This pipeline computes the correlation between cancer subtypes identified by different molecular patterns and selected clinical features.
Testing the association between subtypes identified by 8 different clustering approaches and 14 clinical features across 612 patients, 62 significant findings detected with P value < 0.05 and Q value < 0.25.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes'. These subtypes correlate to 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH', 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE', 'GENDER', 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE', 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES', and 'RACE'.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'METHLYATION CNMF'. These subtypes correlate to 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH', 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE', 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE', and 'RACE'.
-
CNMF clustering analysis on sequencing-based mRNA expression data identified 3 subtypes that correlate to 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH', 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE', 'GENDER', 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE', and 'RACE'.
-
Consensus hierarchical clustering analysis on sequencing-based mRNA expression data identified 5 subtypes that correlate to 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH', 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE', 'GENDER', 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE', and 'RACE'.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRSEQ CNMF'. These subtypes correlate to 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH', 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE', 'GENDER', 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE', and 'RACE'.
-
5 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL'. These subtypes correlate to 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH', 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE', 'GENDER', 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE', 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED', and 'RACE'.
-
3 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes'. These subtypes correlate to 'Time to Death', 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH', 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE', 'GENDER', 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE', 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED', and 'RACE'.
-
5 subtypes identified in current cancer cohort by 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes'. These subtypes correlate to 'Time to Death', 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH', 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE', 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE', 'GENDER', 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE', 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES', 'RACE', and 'ETHNICITY'.
Table 1. Get Full Table Overview of the association between subtypes identified by 8 different clustering approaches and 14 clinical features. Shown in the table are P values (Q values). Thresholded by P value < 0.05 and Q value < 0.25, 62 significant findings detected.
|
Clinical Features |
Statistical Tests |
Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes |
METHLYATION CNMF |
RNAseq CNMF subtypes |
RNAseq cHierClus subtypes |
MIRSEQ CNMF |
MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL |
MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes |
MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes |
| Time to Death | logrank test |
0.106 (0.177) |
0.276 (0.382) |
0.139 (0.226) |
0.445 (0.564) |
0.0803 (0.143) |
0.579 (0.665) |
0.00971 (0.0217) |
0.0462 (0.0834) |
| YEARS TO BIRTH | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.000939 (0.00284) |
8.72e-05 (0.000337) |
3.93e-08 (1.47e-06) |
2.68e-08 (1.47e-06) |
1.52e-06 (3.41e-05) |
4.27e-10 (4.79e-08) |
3.96e-07 (1.11e-05) |
2.08e-06 (3.89e-05) |
| NEOPLASM DISEASESTAGE | Fisher's exact test |
0.0005 (0.0016) |
0.00109 (0.00313) |
2e-05 (8.62e-05) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
2e-05 (8.62e-05) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
0.00151 (0.00403) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
| PATHOLOGY T STAGE | Fisher's exact test |
0.00104 (0.00307) |
0.00424 (0.0106) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
0.00226 (0.00589) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
0.00012 (0.000434) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
| PATHOLOGY N STAGE | Fisher's exact test |
0.033 (0.0649) |
0.0999 (0.17) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
0.00027 (0.000916) |
0.00681 (0.0159) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
0.02 (0.0422) |
5e-05 (2e-04) |
| PATHOLOGY M STAGE | Fisher's exact test |
0.85 (0.895) |
0.0411 (0.0756) |
0.542 (0.648) |
0.513 (0.632) |
0.588 (0.665) |
0.533 (0.648) |
0.285 (0.389) |
0.588 (0.665) |
| GENDER | Fisher's exact test |
2e-05 (8.62e-05) |
0.896 (0.905) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
0.00143 (0.00391) |
0.00033 (0.00109) |
0.0162 (0.0349) |
0.00809 (0.0185) |
0.00503 (0.0121) |
| HISTOLOGICAL TYPE | Fisher's exact test |
0.00011 (0.000411) |
2e-05 (8.62e-05) |
0.0209 (0.0433) |
0.00084 (0.00261) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
0.00018 (0.00063) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
2e-05 (8.62e-05) |
| RADIATIONS RADIATION REGIMENINDICATION | Fisher's exact test |
1 (1.00) |
0.586 (0.665) |
0.0867 (0.149) |
0.18 (0.269) |
0.301 (0.407) |
0.544 (0.648) |
0.855 (0.895) |
0.448 (0.564) |
| NUMBER PACK YEARS SMOKED | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.172 (0.26) |
0.15 (0.24) |
0.353 (0.459) |
0.256 (0.359) |
0.0814 (0.143) |
0.0124 (0.0273) |
0.0412 (0.0756) |
0.246 (0.349) |
| COMPLETENESS OF RESECTION | Fisher's exact test |
0.691 (0.766) |
0.156 (0.243) |
0.233 (0.334) |
0.867 (0.9) |
0.57 (0.665) |
0.887 (0.905) |
0.701 (0.767) |
0.341 (0.449) |
| NUMBER OF LYMPH NODES | Kruskal-Wallis (anova) |
0.0381 (0.0724) |
0.331 (0.441) |
0.139 (0.226) |
0.219 (0.318) |
0.594 (0.665) |
0.155 (0.243) |
0.445 (0.564) |
0.0274 (0.055) |
| RACE | Fisher's exact test |
0.00302 (0.00769) |
0.00506 (0.0121) |
0.0275 (0.055) |
3e-05 (0.000124) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
0.00142 (0.00391) |
1e-05 (5.33e-05) |
| ETHNICITY | Fisher's exact test |
0.705 (0.767) |
0.894 (0.905) |
0.716 (0.772) |
0.159 (0.245) |
0.193 (0.284) |
0.459 (0.571) |
0.795 (0.848) |
0.0342 (0.0661) |
Table S1. Description of clustering approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 163 | 200 | 246 |
P value = 0.106 (logrank test), Q value = 0.18
Table S2. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 575 | 221 | 0.0 - 122.3 (12.8) |
| subtype1 | 154 | 59 | 0.1 - 122.3 (12.3) |
| subtype2 | 192 | 81 | 0.1 - 60.6 (12.6) |
| subtype3 | 229 | 81 | 0.0 - 116.4 (13.4) |
Figure S1. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'

P value = 0.000939 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.0028
Table S3. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 602 | 64.8 (11.3) |
| subtype1 | 160 | 67.1 (9.9) |
| subtype2 | 198 | 62.7 (11.6) |
| subtype3 | 244 | 65.1 (11.5) |
Figure S2. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
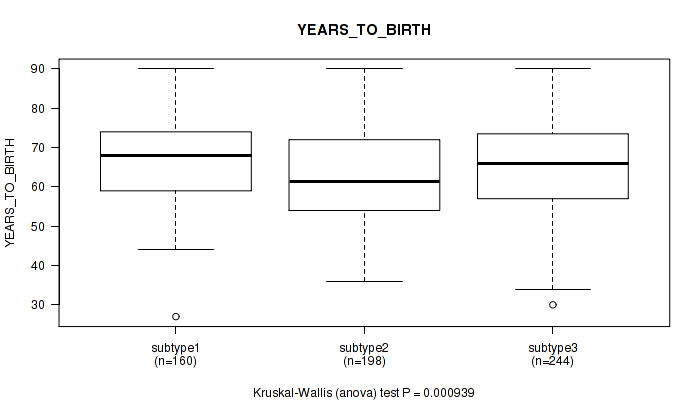
P value = 5e-04 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0016
Table S4. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE II | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 11 | 19 | 48 | 32 | 77 | 84 | 29 | 97 | 72 | 48 | 51 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 25 | 9 | 29 | 17 | 10 | 15 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 3 | 12 | 9 | 39 | 26 | 18 | 30 | 21 | 14 | 12 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 4 | 10 | 24 | 13 | 29 | 33 | 2 | 38 | 34 | 24 | 24 | 0 |
Figure S3. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
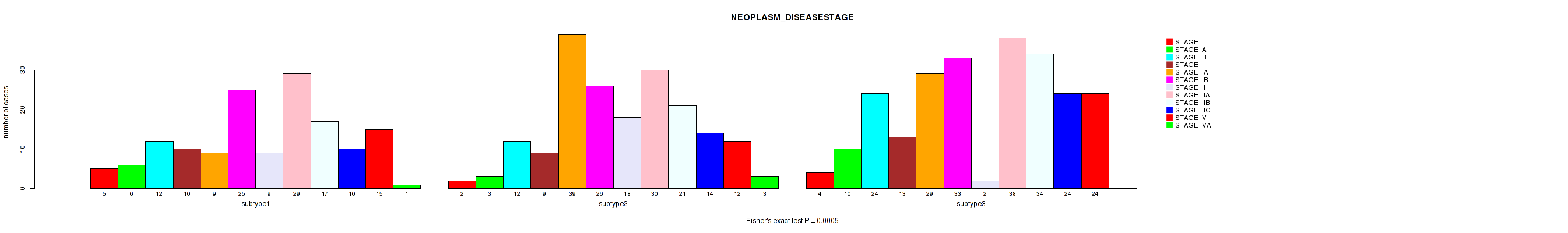
P value = 0.00104 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0031
Table S5. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| nPatients | T0+T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 53 | 126 | 280 | 124 |
| subtype1 | 20 | 31 | 76 | 28 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 46 | 104 | 25 |
| subtype3 | 18 | 49 | 100 | 71 |
Figure S4. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
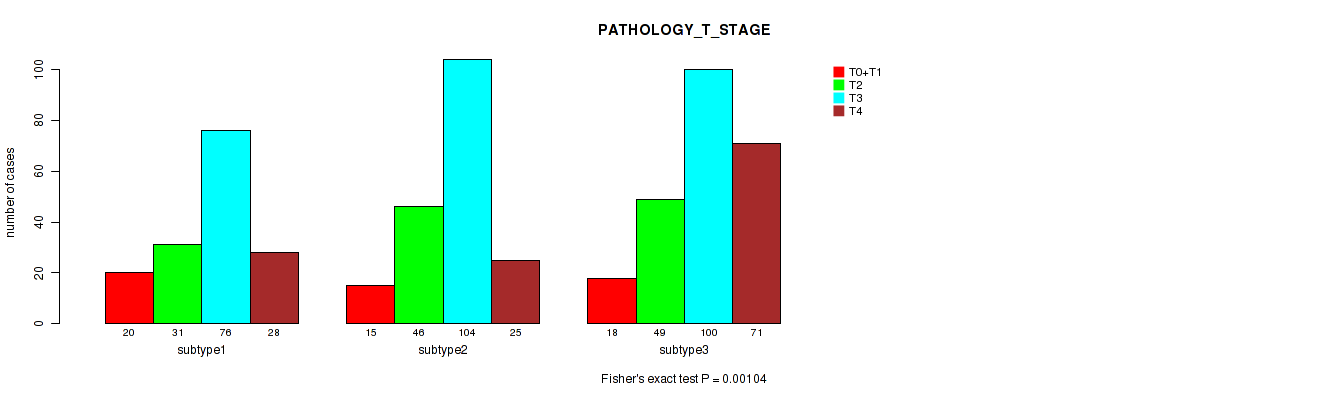
P value = 0.033 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.065
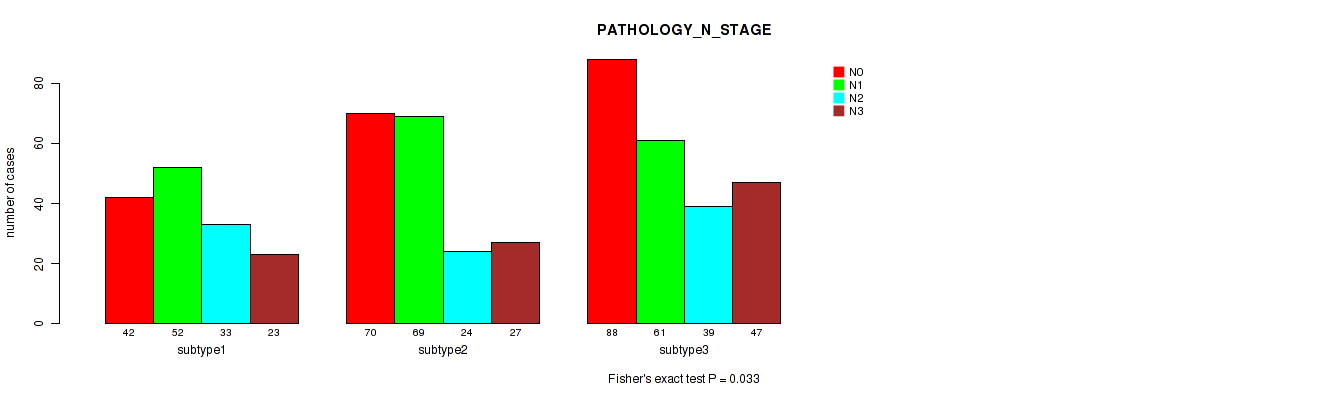
Table S6. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| nPatients | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 200 | 182 | 96 | 97 |
| subtype1 | 42 | 52 | 33 | 23 |
| subtype2 | 70 | 69 | 24 | 27 |
| subtype3 | 88 | 61 | 39 | 47 |
Figure S5. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
P value = 0.85 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.9
Table S7. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 513 | 39 |
| subtype1 | 132 | 9 |
| subtype2 | 169 | 12 |
| subtype3 | 212 | 18 |
Figure S6. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
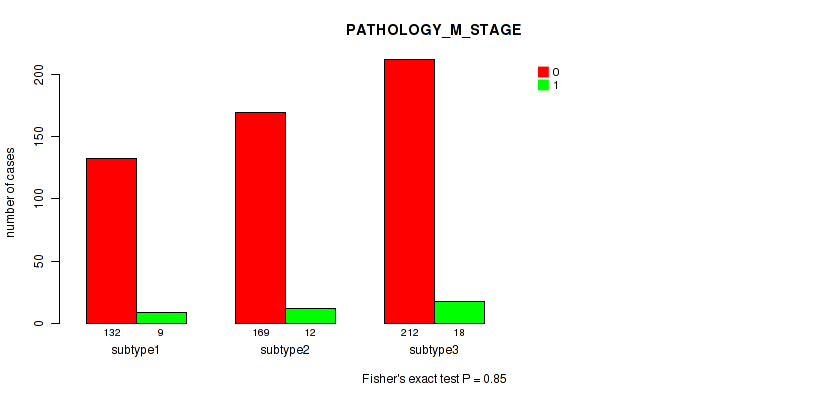
P value = 2e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 8.6e-05
Table S8. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 182 | 427 |
| subtype1 | 45 | 118 |
| subtype2 | 37 | 163 |
| subtype3 | 100 | 146 |
Figure S7. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'

