This pipeline computes the correlation between cancer subtypes identified by different molecular patterns and selected clinical features.
Testing the association between subtypes identified by 2 different clustering approaches and 17 clinical features across 111 patients, 11 significant findings detected with P value < 0.05 and Q value < 0.25.
-
Consensus hierarchical clustering analysis on array-based mRNA expression data identified 3 subtypes that correlate to 'HISTOLOGIC_GRADE', 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE', 'PATHOLOGIC_STAGE', 'GENDER', 'COUNTRY_OF_ORIGIN', and 'ORIGIN_ASIA'.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL'. These subtypes correlate to 'HISTOLOGIC_GRADE', 'GENDER', 'SMOKER', 'COUNTRY_OF_ORIGIN', and 'ORIGIN_ASIA'.
Table 1. Get Full Table Overview of the association between subtypes identified by 2 different clustering approaches and 17 clinical features. Shown in the table are P values (Q values). Thresholded by P value < 0.05 and Q value < 0.25, 11 significant findings detected.
|
Clinical Features |
Statistical Tests |
mRNA cHierClus subtypes |
LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL |
| DAYS TO DEATH OR LAST FUP | logrank test |
0.195 (0.331) |
0.239 (0.387) |
| HISTOLOGICAL TYPE | Fisher's exact test |
0.0597 (0.156) |
0.295 (0.436) |
| HISTOLOGIC GRADE | Fisher's exact test |
0.00081 (0.00688) |
0.00879 (0.046) |
| KARNOFSKY PERFORMANCE SCORE | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.25 (0.387) |
0.105 (0.239) |
| PATHOLOGY T STAGE | Fisher's exact test |
0.0411 (0.127) |
0.136 (0.273) |
| PATHOLOGY N STAGE | Fisher's exact test |
0.777 (0.915) |
0.78 (0.915) |
| PATHOLOGIC STAGE | Fisher's exact test |
0.0123 (0.0521) |
0.0656 (0.159) |
| YEARS TO BIRTH | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.627 (0.79) |
0.177 (0.317) |
| ETHNICITY | Fisher's exact test |
1 (1.00) |
1 (1.00) |
| GENDER | Fisher's exact test |
2e-05 (0.00034) |
1e-05 (0.00034) |
| RACE | Fisher's exact test |
0.852 (0.966) |
0.58 (0.758) |
| RADIATION THERAPY | Fisher's exact test |
0.55 (0.747) |
0.371 (0.525) |
| BMI | Fisher's exact test |
0.162 (0.307) |
0.134 (0.273) |
| NUMBER PACK YEARS SMOKED | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.986 (1.00) |
0.945 (1.00) |
| SMOKER | Fisher's exact test |
0.0555 (0.156) |
0.0245 (0.0926) |
| COUNTRY OF ORIGIN | Fisher's exact test |
0.00947 (0.046) |
0.00014 (0.00159) |
| ORIGIN ASIA | Fisher's exact test |
0.0388 (0.127) |
0.00495 (0.0337) |
Table S1. Description of clustering approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 33 | 27 | 51 |
