01D-1130-01 | 1 | 0.23 |
| TCGA-BR-4294-01A-01D-1130-01 | 1 | -0.0061 |
| TCGA-BR-4357-01A-01D-1155-01 | 1 | 0.0097 |
| TCGA-BR-4366-01A-01D-1155-01 | 1 | -0.088 |
Table 2. Get Full Table List of samples belonging to each cluster in different k clusters.
| SampleName | K=2 | K=3 | K=4 | K=5 | K=6 | K=7 | K=8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCGA-3M-AB46-01A-11D-A40Z-01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TCGA-B7-5818-01A-11D-1599-01 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| TCGA-B7-A5TI-01A-11D-A31K-01 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 5 |
| TCGA-B7-A5TJ-01A-11D-A31K-01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TCGA-B7-A5TN-01A-21D-A31K-01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TCGA-BR-4183-01A-02D-1130-01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| TCGA-BR-4184-01A-01D-1130-01 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| TCGA-BR-4191-01A-02D-1130-01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TCGA-BR-4255-01A-01D-1130-01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 6 |
| TCGA-BR-4257-01A-01D-1130-01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Samples most representative of the clusters, hereby called core samples were identified based on positive silhouette width, indicating higher similarity to their own class than to any other class member. Core samples were used to select differentially expressed marker focal events for each subtype by comparing the subclass versus the other subclasses, using Student's t-test.
Table 3. Get Full Table List of marker focal events with p <= 0.05.
| Composite.Element.REF | p | difference | q | subclass |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMP PEAK 35(20Q13.2) | 2.9e-18 | 0.72 | 1.3e-16 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 33(19Q12) | 6.4e-07 | 0.55 | 2.9e-06 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 31(17Q12) | 6.6e-06 | 0.53 | 0.000025 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 32(18Q11.2) | 4.6e-06 | 0.39 | 0.000019 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 12(7Q21.2) | 0.000026 | 0.39 | 0.000085 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 15(8Q24.21) | 0.000034 | 0.36 | 0.0001 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 3(1Q42.3) | 1.5e-07 | 0.35 | 1e-06 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 11(7P11.2) | 0.00017 | 0.33 | 0.00045 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 7(6P21.1) | 2.9e-07 | 0.32 | 1.6e-06 | 1 |
| AMP PEAK 24(11Q13.3) | 0.00012 | 0.32 | 0.00033 | 1 |
The actual copy number part from all_lesions.conf_##.txt was used in this clustering. The all lesions file contains data about the significant regions of amplification and deletion as well as which samples are amplified or deleted in each of these regions. The identified regions are listed down the first column, and the samples are listed across the first row, starting in column 10.
-
Input file for whole clustering pipeline = all_lesions.conf_##.txt (where ## is the confidence level) from GISTIC pipeline
-
Input file for the clustering module = /xchip/cga/gdac-prod/tcga-gdac/jobResults/GDAC_TopgenesforCluster/STAD-TP/22533990/STAD-TP.expclu.gct
Non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) is an unsupervised learning algorithm that has been shown to identify molecular patterns when applied to gene expression data , . Rather than separating gene clusters based on distance computation, NMF detects contextdependent patterns of gene expression in complex biological systems.
We use the cophenetic correlation coefficient to determine the cluster that yields the most robust clustering. The cophenetic correlation coefficient is computed based on the consensus matrix of the CNMF clustering, and measures how reliably the same samples are assigned to the same cluster across many iterations of the clustering lgorithm with random initializations. The cophenetic correlation coefficient lies between 0 and 1, with higher values indicating more stable cluster assignments. We select the number of clusters k based on the largest observed correlation coefficient for all tested values of k.
Silhouette width is defined as the ratio of average distance of each sample to samples in the same cluster to the smallest distance to samples not in the same cluster. If silhouette width is close to 1, it means that sample is well clustered. If silhouette width is close to -1, it means that sample is misclassified .
In addition to the links below, the full results of the analysis summarized in this report can also be downloaded programmatically using firehose_get, or interactively from either the Broad GDAC website or TCGA Data Coordination Center Portal.