P value = 0.00011 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.00041
Table S9. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA DIFFUSE TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA TUBULAR TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA MUCINOUS TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA PAPILLARY TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA SIGNET RING TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 71 | 162 | 81 | 78 | 21 | 8 | 13 |
| subtype1 | 6 | 42 | 30 | 32 | 5 | 5 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 34 | 18 | 18 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 50 | 86 | 33 | 28 | 13 | 3 | 9 |
Figure S8. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
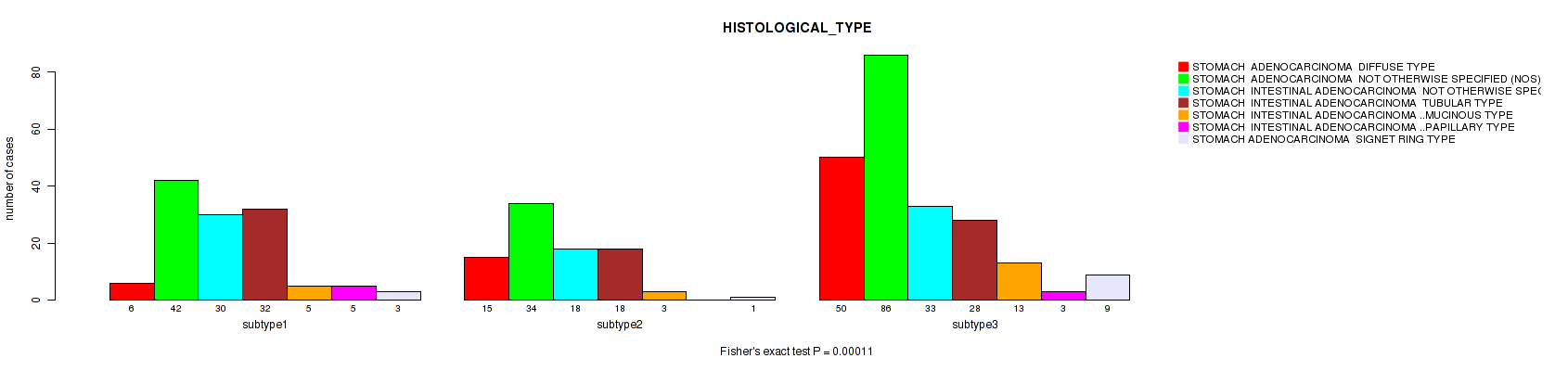
P value = 1 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 1
Table S10. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 603 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 162 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 198 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 243 |
Figure S9. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'

P value = 0.172 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.26
Table S11. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 92 | 35.2 (21.9) |
| subtype1 | 22 | 39.0 (25.1) |
| subtype2 | 57 | 31.9 (20.0) |
| subtype3 | 13 | 43.0 (22.6) |
Figure S10. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'

P value = 0.691 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.77
Table S12. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 347 | 18 | 19 | 25 |
| subtype1 | 95 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 73 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 179 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
Figure S11. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'

P value = 0.0381 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.072
Table S13. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 387 | 5.7 (8.4) |
| subtype1 | 106 | 6.2 (9.9) |
| subtype2 | 79 | 7.3 (9.6) |
| subtype3 | 202 | 4.8 (6.9) |
Figure S12. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
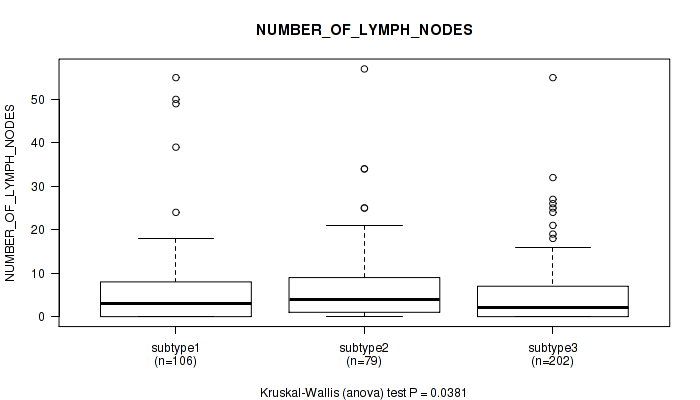
P value = 0.00302 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0077
Table S14. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | NATIVE HAWAIIAN OR OTHER PACIFIC ISLANDER | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 129 | 13 | 1 | 385 |
| subtype1 | 22 | 5 | 1 | 107 |
| subtype2 | 60 | 3 | 0 | 113 |
| subtype3 | 47 | 5 | 0 | 165 |
Figure S13. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'

P value = 0.705 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.77
Table S15. Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 394 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 99 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 121 |
| subtype3 | 4 | 174 |
Figure S14. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #1: 'Copy Number Ratio CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
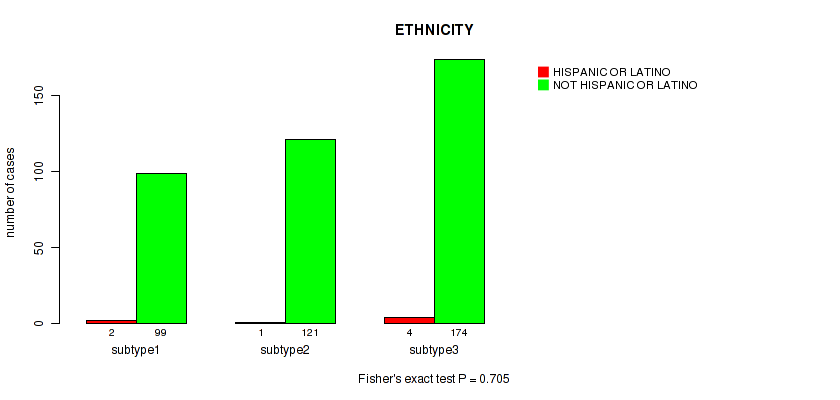
Table S16. Description of clustering approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 244 | 149 | 171 |
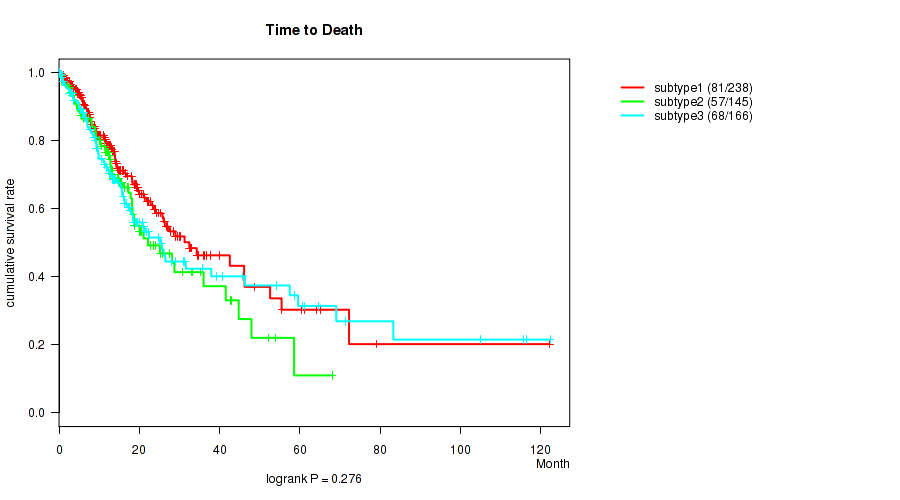
P value = 0.276 (logrank test), Q value = 0.38
Table S17. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 549 | 206 | 0.1 - 122.3 (12.8) |
| subtype1 | 238 | 81 | 0.1 - 122.1 (13.3) |
| subtype2 | 145 | 57 | 0.1 - 68.0 (12.6) |
| subtype3 | 166 | 68 | 0.1 - 122.3 (12.5) |
Figure S15. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
P value = 8.72e-05 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.00034
Table S18. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
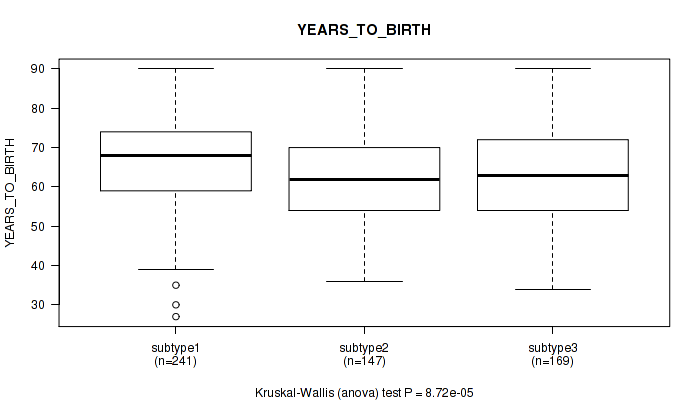
| ALL | 557 | 64.4 (11.2) |
| subtype1 | 241 | 66.4 (10.9) |
| subtype2 | 147 | 62.3 (11.0) |
| subtype3 | 169 | 63.2 (11.3) |
Figure S16. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
P value = 0.00109 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0031
Table S19. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE II | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 11 | 18 | 42 | 29 | 78 | 83 | 29 | 91 | 71 | 47 | 40 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 9 | 10 | 18 | 11 | 24 | 43 | 12 | 35 | 35 | 21 | 13 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 31 | 21 | 15 | 21 | 14 | 9 | 8 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 4 | 14 | 10 | 23 | 19 | 2 | 35 | 22 | 17 | 19 | 2 |
Figure S17. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'