P value = 0.195 (logrank test), Q value = 0.33
Table S2. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'DAYS_TO_DEATH_OR_LAST_FUP'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 111 | 11 | 0.2 - 35.0 (13.1) |
| subtype1 | 32 | 6 | 1.4 - 26.9 (13.9) |
| subtype2 | 25 | 3 | 0.2 - 27.4 (12.9) |
| subtype3 | 46 | 2 | 0.5 - 35.0 (12.2) |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'DAYS_TO_DEATH_OR_LAST_FUP'
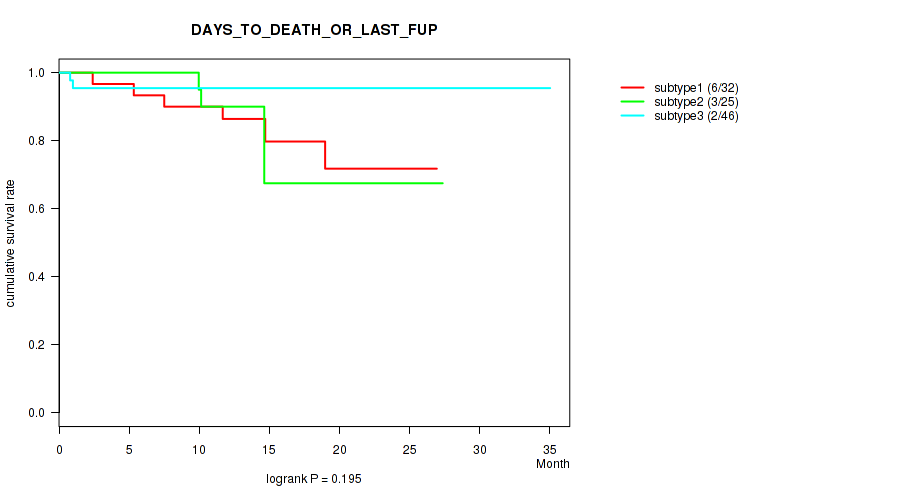
P value = 0.0597 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.16
Table S3. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | ACINAR ADENOCARCINOMA | ADENOCARCINOMA | BASALOID SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA | INVASIVE MUCINOUS ADENOCARCINOMA | LEPIDIC ADENOCARCINOMA | MICROPAPILLARY ADENOCARCINOMA | OTHER | PAPILLARY ADENOCARCINOMA | SOLID ADENOCARCINOMA | SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 13 | 68 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 4 | 20 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 16 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 7 | 32 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
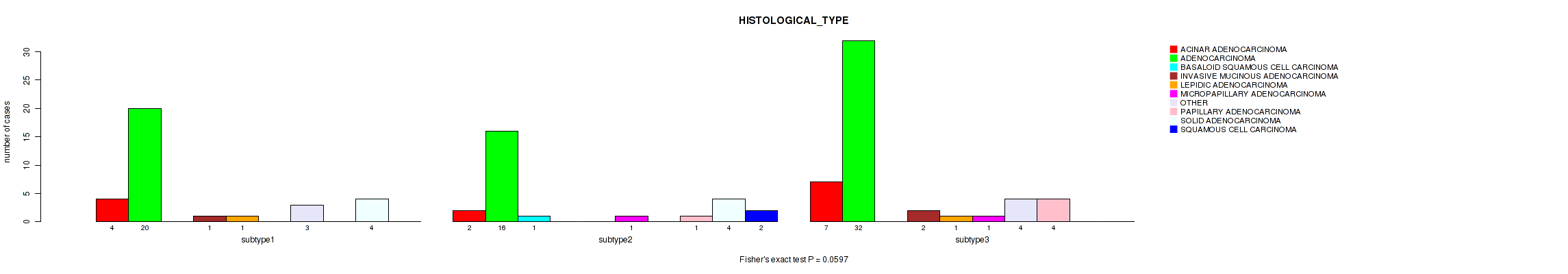
P value = 0.00081 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0069
Table S4. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'HISTOLOGIC_GRADE'
| nPatients | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | GX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 8 | 65 | 31 | 1 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 23 | 7 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 9 | 16 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 7 | 33 | 8 | 1 | 2 |
Figure S3. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'HISTOLOGIC_GRADE'
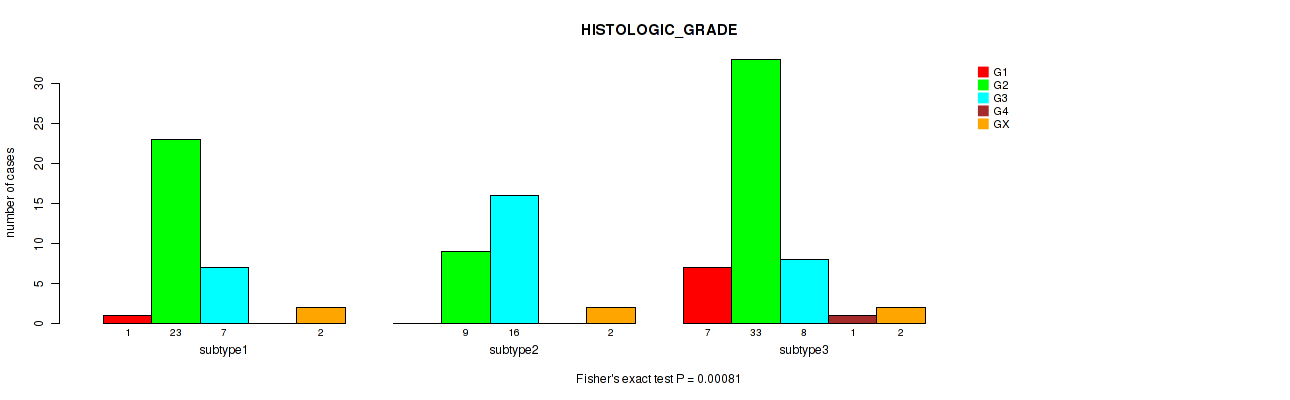
P value = 0.25 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.39
Table S5. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'KARNOFSKY_PERFORMANCE_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 70 | 81.7 (9.0) |
| subtype1 | 18 | 78.9 (7.6) |
| subtype2 | 24 | 81.7 (9.2) |
| subtype3 | 28 | 83.6 (9.5) |
Figure S4. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'KARNOFSKY_PERFORMANCE_SCORE'
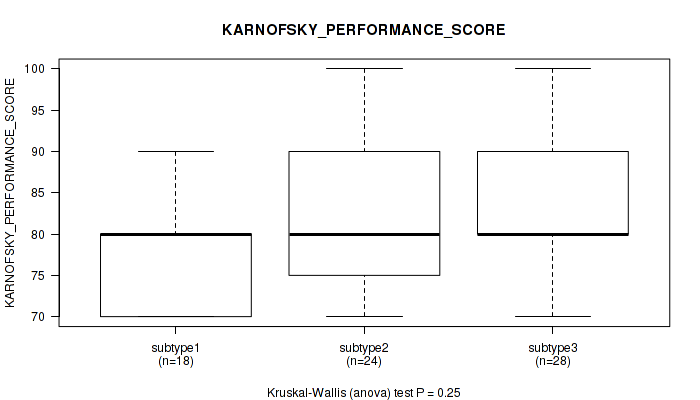
P value = 0.0411 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.13
Table S6. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| T1 | T2 | T3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 28 | 70 | 13 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 21 | 7 |
