This pipeline uses various statistical tests to identify genes whose promoter methylation levels correlated to selected clinical features.
Testing the association between 17147 genes and 3 clinical features across 131 samples, statistically thresholded by Q value < 0.05, 2 clinical features related to at least one genes.
-
2 genes correlated to 'AGE'.
-
AOC2 , ARFGAP1
-
1 gene correlated to 'GENDER'.
-
UTP14C
-
No genes correlated to 'Time to Death'
Complete statistical result table is provided in Supplement Table 1
Table 1. Get Full Table This table shows the clinical features, statistical methods used, and the number of genes that are significantly associated with each clinical feature at Q value < 0.05.
| Clinical feature | Statistical test | Significant genes | Associated with | Associated with | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to Death | Cox regression test | N=0 | ||||
| AGE | Spearman correlation test | N=2 | older | N=2 | younger | N=0 |
| GENDER | t test | N=1 | male | N=1 | female | N=0 |
Table S1. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'Time to Death'
| Time to Death | Duration (Months) | 0.2-131.1 (median=41.8) |
| censored | N = 6 | |
| death | N = 10 | |
| Significant markers | N = 0 |
Table S2. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'AGE'
| AGE | Mean (SD) | 55.59 (17) |
| Significant markers | N = 2 | |
| pos. correlated | 2 | |
| neg. correlated | 0 |
Table S3. Get Full Table List of 2 genes significantly correlated to 'AGE' by Spearman correlation test
| SpearmanCorr | corrP | Q | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AOC2 | 0.8964 | 1.118e-06 | 0.0192 |
| ARFGAP1 | 0.8817 | 2.895e-06 | 0.0496 |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of AOC2 to 'AGE'. P value = 1.12e-06 with Spearman correlation analysis. The straight line presents the best linear regression.
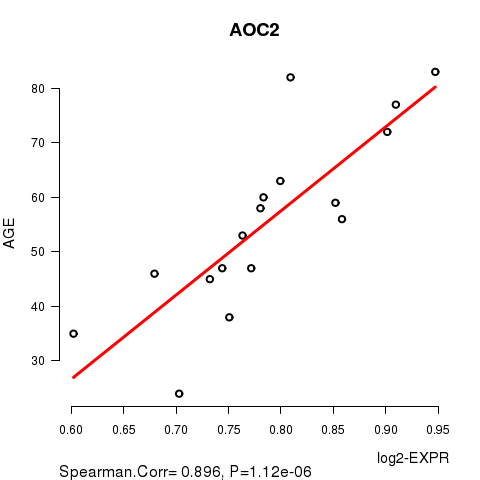
Table S4. Basic characteristics of clinical feature: 'GENDER'
| GENDER | Labels | N |
| FEMALE | 44 | |
| MALE | 87 | |
| Significant markers | N = 1 | |
| Higher in MALE | 1 | |
| Higher in FEMALE | 0 |
Table S5. Get Full Table List of one gene differentially expressed by 'GENDER'
| T(pos if higher in 'MALE') | ttestP | Q | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
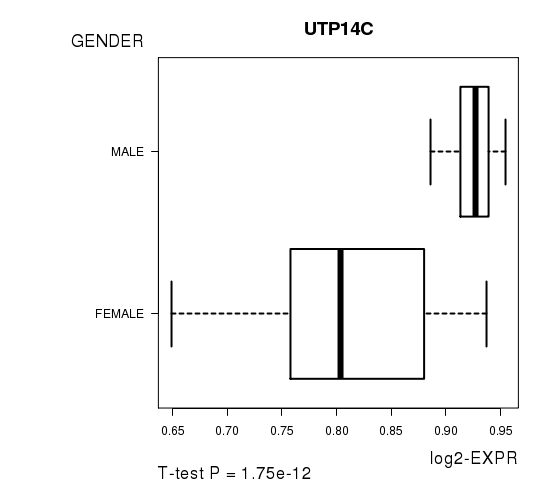
| UTP14C | 9.44 | 1.747e-12 | 3e-08 | 0.9399 |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image As an example, this figure shows the association of UTP14C to 'GENDER'. P value = 1.75e-12 with T-test analysis.
-
Expresson data file = SKCM.meth.for_correlation.filtered_data.txt
-
Clinical data file = SKCM.clin.merged.picked.txt
-
Number of patients = 131
-
Number of genes = 17147
-
Number of clinical features = 3
For survival clinical features, Wald's test in univariate Cox regression analysis with proportional hazards model (Andersen and Gill 1982) was used to estimate the P values using the 'coxph' function in R. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were plot using the four quartile subgroups of patients based on expression levels
For continuous numerical clinical features, Spearman's rank correlation coefficients (Spearman 1904) and two-tailed P values were estimated using 'cor.test' function in R
For two-class clinical features, two-tailed Student's t test with unequal variance (Lehmann and Romano 2005) was applied to compare the log2-expression levels between the two clinical classes using 't.test' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.
This is an experimental feature. The full results of the analysis summarized in this report can be downloaded from the TCGA Data Coordination Center.