P value = 0.00424 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.011
Table S20. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| nPatients | T0+T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 51 | 111 | 271 | 115 |
| subtype1 | 32 | 39 | 115 | 48 |
| subtype2 | 12 | 38 | 74 | 22 |
| subtype3 | 7 | 34 | 82 | 45 |
Figure S18. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'

P value = 0.0999 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.17
Table S21. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| nPatients | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
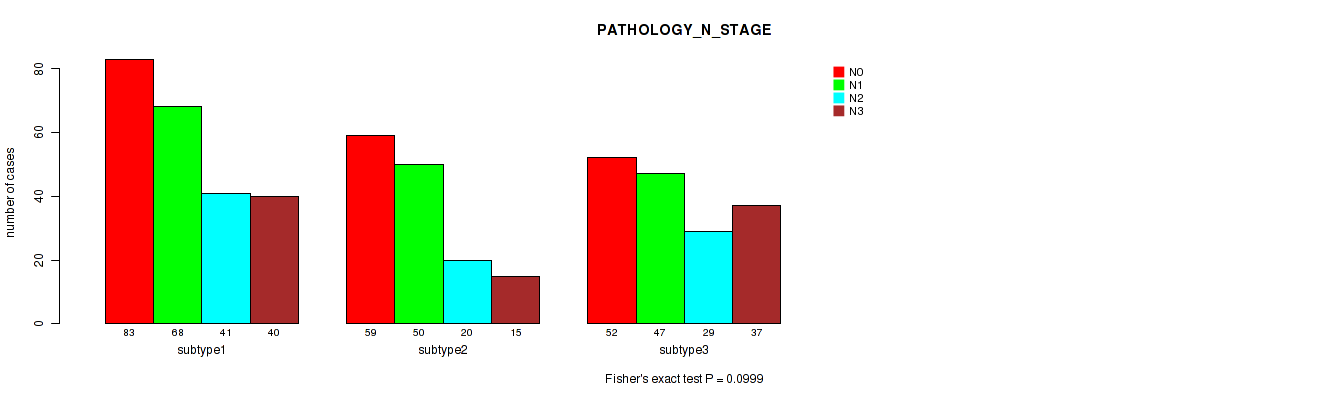
| ALL | 194 | 165 | 90 | 92 |
| subtype1 | 83 | 68 | 41 | 40 |
| subtype2 | 59 | 50 | 20 | 15 |
| subtype3 | 52 | 47 | 29 | 37 |
Figure S19. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
P value = 0.0411 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.076
Table S22. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
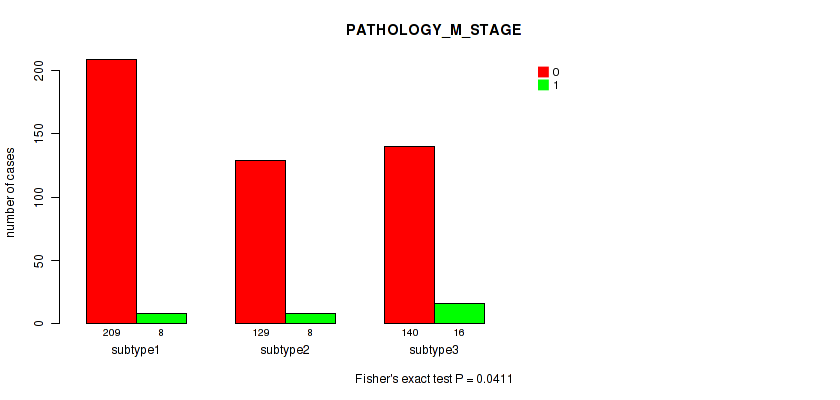
| ALL | 478 | 32 |
| subtype1 | 209 | 8 |
| subtype2 | 129 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 140 | 16 |
Figure S20. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
P value = 0.896 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.9
Table S23. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 160 | 404 |
| subtype1 | 70 | 174 |
| subtype2 | 40 | 109 |
| subtype3 | 50 | 121 |
Figure S21. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
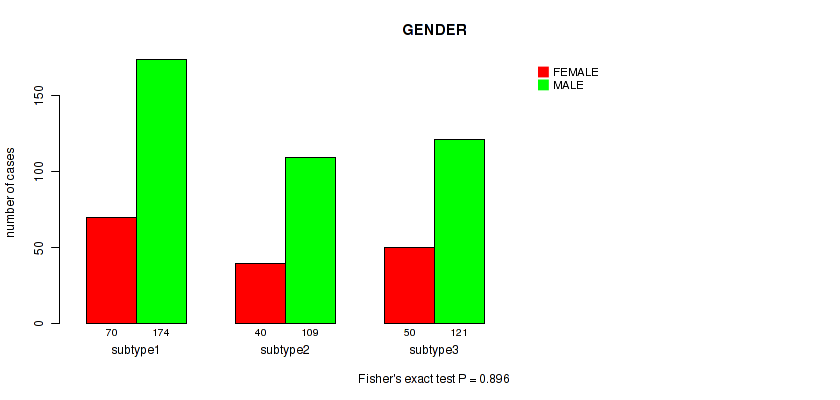
P value = 2e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 8.6e-05
Table S24. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA DIFFUSE TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA TUBULAR TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA MUCINOUS TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA PAPILLARY TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA SIGNET RING TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 66 | 134 | 72 | 77 | 20 | 8 | 13 |
| subtype1 | 23 | 63 | 35 | 44 | 10 | 3 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 24 | 14 | 19 | 0 | 3 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 41 | 47 | 23 | 14 | 10 | 2 | 8 |
Figure S22. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'

P value = 0.586 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.66
Table S25. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 558 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 242 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 148 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 168 |
Figure S23. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'

P value = 0.15 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.24
Table S26. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 92 | 35.2 (21.9) |
| subtype1 | 31 | 41.1 (25.2) |
| subtype2 | 49 | 30.8 (18.6) |
| subtype3 | 12 | 37.7 (23.1) |
Figure S24. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
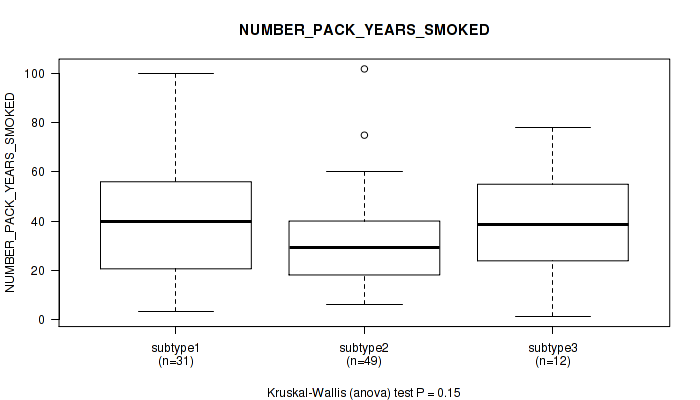
P value = 0.156 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.24
Table S27. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 333 | 17 | 12 |
| subtype1 | 163 | 4 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 51 | 3 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 119 | 10 | 5 |
Figure S25. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'

P value = 0.331 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.44
Table S28. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 353 | 5.6 (8.4) |
| subtype1 | 167 | 5.4 (8.9) |
| subtype2 | 56 | 4.8 (5.5) |
| subtype3 | 130 | 6.3 (8.9) |
Figure S26. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'

P value = 0.00506 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.012
Table S29. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | NATIVE HAWAIIAN OR OTHER PACIFIC ISLANDER | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 130 | 14 | 1 | 360 |
| subtype1 | 44 | 6 | 1 | 163 |
| subtype2 | 52 | 4 | 0 | 80 |
| subtype3 | 34 | 4 | 0 | 117 |
Figure S27. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'

P value = 0.894 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.9
Table S30. Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 371 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 150 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 97 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 124 |
Figure S28. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #2: 'METHLYATION CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'

Table S31. Description of clustering approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 235 | 121 | 92 |
P value = 0.139 (logrank test), Q value = 0.23
Table S32. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 414 | 144 | 0.0 - 122.1 (12.8) |
| subtype1 | 211 | 64 | 0.0 - 122.1 (12.9) |
| subtype2 | 119 | 46 | 0.1 - 105.1 (12.4) |
| subtype3 | 84 | 34 | 0.1 - 83.2 (13.0) |
Figure S29. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'

P value = 3.93e-08 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1.5e-06
Table S33. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 441 | 64.5 (11.4) |
| subtype1 | 228 | 67.5 (10.7) |
| subtype2 | 121 | 60.3 (11.6) |
| subtype3 | 92 | 62.7 (10.9) |
Figure S30. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
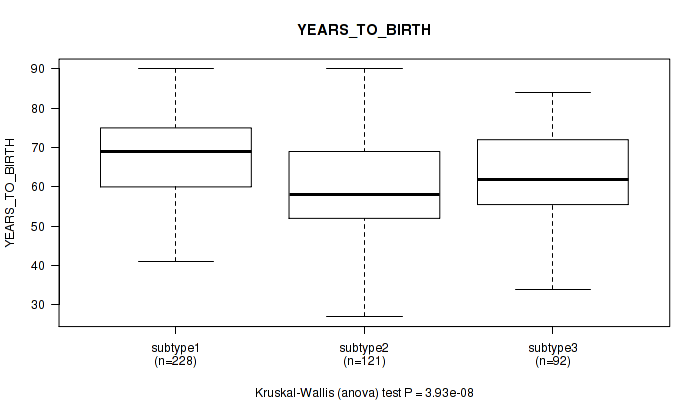
P value = 2e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 8.6e-05
Table S34. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE II | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 10 | 15 | 34 | 24 | 68 | 73 | 29 | 54 | 41 | 30 | 30 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 8 | 10 | 22 | 14 | 24 | 41 | 13 | 31 | 16 | 14 | 20 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 33 | 19 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 13 | 3 | 13 | 16 | 13 | 6 | 0 |
Figure S31. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'