| subtype2 | 4 | 20 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 19 | 29 | 3 |
Figure S5. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
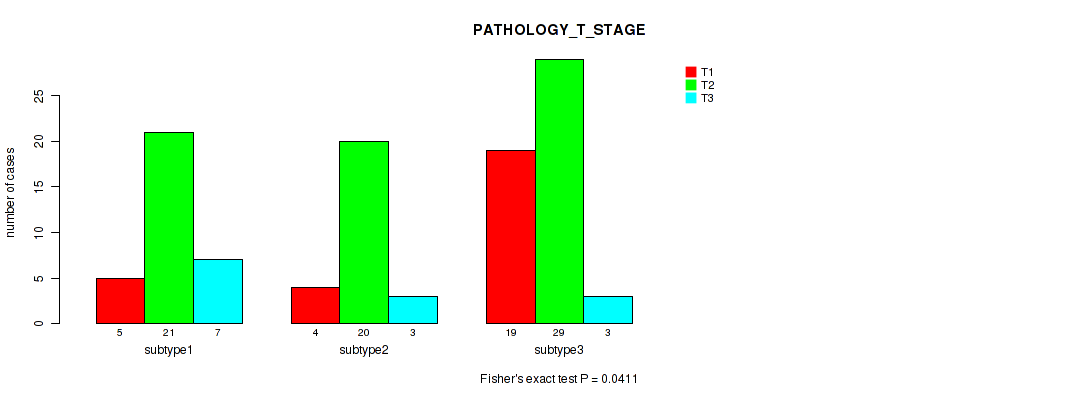
P value = 0.777 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.91
Table S7. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| N0 | N1 | N2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 74 | 17 | 19 |
| subtype1 | 24 | 3 | 6 |
| subtype2 | 18 | 4 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 32 | 10 | 8 |
Figure S6. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
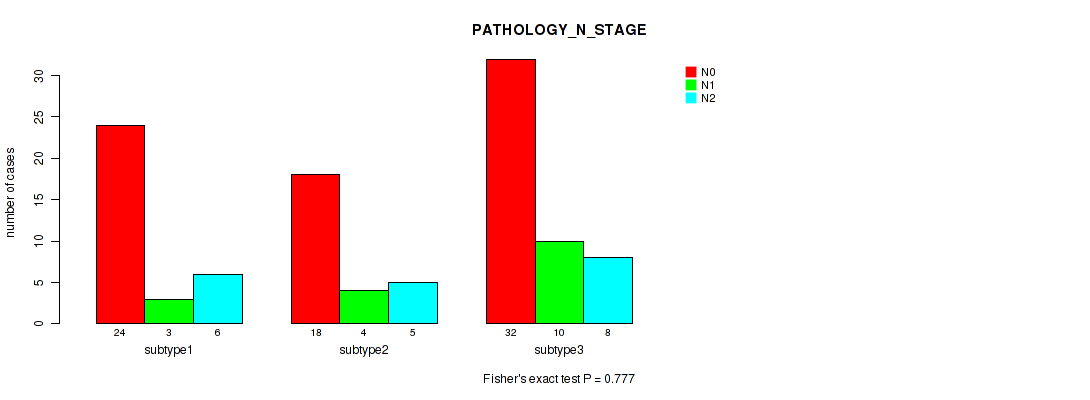
P value = 0.0123 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.052
Table S8. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'PATHOLOGIC_STAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 23 | 34 | 17 | 13 | 1 | 20 | 1 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 4 | 12 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 3 | 11 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 16 | 11 | 11 | 1 | 0 | 9 | 1 |
Figure S7. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'PATHOLOGIC_STAGE'
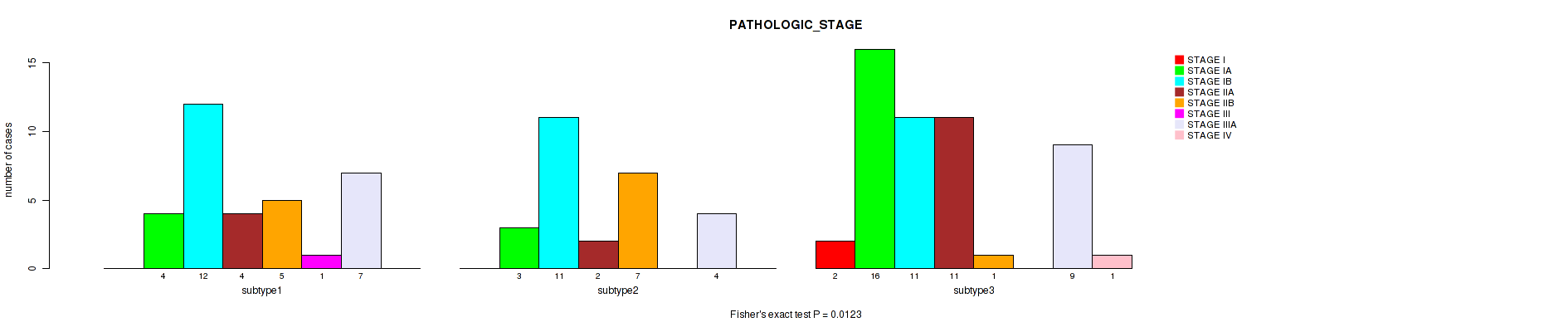
P value = 0.627 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.79
Table S9. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 111 | 62.6 (9.6) |
| subtype1 | 33 | 63.4 (8.4) |
| subtype2 | 27 | 61.8 (7.5) |
| subtype3 | 51 | 62.5 (11.3) |
Figure S8. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
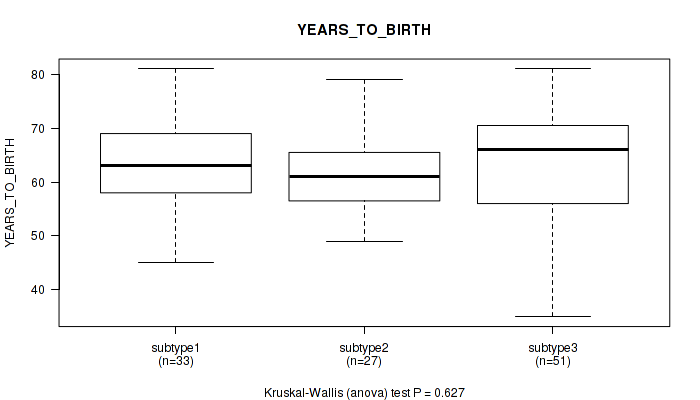
P value = 1 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S10. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 3 | 35 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 13 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 19 |
Figure S9. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'ETHNICITY'
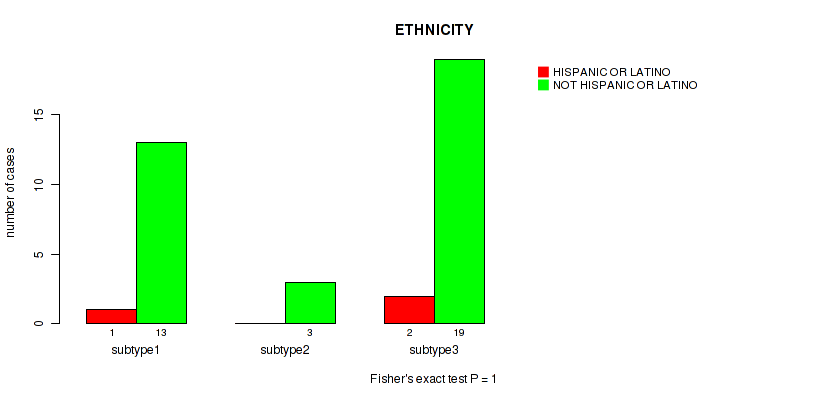
P value = 2e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.00034
Table S11. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 38 | 73 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 30 |
| subtype2 | 6 | 21 |
| subtype3 | 29 | 22 |
Figure S10. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GENDER'
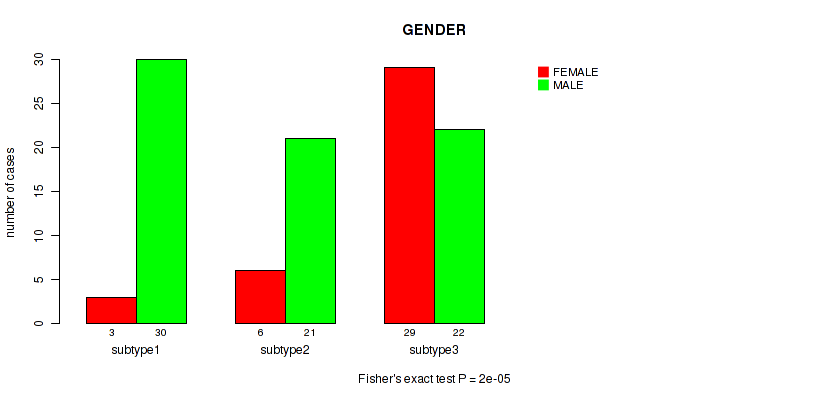
P value = 0.852 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.97
Table S12. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'RACE'
| nPatients | AMERICAN INDIAN OR ALASKA NATIVE | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 1 | 1 | 1 | 34 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 13 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 18 |
Figure S11. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'RACE'
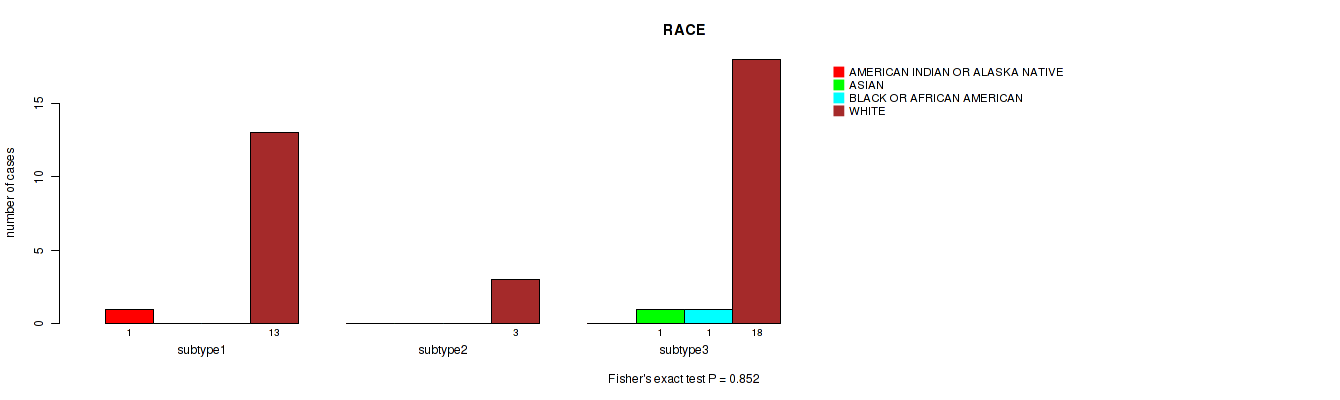
P value = 0.55 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.75
Table S13. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'RADIATION_THERAPY'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 72 | 22 |
| subtype1 | 21 | 9 |
| subtype2 | 17 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 34 | 8 |
Figure S12. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'RADIATION_THERAPY'
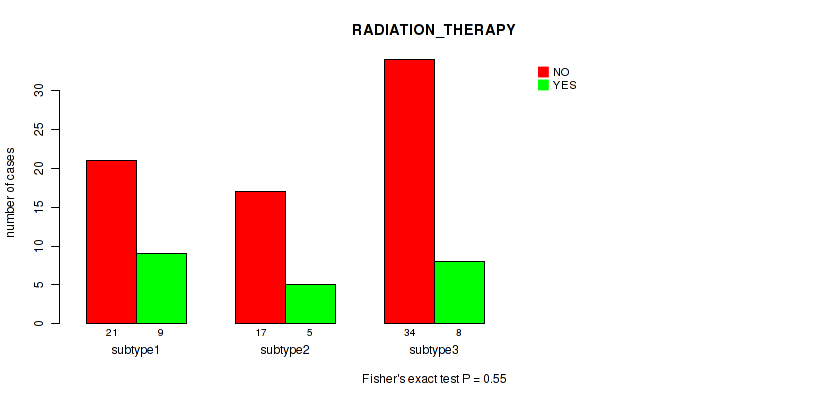
P value = 0.162 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.31
Table S14. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'BMI'
| nPatients | NORMAL | OBESE | OVERWEIGHT | SEVERELY OBESE | UNDERWEIGHT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 54 | 10 | 28 | 3 | 16 |
| subtype1 | 13 | 3 | 11 | 2 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 14 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 27 | 6 | 13 | 1 | 4 |
Figure S13. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'BMI'
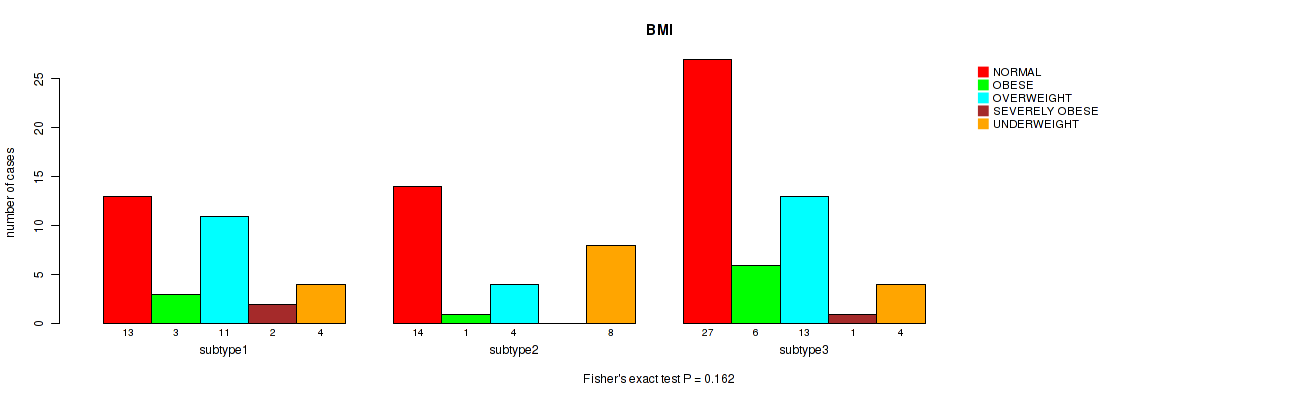
P value = 0.986 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S15. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 55 | 27.4 (23.4) |
| subtype1 | 20 | 28.2 (25.1) |
| subtype2 | 14 | 28.9 (27.5) |
| subtype3 | 21 | 25.7 (19.6) |
Figure S14. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
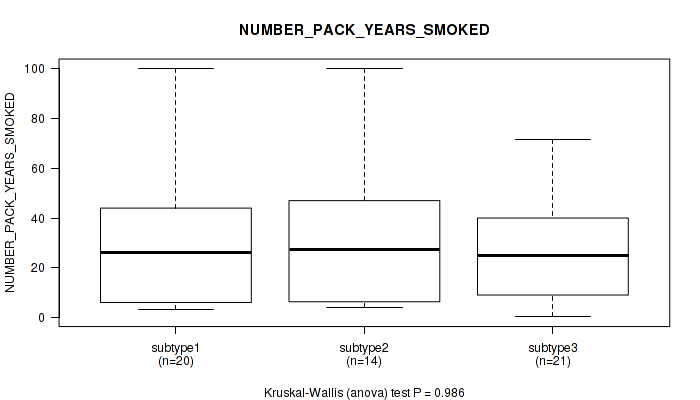
P value = 0.0555 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.16
Table S16. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #15: 'SMOKER'
| nPatients | NON-SMOKER | SMOKER |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 46 | 62 |
| subtype1 | 8 | 24 |
| subtype2 | 13 | 14 |
| subtype3 | 25 | 24 |
Figure S15. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #15: 'SMOKER'
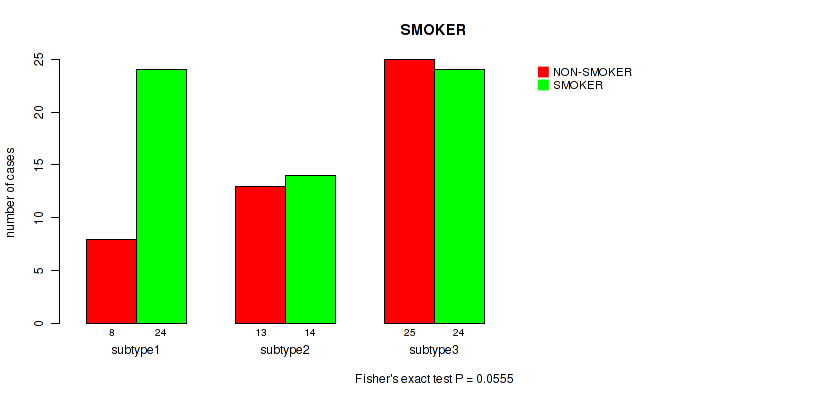
P value = 0.00947 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.046
Table S17. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #16: 'COUNTRY_OF_ORIGIN'
| nPatients | BULGARIA | CANADA | CHINA | JAMAICA | MEXICO | POLAND | RUSSIA | UKRAINE | UNITED STATES | VIETNAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 1 | 18 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 34 | 45 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 14 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 16 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 15 |
Figure S16. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #16: 'COUNTRY_OF_ORIGIN'