P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S35. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| nPatients | T0+T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 44 | 106 | 193 | 80 |
| subtype1 | 31 | 56 | 88 | 46 |
| subtype2 | 13 | 37 | 57 | 6 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 13 | 48 | 28 |
Figure S32. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'

P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S36. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| nPatients | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 162 | 141 | 58 | 57 |
| subtype1 | 79 | 79 | 38 | 25 |
| subtype2 | 58 | 38 | 11 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 25 | 24 | 9 | 27 |
Figure S33. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
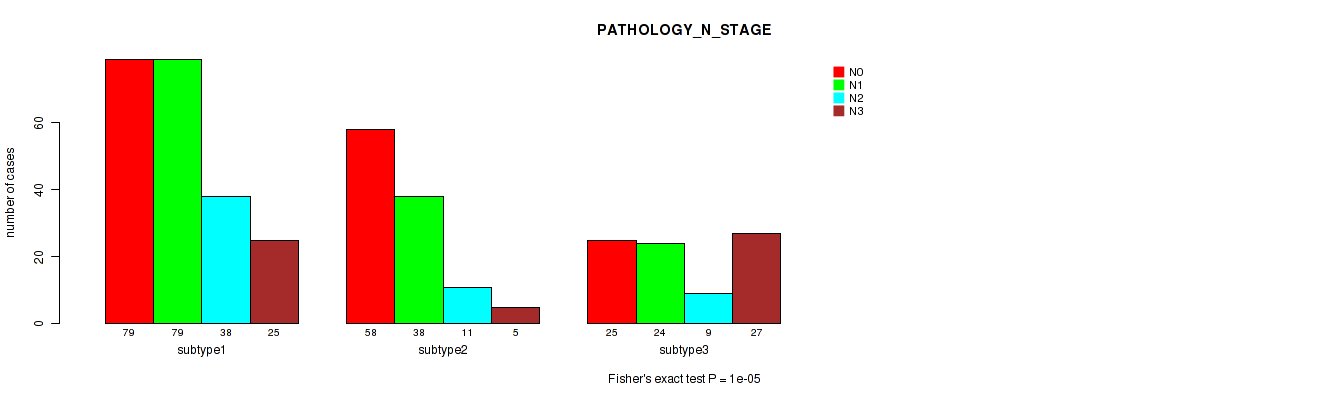
P value = 0.542 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.65
Table S37. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 370 | 27 |
| subtype1 | 190 | 17 |
| subtype2 | 97 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 83 | 5 |
Figure S34. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'

P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S38. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 127 | 321 |
| subtype1 | 76 | 159 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 106 |
| subtype3 | 36 | 56 |
Figure S35. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'

P value = 0.0209 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.043
Table S39. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA DIFFUSE TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA TUBULAR TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA MUCINOUS TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA PAPILLARY TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA SIGNET RING TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 51 | 131 | 34 | 36 | 14 | 5 | 1 |
| subtype1 | 26 | 80 | 25 | 31 | 8 | 5 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 23 | 41 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 0 | 1 |
Figure S36. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'

P value = 0.0867 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.15
Table S40. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 442 |
| subtype1 | 6 | 229 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 121 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 92 |
Figure S37. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
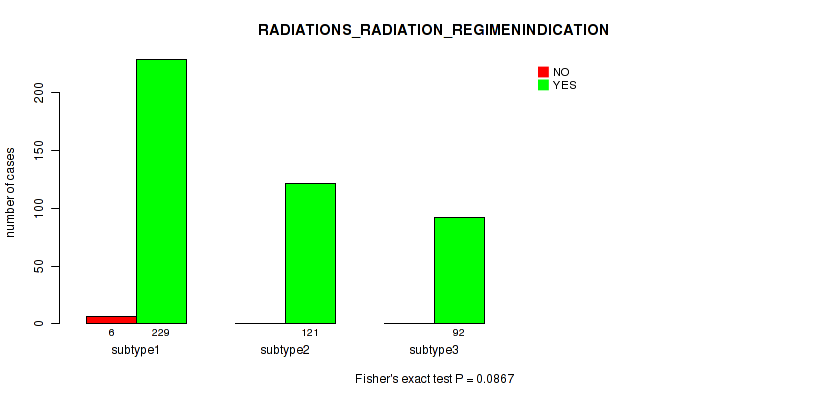
P value = 0.353 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.46
Table S41. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 92 | 35.2 (21.9) |
| subtype1 | 23 | 41.6 (26.0) |
| subtype2 | 66 | 33.2 (19.9) |
| subtype3 | 3 | 29.5 (28.9) |
Figure S38. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
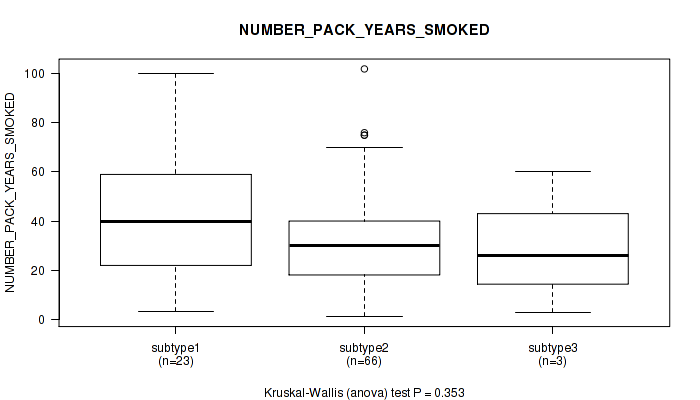
P value = 0.233 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.33
Table S42. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 217 | 9 | 10 | 22 |
| subtype1 | 140 | 6 | 9 | 13 |
| subtype2 | 13 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 64 | 3 | 0 | 9 |
Figure S39. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
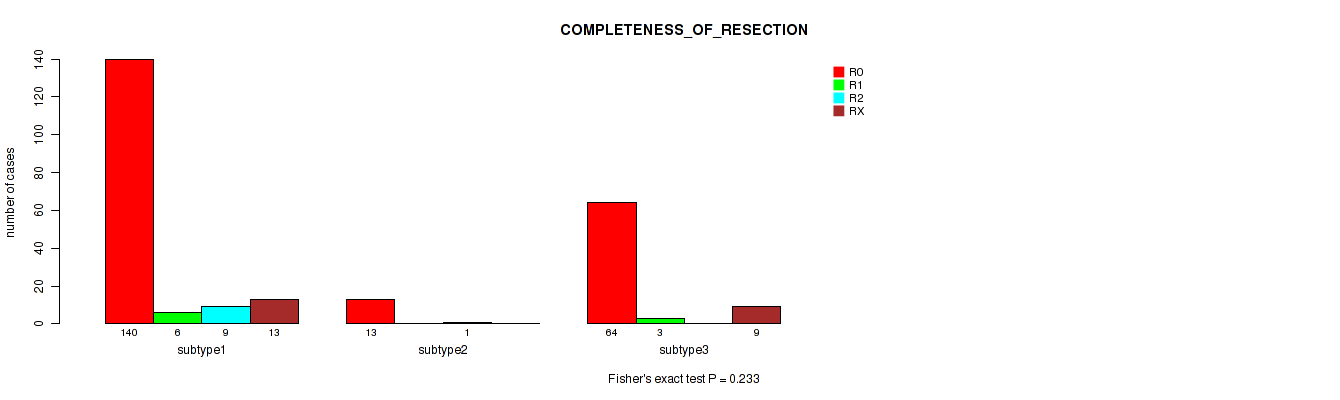
P value = 0.139 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.23
Table S43. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 238 | 4.8 (7.1) |
| subtype1 | 153 | 4.7 (7.5) |
| subtype2 | 14 | 4.5 (8.9) |
| subtype3 | 71 | 5.3 (5.6) |
Figure S40. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'

P value = 0.0275 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.055
Table S44. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 114 | 6 | 267 |
| subtype1 | 49 | 3 | 136 |
| subtype2 | 43 | 3 | 63 |
| subtype3 | 22 | 0 | 68 |
Figure S41. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
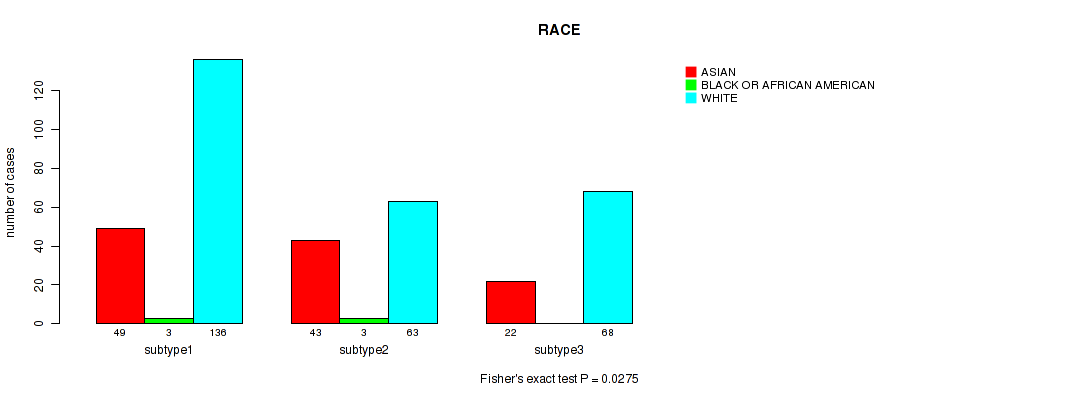
P value = 0.716 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.77
Table S45. Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 5 | 312 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 156 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 73 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 83 |
Figure S42. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #3: 'RNAseq CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
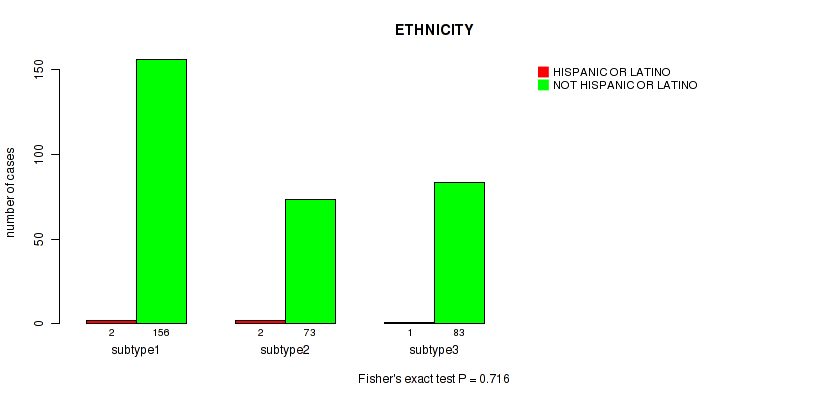
Table S46. Description of clustering approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 76 | 150 | 25 | 80 | 117 |
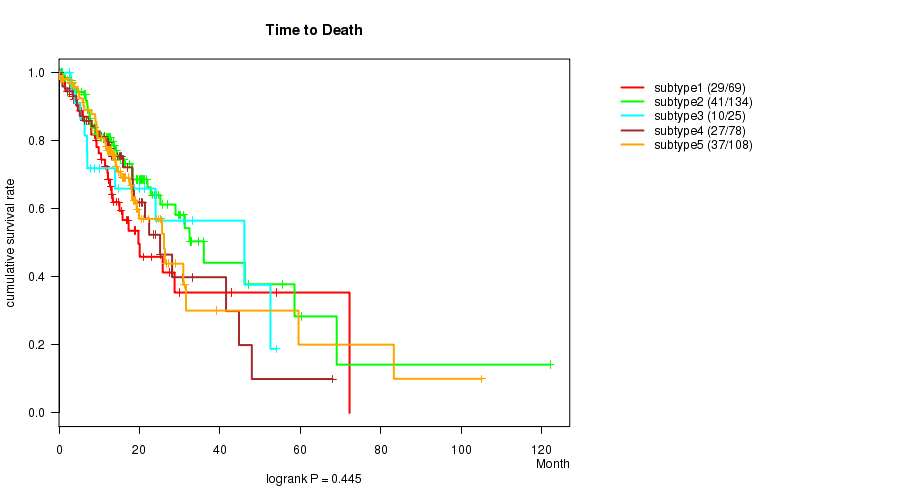
P value = 0.445 (logrank test), Q value = 0.56
Table S47. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 414 | 144 | 0.0 - 122.1 (12.8) |
| subtype1 | 69 | 29 | 0.1 - 72.2 (12.2) |
| subtype2 | 134 | 41 | 0.1 - 122.1 (12.9) |
| subtype3 | 25 | 10 | 0.4 - 54.0 (10.2) |
| subtype4 | 78 | 27 | 0.1 - 68.0 (12.5) |
| subtype5 | 108 | 37 | 0.0 - 105.1 (13.2) |
Figure S43. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
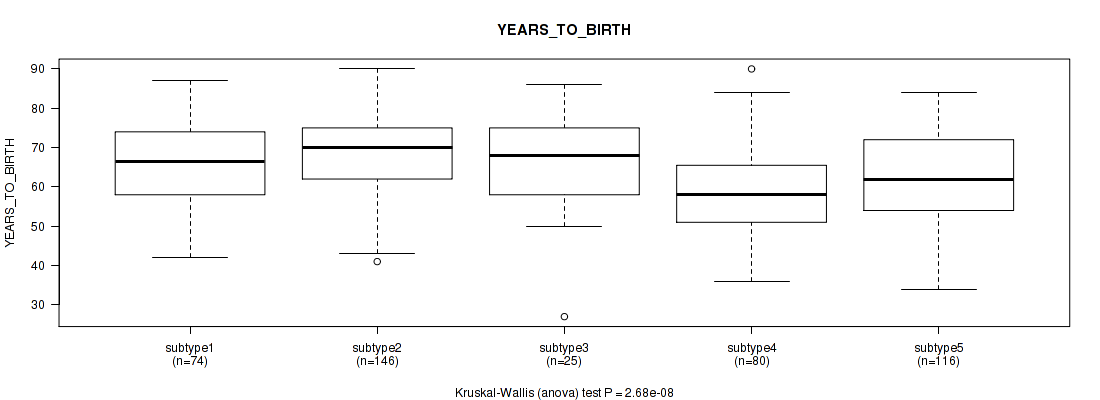
P value = 2.68e-08 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1.5e-06
Table S48. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 441 | 64.5 (11.4) |
| subtype1 | 74 | 65.9 (10.3) |
| subtype2 | 146 | 68.3 (10.7) |
| subtype3 | 25 | 65.2 (12.9) |
| subtype4 | 80 | 59.0 (10.7) |
| subtype5 | 116 | 62.6 (11.3) |
Figure S44. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
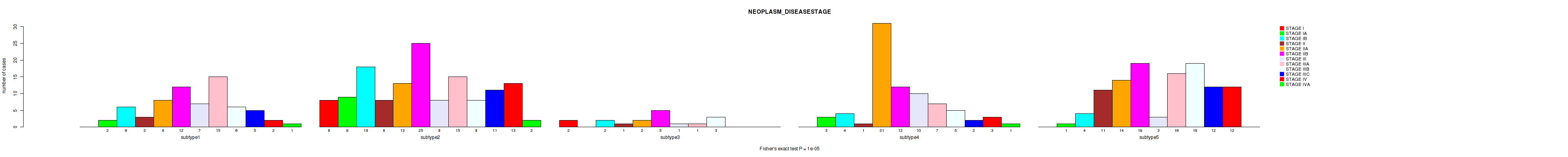
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S49. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE II | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 10 | 15 | 34 | 24 | 68 | 73 | 29 | 54 | 41 | 30 | 30 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 12 | 7 | 15 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 8 | 9 | 18 | 8 | 13 | 25 | 8 | 15 | 8 | 11 | 13 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 31 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 11 | 14 | 19 | 3 | 16 | 19 | 12 | 12 | 0 |
Figure S45. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S50. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| nPatients | T0+T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 44 | 106 | 193 | 80 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 19 | 37 | 12 |
| subtype2 | 28 | 40 | 44 | 29 |
| subtype3 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 7 | 24 | 44 | 4 |
| subtype5 | 1 | 18 | 59 | 35 |
Figure S46. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
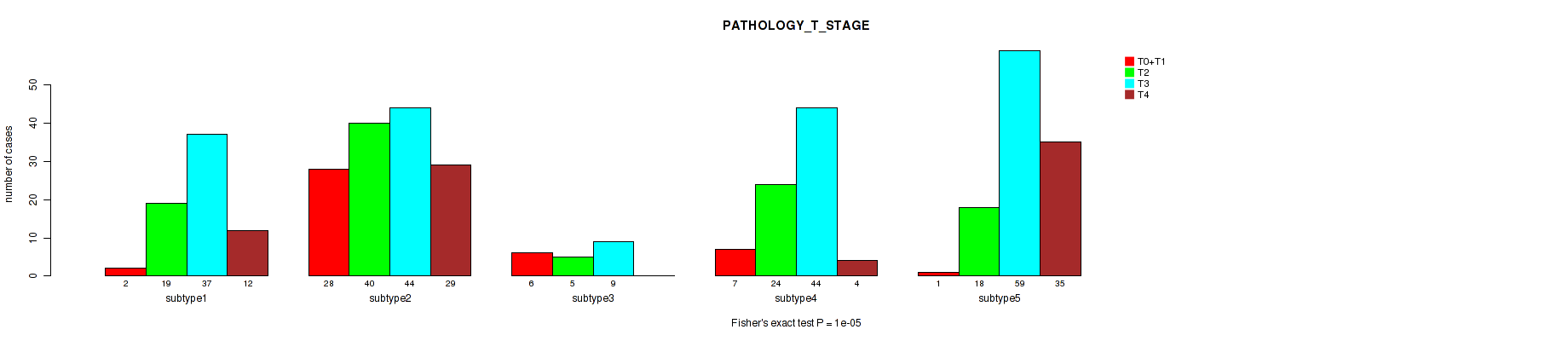
P value = 0.00027 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.00092
Table S51. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| nPatients | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 162 | 141 | 58 | 57 |
| subtype1 | 22 | 24 | 12 | 10 |
| subtype2 | 56 | 43 | 25 | 17 |
| subtype3 | 7 | 10 | 3 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 45 | 24 | 6 | 3 |
| subtype5 | 32 | 40 | 12 | 27 |
Figure S47. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'