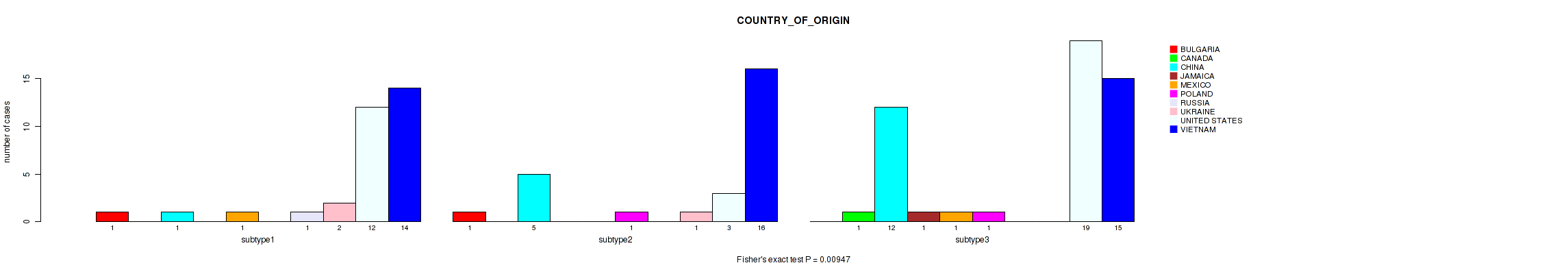
P value = 0.0388 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.13
Table S18. Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #17: 'ORIGIN_ASIA'
| nPatients | ASIAN | WESTERN |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 63 | 46 |
| subtype1 | 15 | 17 |
| subtype2 | 21 | 6 |
| subtype3 | 27 | 23 |
Figure S17. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'mRNA cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #17: 'ORIGIN_ASIA'
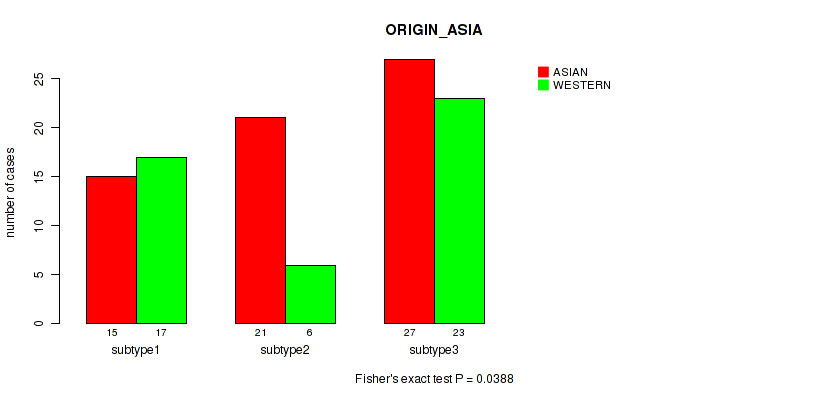
Table S19. Description of clustering approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 33 | 30 | 48 |
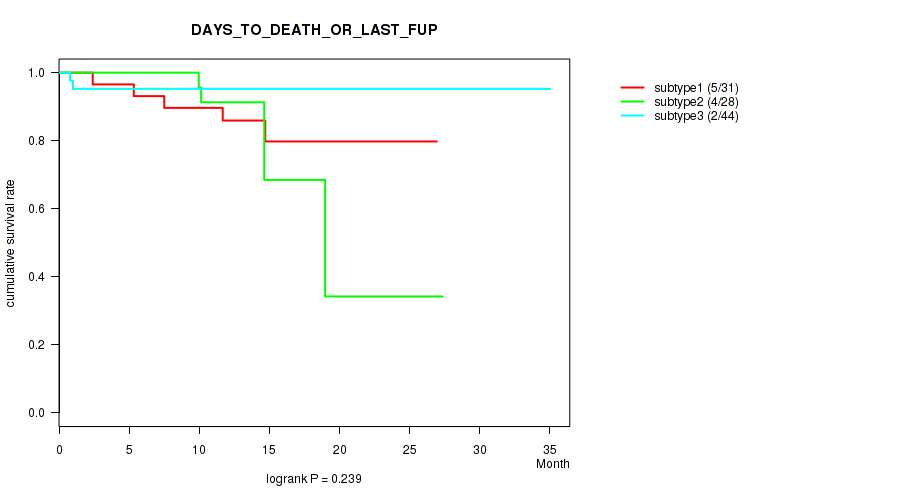
P value = 0.239 (logrank test), Q value = 0.39
Table S20. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'DAYS_TO_DEATH_OR_LAST_FUP'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 111 | 11 | 0.2 - 35.0 (13.1) |
| subtype1 | 31 | 5 | 1.4 - 26.9 (14.1) |
| subtype2 | 28 | 4 | 0.2 - 27.4 (12.7) |
| subtype3 | 44 | 2 | 0.5 - 35.0 (12.2) |
Figure S18. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'DAYS_TO_DEATH_OR_LAST_FUP'
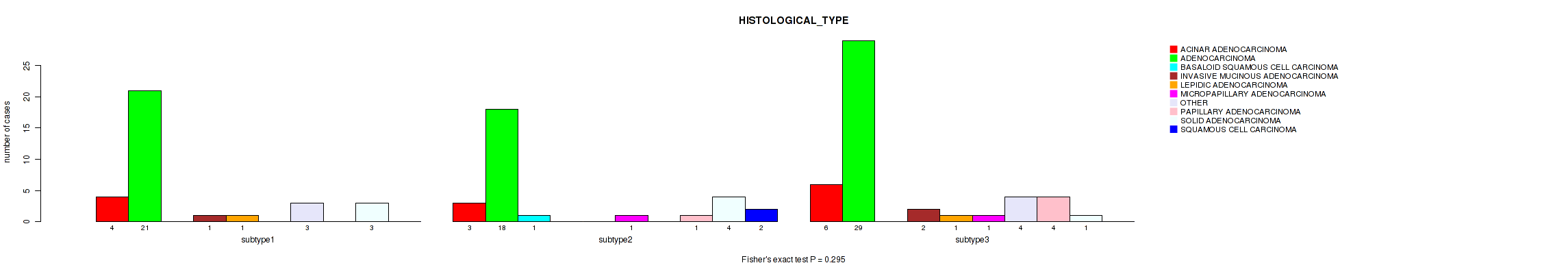
P value = 0.295 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.44
Table S21. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | ACINAR ADENOCARCINOMA | ADENOCARCINOMA | BASALOID SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA | INVASIVE MUCINOUS ADENOCARCINOMA | LEPIDIC ADENOCARCINOMA | MICROPAPILLARY ADENOCARCINOMA | OTHER | PAPILLARY ADENOCARCINOMA | SOLID ADENOCARCINOMA | SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 13 | 68 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 2 |
| subtype1 | 4 | 21 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 3 | 18 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 6 | 29 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
Figure S19. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
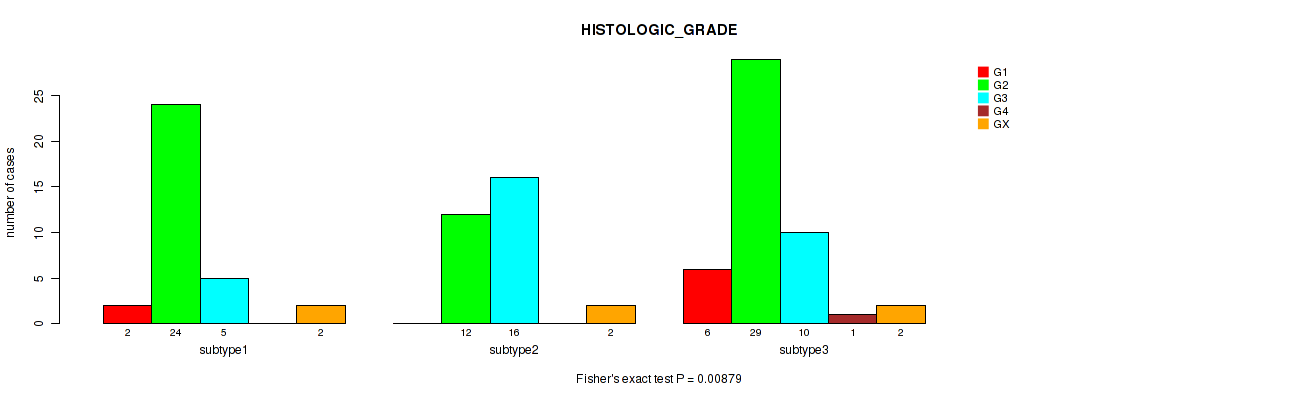
P value = 0.00879 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.046
Table S22. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'HISTOLOGIC_GRADE'
| nPatients | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | GX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 8 | 65 | 31 | 1 | 6 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 24 | 5 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 12 | 16 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 6 | 29 | 10 | 1 | 2 |
Figure S20. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'HISTOLOGIC_GRADE'