P value = 0.513 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.63
Table S52. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 370 | 27 |
| subtype1 | 63 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 120 | 12 |
| subtype3 | 14 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 69 | 4 |
| subtype5 | 104 | 9 |
Figure S48. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
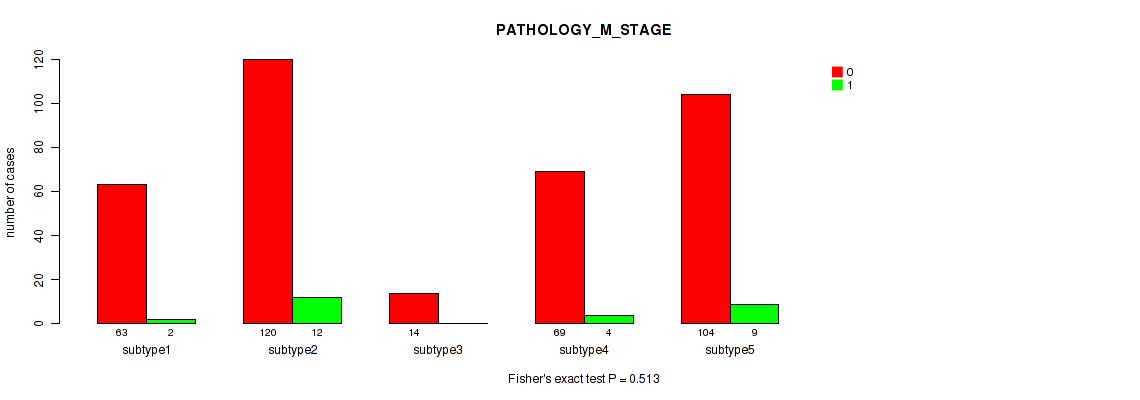
P value = 0.00143 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0039
Table S53. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 127 | 321 |
| subtype1 | 18 | 58 |
| subtype2 | 53 | 97 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 22 |
| subtype4 | 12 | 68 |
| subtype5 | 41 | 76 |
Figure S49. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
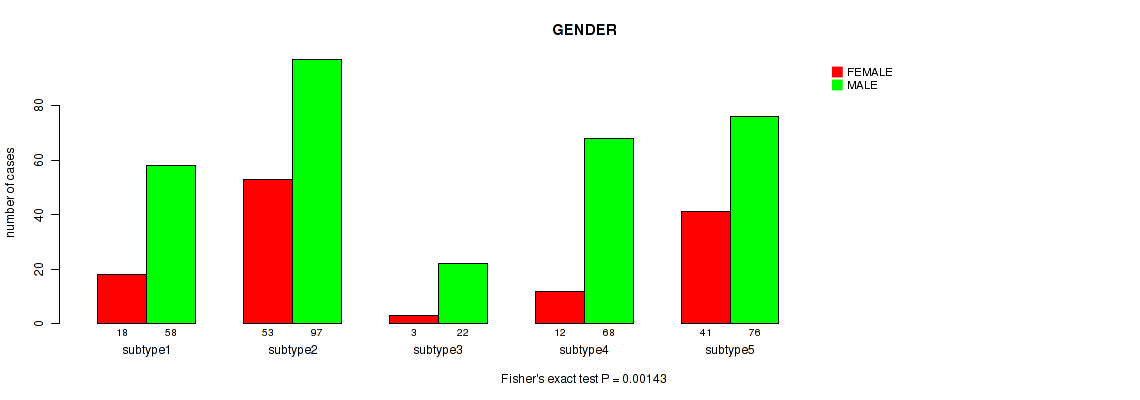
P value = 0.00084 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0026
Table S54. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA DIFFUSE TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA TUBULAR TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA MUCINOUS TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA PAPILLARY TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA SIGNET RING TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 51 | 131 | 34 | 36 | 14 | 5 | 1 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 32 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 15 | 51 | 16 | 21 | 5 | 2 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 32 | 46 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 1 | 1 |
Figure S50. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
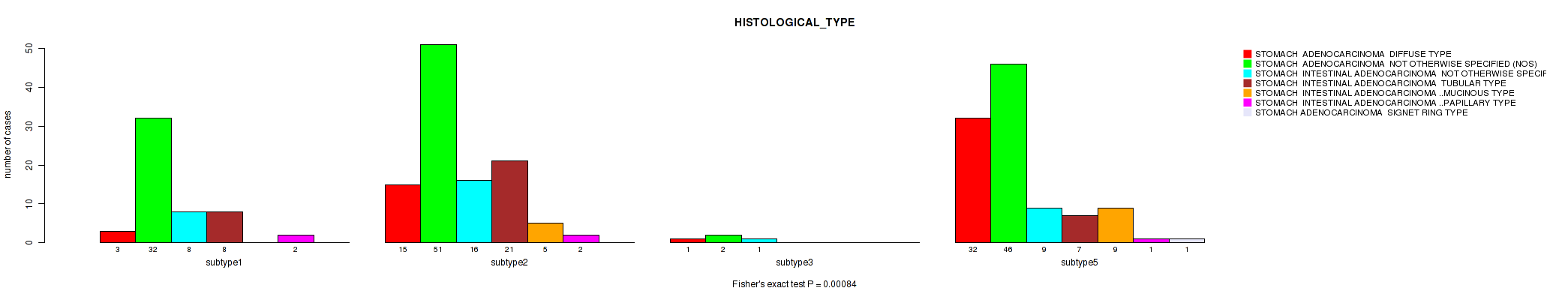
P value = 0.18 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.27
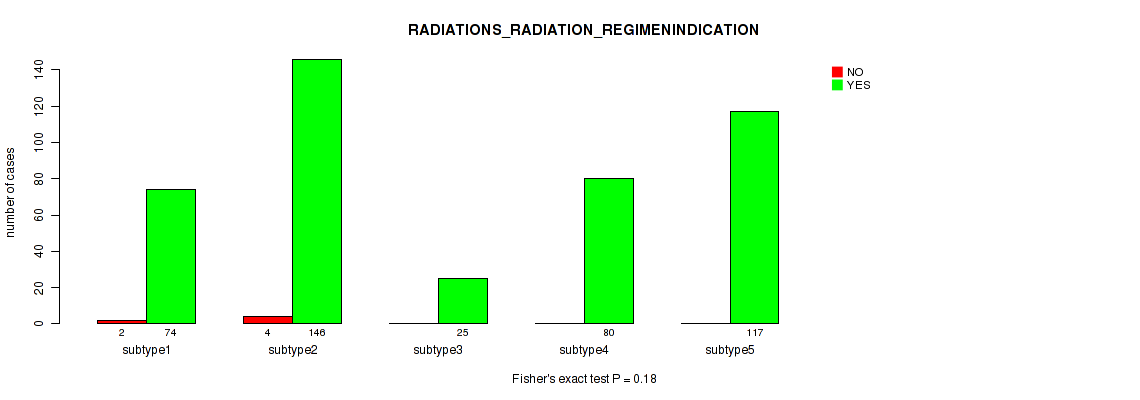
Table S55. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 442 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 74 |
| subtype2 | 4 | 146 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 25 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 80 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 117 |
Figure S51. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
P value = 0.256 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.36
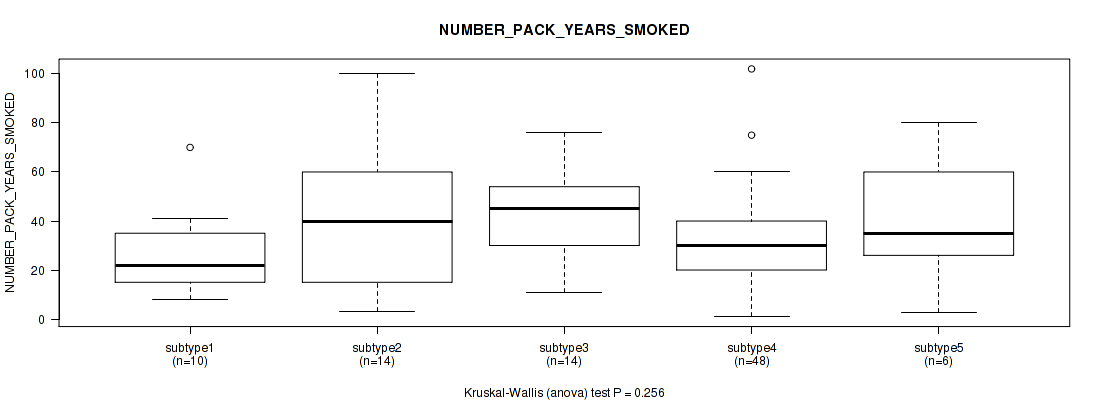
Table S56. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 92 | 35.2 (21.9) |
| subtype1 | 10 | 27.4 (18.6) |
| subtype2 | 14 | 41.1 (28.5) |
| subtype3 | 14 | 43.8 (21.9) |
| subtype4 | 48 | 31.9 (19.1) |
| subtype5 | 6 | 39.8 (27.2) |
Figure S52. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
P value = 0.867 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.9
Table S57. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 217 | 9 | 10 | 22 |
| subtype1 | 44 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 87 | 4 | 7 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 82 | 3 | 2 | 10 |
Figure S53. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
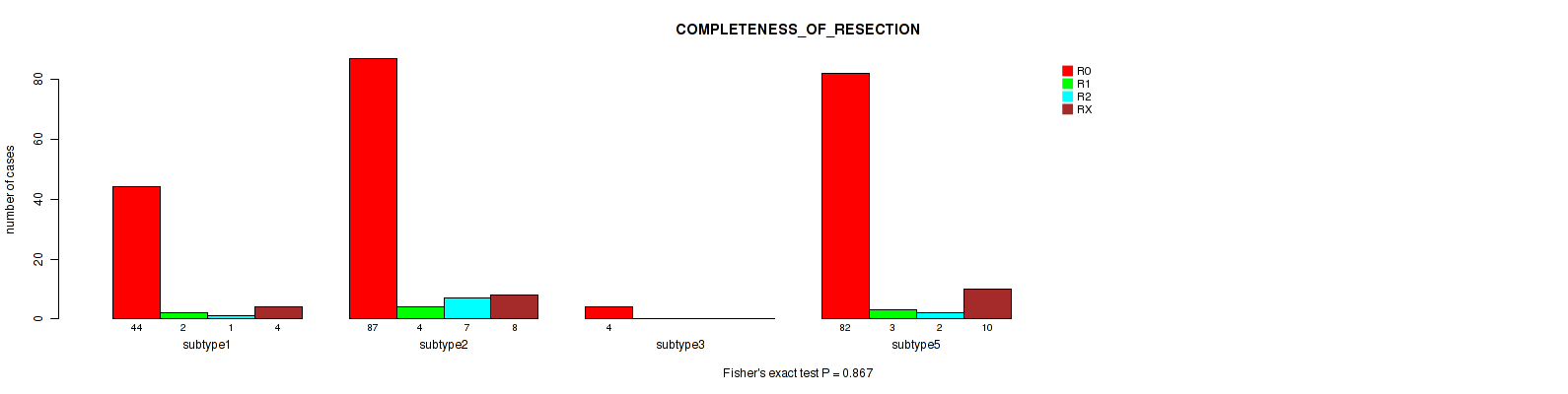
P value = 0.219 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.32
Table S58. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 238 | 4.8 (7.1) |
| subtype1 | 46 | 4.6 (6.4) |
| subtype2 | 99 | 4.3 (6.5) |
| subtype3 | 4 | 1.8 (1.3) |
| subtype5 | 89 | 5.7 (8.0) |
Figure S54. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
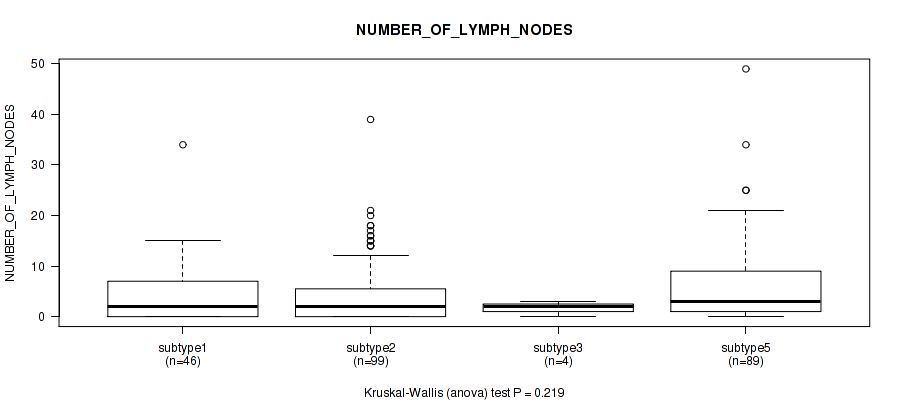
P value = 3e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.00012
Table S59. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 114 | 6 | 267 |
| subtype1 | 14 | 1 | 49 |
| subtype2 | 31 | 3 | 82 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| subtype4 | 38 | 2 | 37 |
| subtype5 | 31 | 0 | 79 |
Figure S55. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
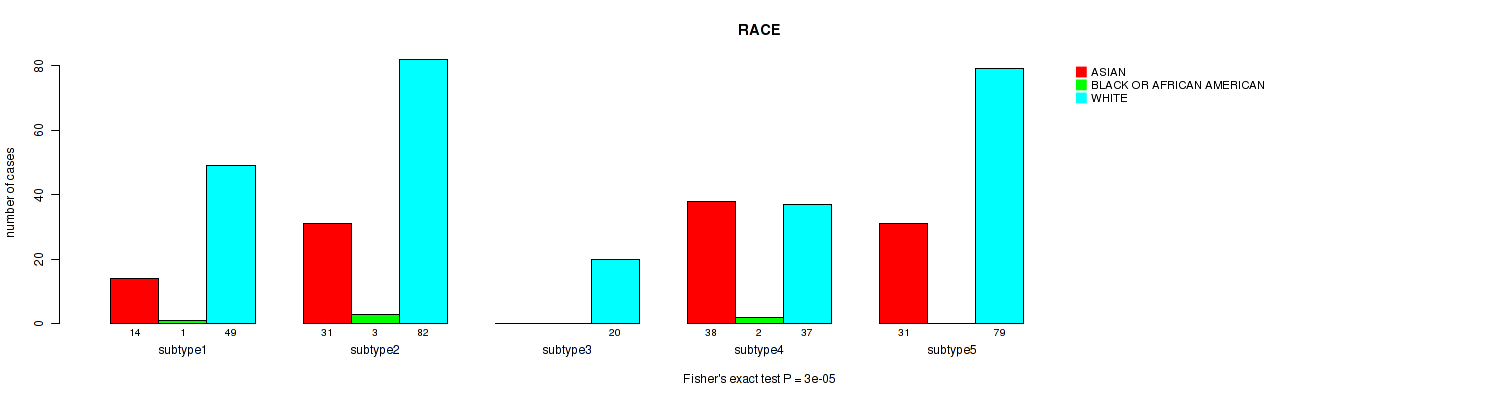
P value = 0.159 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.24
Table S60. Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 5 | 312 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 53 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 93 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 11 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 55 |
| subtype5 | 1 | 100 |
Figure S56. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #4: 'RNAseq cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
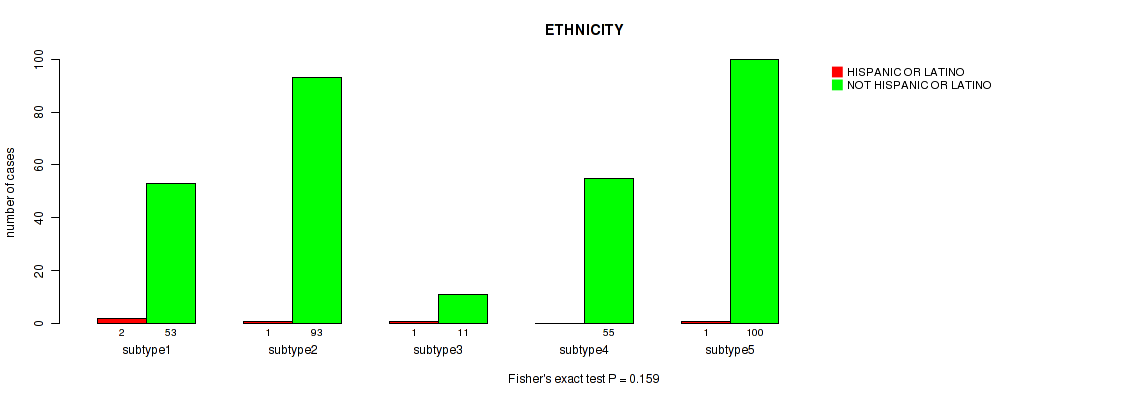
Table S61. Description of clustering approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 154 | 326 | 130 |
P value = 0.0803 (logrank test), Q value = 0.14
Table S62. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 576 | 221 | 0.0 - 122.3 (12.8) |
| subtype1 | 151 | 65 | 0.1 - 68.0 (12.4) |
| subtype2 | 299 | 111 | 0.0 - 122.3 (13.9) |
| subtype3 | 126 | 45 | 0.1 - 116.4 (11.2) |
Figure S57. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'