P value = 0.105 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.24
Table S23. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'KARNOFSKY_PERFORMANCE_SCORE'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 70 | 81.7 (9.0) |
| subtype1 | 16 | 78.8 (7.2) |
| subtype2 | 27 | 80.7 (9.2) |
| subtype3 | 27 | 84.4 (9.3) |
Figure S21. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'KARNOFSKY_PERFORMANCE_SCORE'
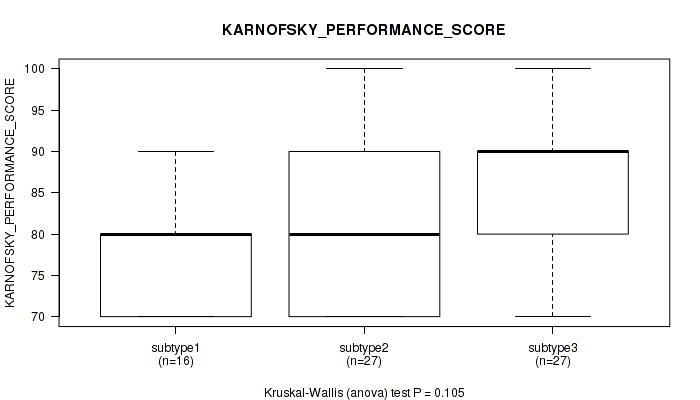
P value = 0.136 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.27
Table S24. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| T1 | T2 | T3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 28 | 70 | 13 |
| subtype1 | 7 | 20 | 6 |
| subtype2 | 4 | 22 | 4 |
| subtype3 | 17 | 28 | 3 |
Figure S22. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
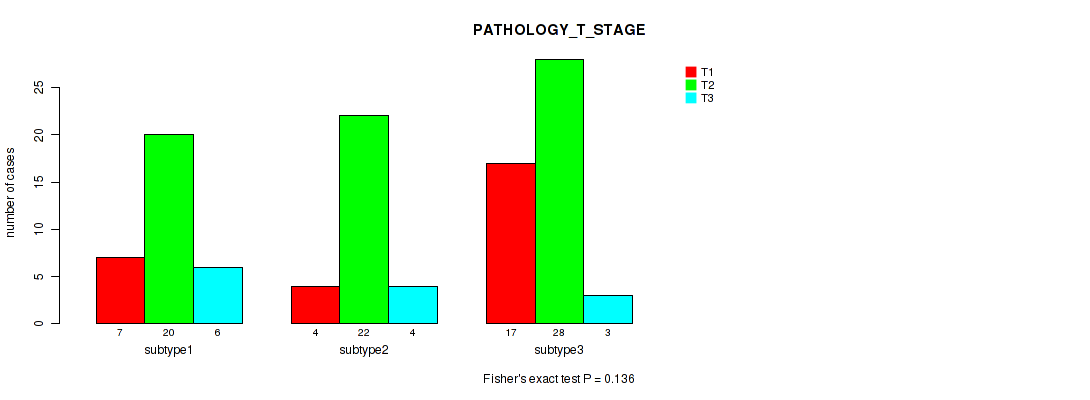
P value = 0.78 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.91
Table S25. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| N0 | N1 | N2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 74 | 17 | 19 |
| subtype1 | 23 | 3 | 7 |
| subtype2 | 20 | 5 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 31 | 9 | 7 |
Figure S23. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
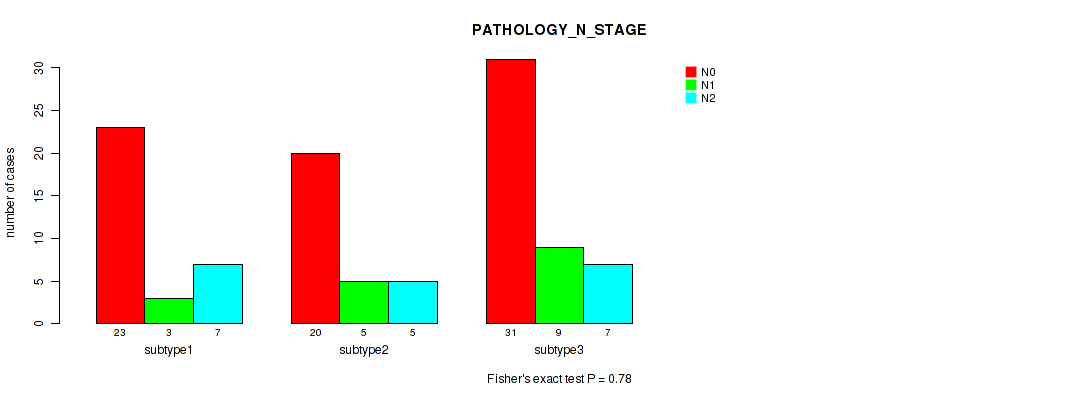
P value = 0.0656 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.16
Table S26. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'PATHOLOGIC_STAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 23 | 34 | 17 | 13 | 1 | 20 | 1 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 6 | 12 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 7 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 3 | 12 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 14 | 10 | 11 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 1 |
Figure S24. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'PATHOLOGIC_STAGE'
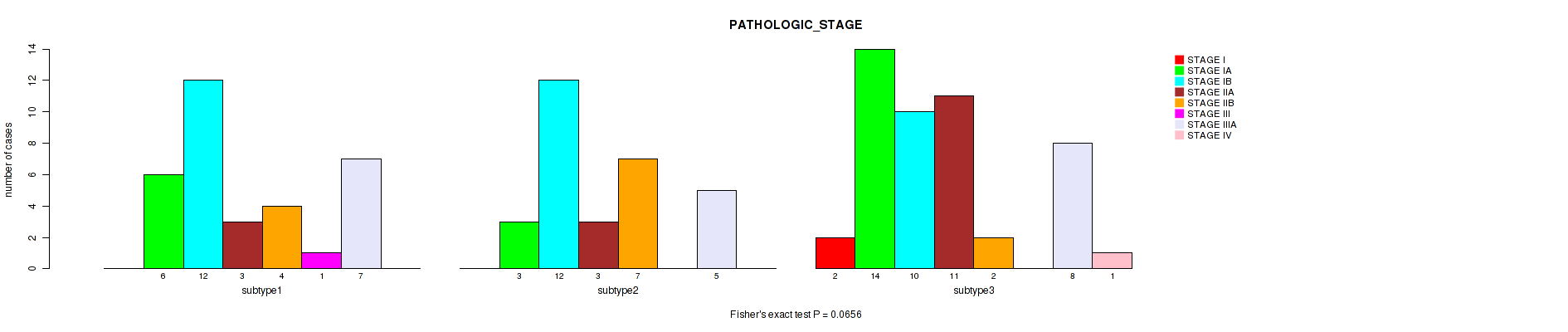
P value = 0.177 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.32
Table S27. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 111 | 62.6 (9.6) |
| subtype1 | 33 | 64.4 (7.8) |
| subtype2 | 30 | 60.3 (8.4) |
| subtype3 | 48 | 62.7 (11.2) |
Figure S25. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
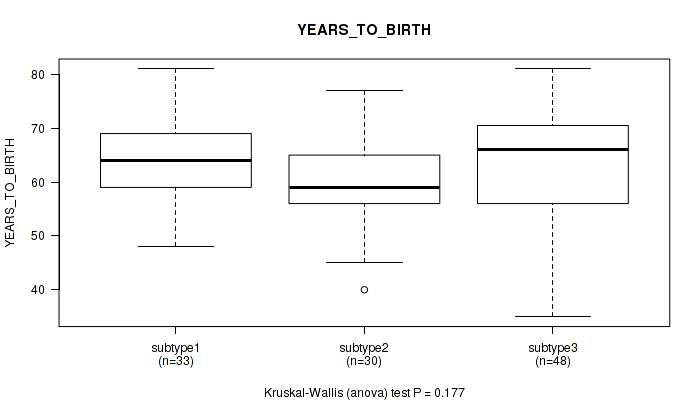
P value = 1 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S28. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 3 | 35 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 15 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 17 |