P value = 1.52e-06 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 3.4e-05
Table S63. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 603 | 64.8 (11.2) |
| subtype1 | 154 | 61.2 (11.1) |
| subtype2 | 319 | 66.8 (10.6) |
| subtype3 | 130 | 64.2 (11.9) |
Figure S58. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'

P value = 2e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 8.6e-05
Table S64. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE II | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 11 | 19 | 48 | 33 | 77 | 84 | 30 | 97 | 72 | 48 | 50 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 5 | 12 | 3 | 36 | 19 | 16 | 19 | 14 | 6 | 11 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 11 | 12 | 27 | 21 | 28 | 45 | 13 | 51 | 39 | 29 | 26 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 9 | 13 | 20 | 1 | 27 | 19 | 13 | 13 | 0 |
Figure S59. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
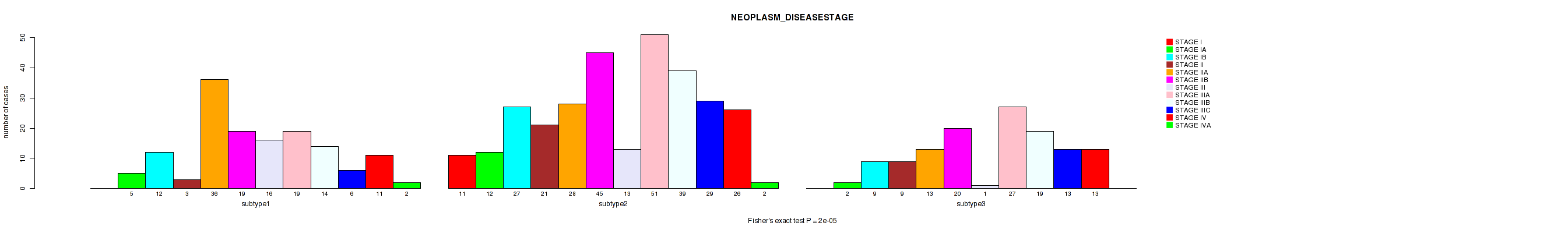
P value = 0.00226 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0059
Table S65. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| nPatients | T0+T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 53 | 126 | 281 | 124 |
| subtype1 | 13 | 38 | 78 | 17 |
| subtype2 | 35 | 66 | 139 | 71 |
| subtype3 | 5 | 22 | 64 | 36 |
Figure S60. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
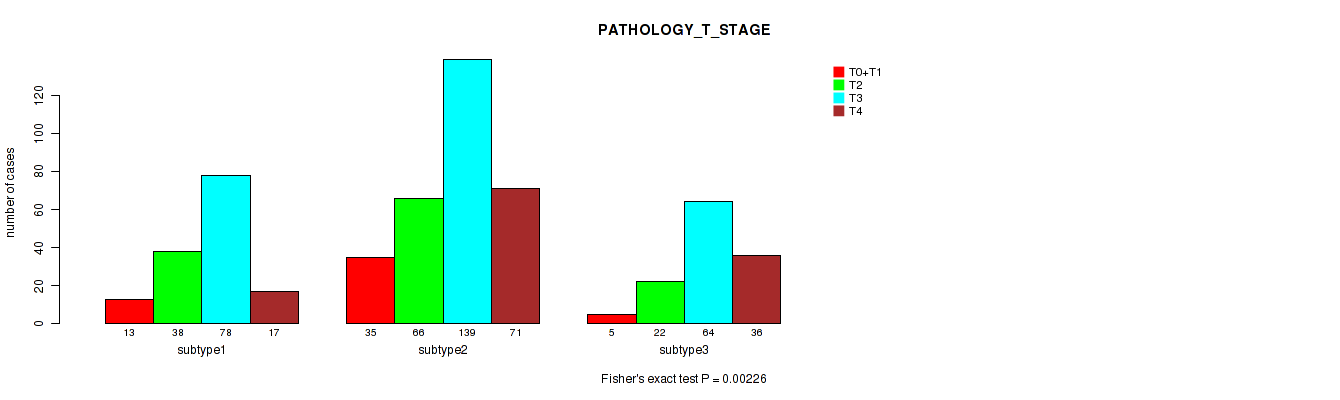
P value = 0.00681 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.016
Table S66. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| nPatients | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 201 | 183 | 96 | 96 |
| subtype1 | 62 | 52 | 16 | 14 |
| subtype2 | 102 | 92 | 60 | 52 |
| subtype3 | 37 | 39 | 20 | 30 |
Figure S61. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
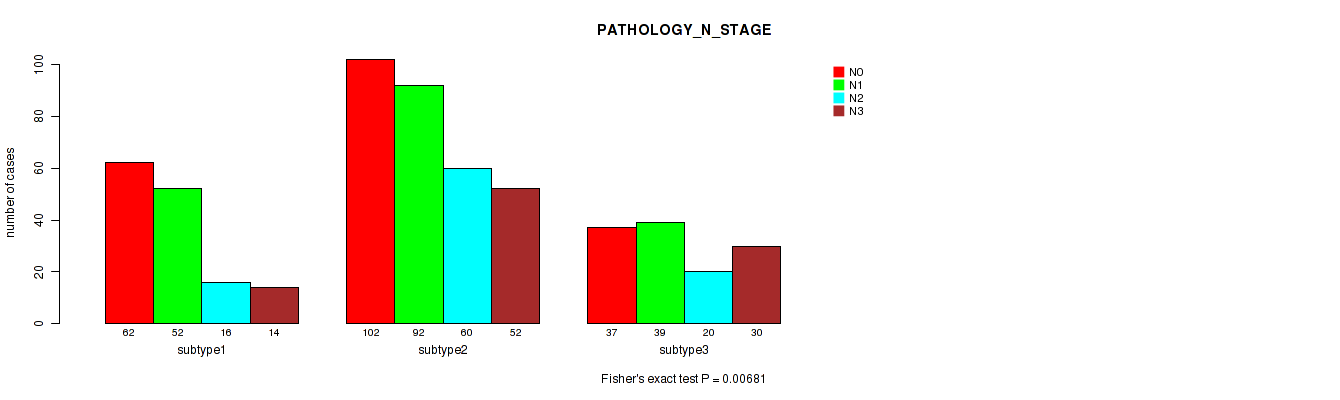
P value = 0.588 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.66
Table S67. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 514 | 39 |
| subtype1 | 125 | 11 |
| subtype2 | 278 | 18 |
| subtype3 | 111 | 10 |
Figure S62. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'

P value = 0.00033 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0011
Table S68. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 182 | 428 |
| subtype1 | 27 | 127 |
| subtype2 | 107 | 219 |
| subtype3 | 48 | 82 |
Figure S63. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
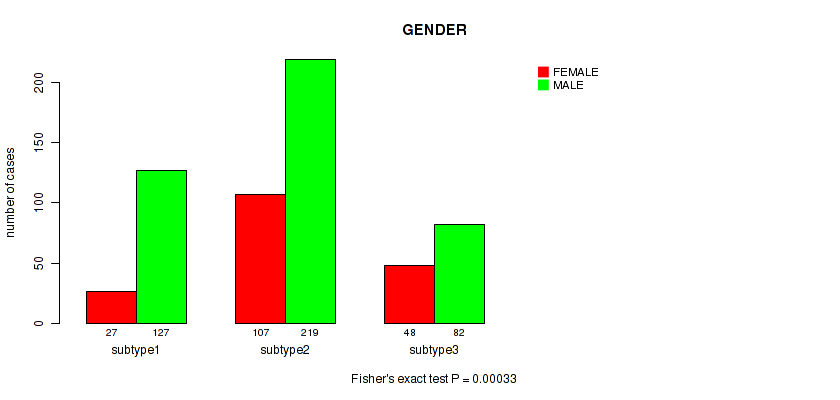
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S69. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA DIFFUSE TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA TUBULAR TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA MUCINOUS TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA PAPILLARY TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA SIGNET RING TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 71 | 163 | 80 | 78 | 22 | 8 | 13 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 18 | 9 | 15 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 31 | 103 | 58 | 55 | 11 | 4 | 10 |
| subtype3 | 35 | 42 | 13 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 2 |
Figure S64. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'