Figure S26. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'ETHNICITY'
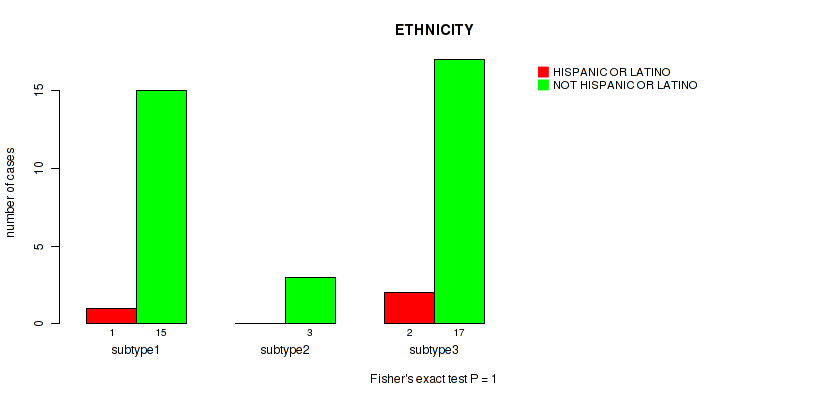
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.00034
Table S29. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 38 | 73 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 28 |
| subtype2 | 4 | 26 |
| subtype3 | 29 | 19 |
Figure S27. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'GENDER'
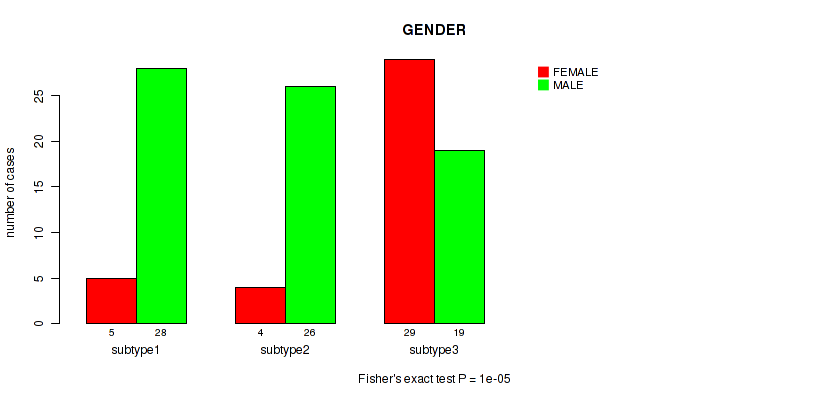
P value = 0.58 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.76
Table S30. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'RACE'
| nPatients | AMERICAN INDIAN OR ALASKA NATIVE | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 1 | 1 | 1 | 34 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 14 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 17 |
Figure S28. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'RACE'
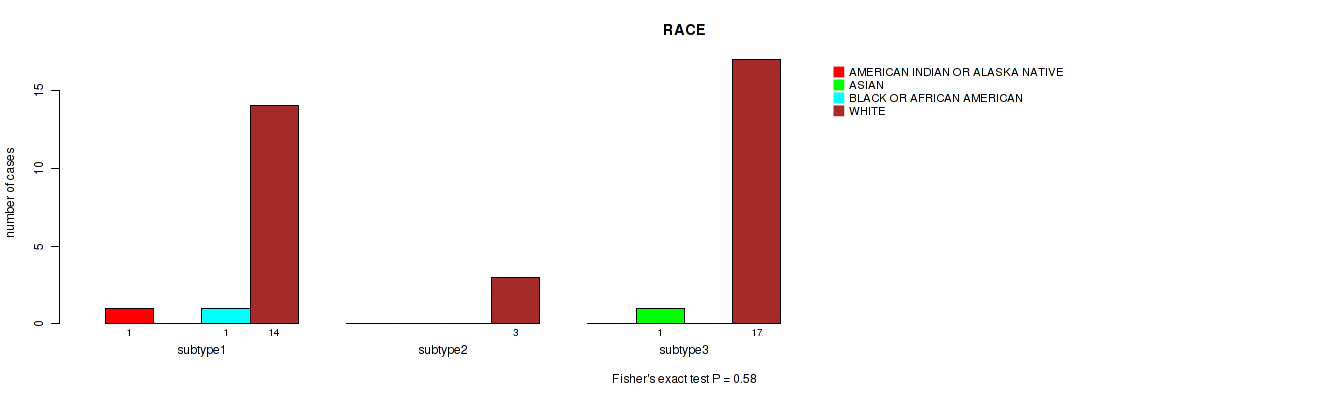
P value = 0.371 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.53
Table S31. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'RADIATION_THERAPY'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 72 | 22 |
| subtype1 | 22 | 7 |
| subtype2 | 17 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 33 | 7 |
Figure S29. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'RADIATION_THERAPY'
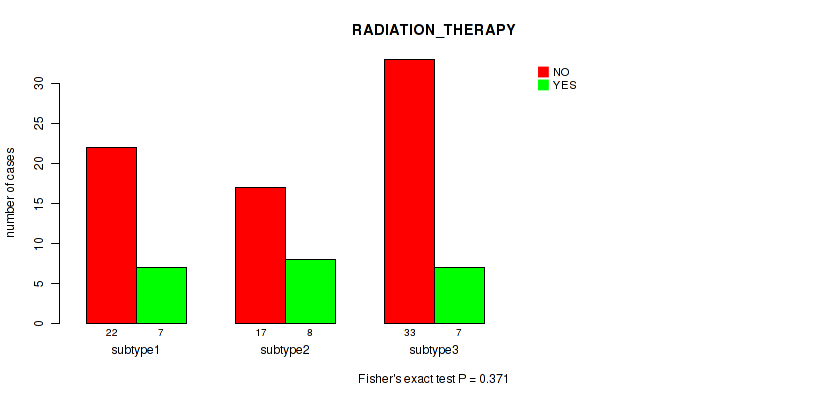
P value = 0.134 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.27
Table S32. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'BMI'
| nPatients | NORMAL | OBESE | OVERWEIGHT | SEVERELY OBESE | UNDERWEIGHT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 54 | 10 | 28 | 3 | 16 |
| subtype1 | 13 | 3 | 11 | 2 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 18 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 7 |
| subtype3 | 23 | 7 | 12 | 1 | 5 |
Figure S30. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'BMI'
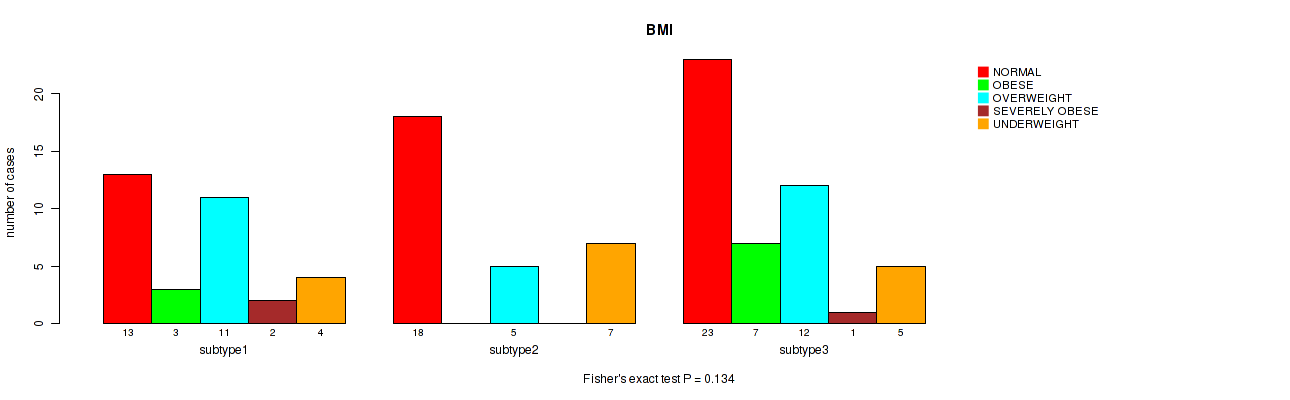
P value = 0.945 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1
Table S33. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 55 | 27.4 (23.4) |
| subtype1 | 20 | 26.3 (23.2) |
| subtype2 | 16 | 28.6 (28.0) |
| subtype3 | 19 | 27.5 (20.4) |
Figure S31. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
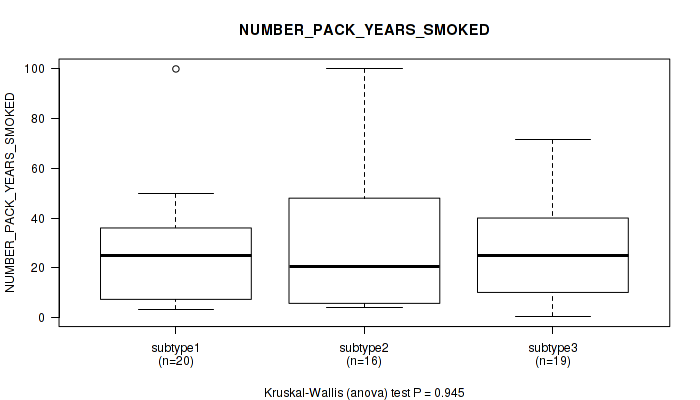
P value = 0.0245 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.093
Table S34. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #15: 'SMOKER'
| nPatients | NON-SMOKER | SMOKER |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 46 | 62 |
| subtype1 | 8 | 25 |
| subtype2 | 13 | 16 |
| subtype3 | 25 | 21 |
Figure S32. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #15: 'SMOKER'
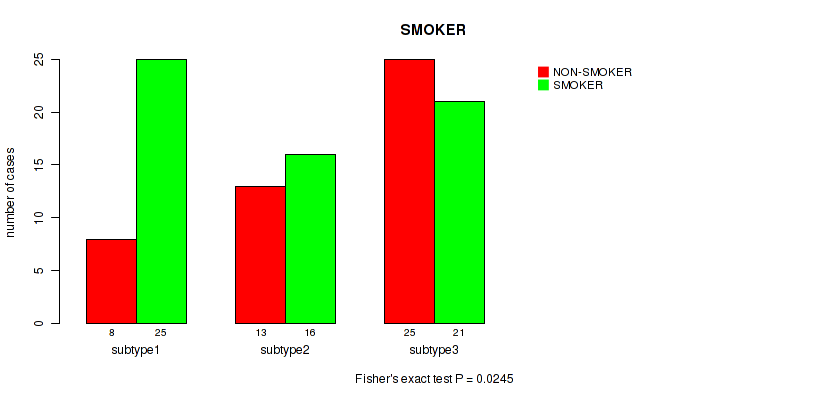
P value = 0.00014 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0016
Table S35. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #16: 'COUNTRY_OF_ORIGIN'
| nPatients | BULGARIA | CANADA | CHINA | JAMAICA | MEXICO | POLAND | RUSSIA | UKRAINE | UNITED STATES | VIETNAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 2 | 1 | 18 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 34 | 45 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 13 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 19 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 13 |
Figure S33. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #16: 'COUNTRY_OF_ORIGIN'
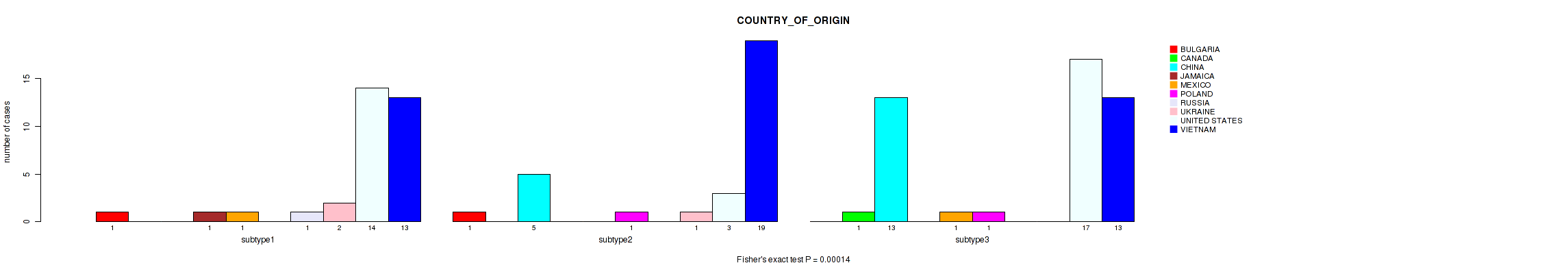
P value = 0.00495 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.034
Table S36. Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #17: 'ORIGIN_ASIA'
| nPatients | ASIAN | WESTERN |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 63 | 46 |
| subtype1 | 13 | 20 |
| subtype2 | 24 | 6 |
| subtype3 | 26 | 20 |
Figure S34. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'LINCRNA CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #17: 'ORIGIN_ASIA'
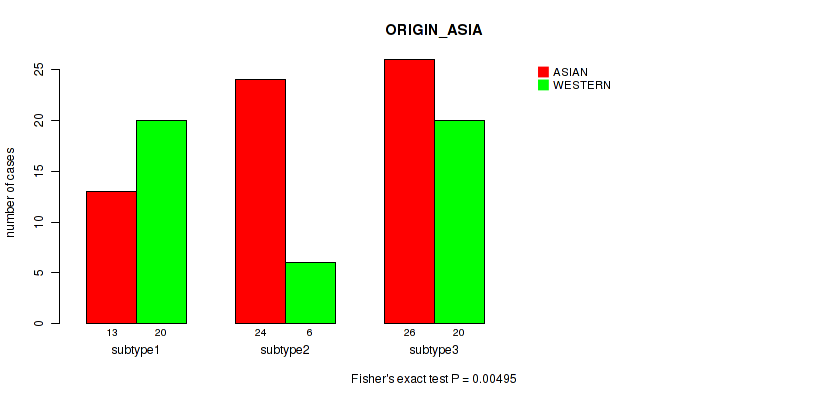
-
Cluster data file = /cromwell_root/fc-e7058367-eaa6-44b5-aab5-1ec08acf146a/69dd18b3-97fe-4143-b0f4-32e5d55e929d/aggregate_clusters_workflow/d44c315a-761b-4b72-be1f-cb969be36102/call-aggregate_clusters/CPTAC3-LUAD-TP.mergedcluster.txt
-
Clinical data file = /cromwell_root/fc-e7058367-eaa6-44b5-aab5-1ec08acf146a/39eab10a-1791-41cf-866c-13e6472ce02e/normalize_clinical_cptac/df4eac3a-77b6-4ce7-961f-e1027c1ad609/call-normalize_clinical_cptac_task_1/CPTAC3-LUAD-TP.clin.merged.picked.txt
-
Number of patients = 111
-
Number of clustering approaches = 2
-
Number of selected clinical features = 17
-
Exclude small clusters that include fewer than K patients, K = 3
Resampling-based clustering method (Monti et al. 2003)
For survival clinical features, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of tumors with and without gene mutations were plotted and the statistical significance P values were estimated by logrank test (Bland and Altman 2004) using the 'survdiff' function in R
For binary clinical features, two-tailed Fisher's exact tests (Fisher 1922) were used to estimate the P values using the 'fisher.test' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.