P value = 0.301 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.41
Table S70. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 604 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 154 |
| subtype2 | 5 | 321 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 129 |
Figure S65. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'

P value = 0.0814 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.14
Table S71. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 91 | 35.4 (21.9) |
| subtype1 | 60 | 31.3 (18.8) |
| subtype2 | 22 | 43.7 (25.7) |
| subtype3 | 9 | 42.3 (26.2) |
Figure S66. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'

P value = 0.57 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.66
Table S72. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 348 | 18 | 18 | 25 |
| subtype1 | 39 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 217 | 11 | 10 | 19 |
| subtype3 | 92 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
Figure S67. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
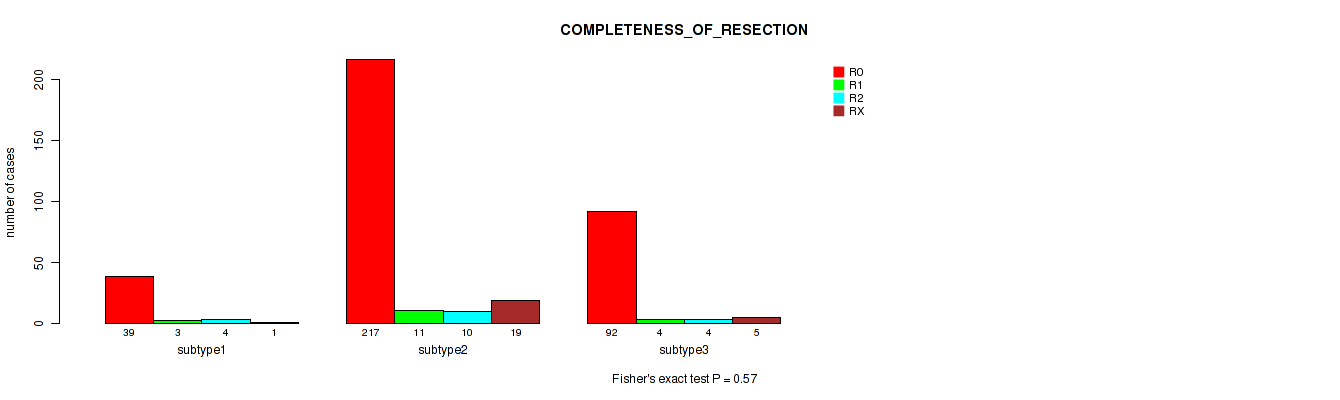
P value = 0.594 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.67
Table S73. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 387 | 5.5 (8.1) |
| subtype1 | 46 | 6.0 (9.5) |
| subtype2 | 240 | 5.4 (8.1) |
| subtype3 | 101 | 5.6 (7.3) |
Figure S68. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'

P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S74. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 129 | 14 | 385 |
| subtype1 | 56 | 4 | 77 |
| subtype2 | 46 | 10 | 213 |
| subtype3 | 27 | 0 | 95 |
Figure S69. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
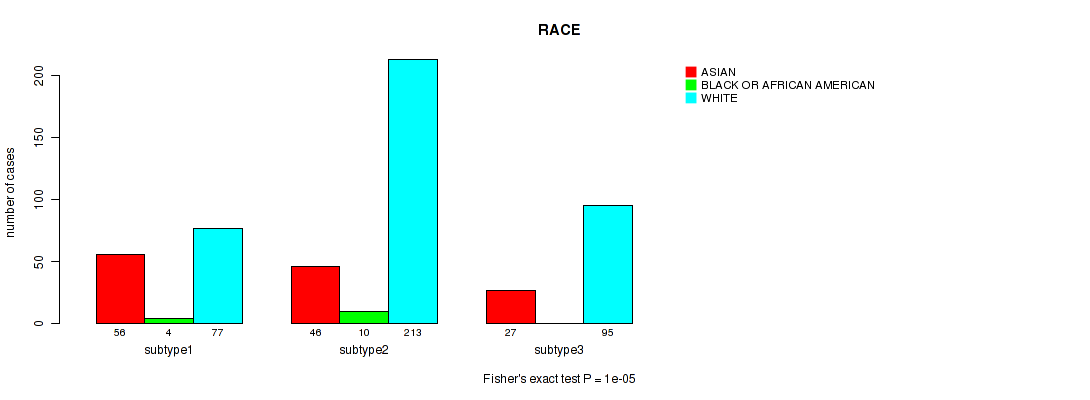
P value = 0.193 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.28
Table S75. Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 394 |
| subtype1 | 4 | 95 |
| subtype2 | 2 | 191 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 108 |
Figure S70. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #5: 'MIRSEQ CNMF' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
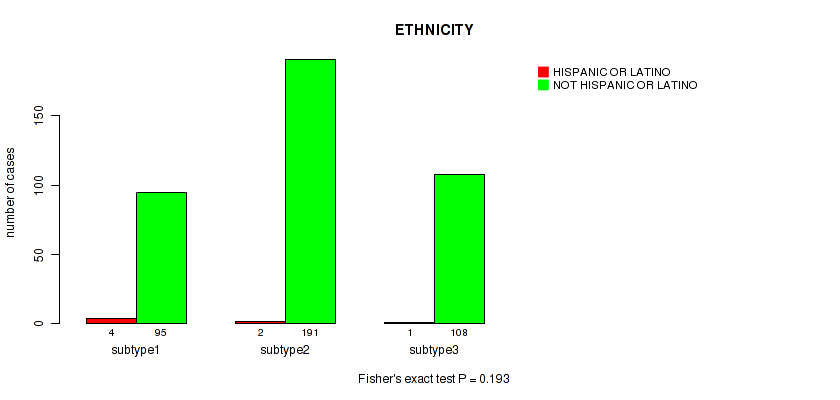
Table S76. Description of clustering approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 125 | 106 | 227 | 85 | 67 |
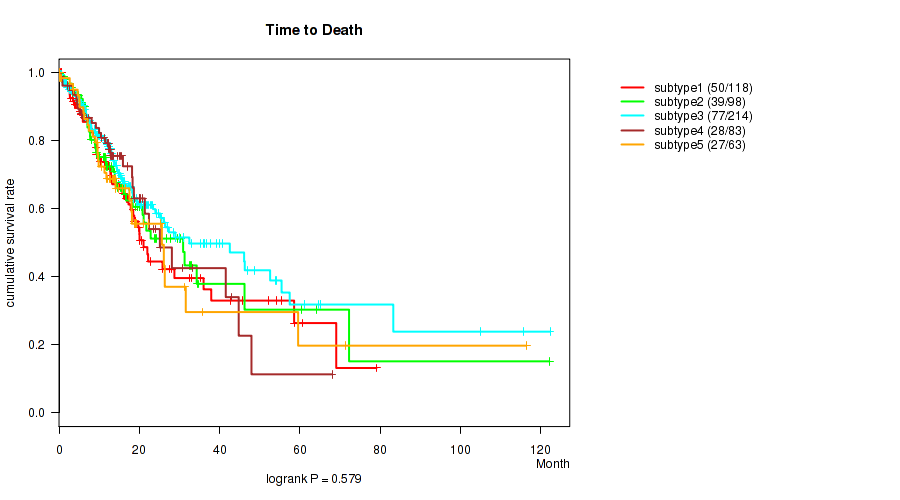
P value = 0.579 (logrank test), Q value = 0.66
Table S77. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 576 | 221 | 0.0 - 122.3 (12.8) |
| subtype1 | 118 | 50 | 0.1 - 79.1 (12.0) |
| subtype2 | 98 | 39 | 0.0 - 122.1 (12.3) |
| subtype3 | 214 | 77 | 0.1 - 122.3 (13.3) |
| subtype4 | 83 | 28 | 0.1 - 68.0 (12.6) |
| subtype5 | 63 | 27 | 0.1 - 116.4 (13.4) |
Figure S71. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
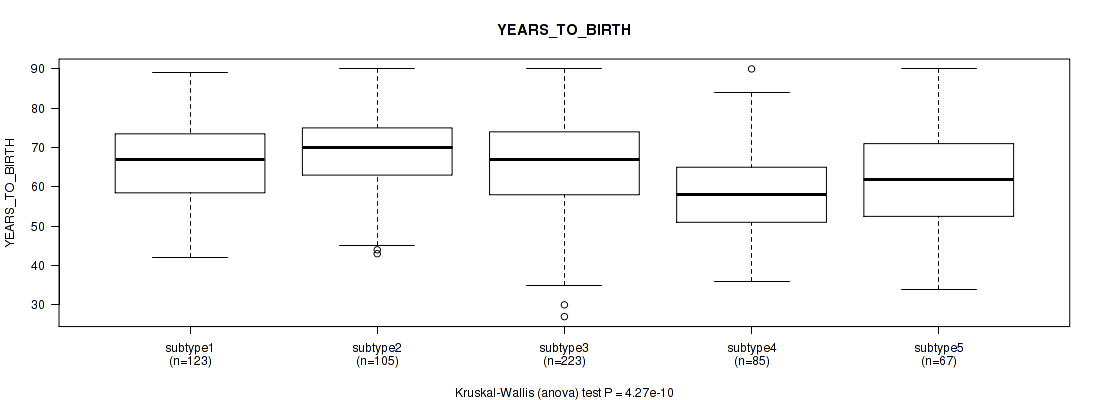
P value = 4.27e-10 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 4.8e-08
Table S78. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 603 | 64.8 (11.2) |
| subtype1 | 123 | 66.5 (10.0) |
| subtype2 | 105 | 68.6 (9.8) |
| subtype3 | 223 | 65.5 (11.5) |
| subtype4 | 85 | 58.6 (10.8) |
| subtype5 | 67 | 61.5 (11.4) |
Figure S72. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
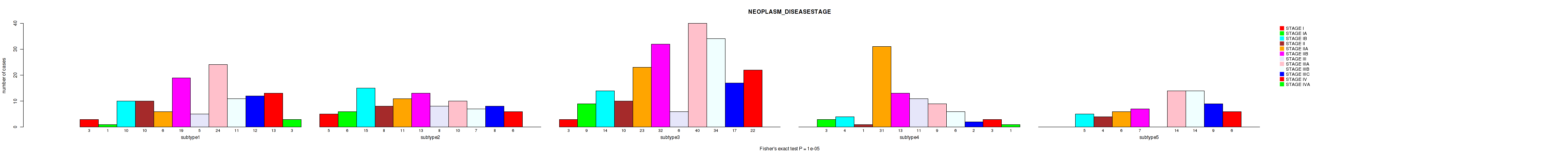
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S79. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE II | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 11 | 19 | 48 | 33 | 77 | 84 | 30 | 97 | 72 | 48 | 50 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 6 | 19 | 5 | 24 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 5 | 6 | 15 | 8 | 11 | 13 | 8 | 10 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 0 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 9 | 14 | 10 | 23 | 32 | 6 | 40 | 34 | 17 | 22 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 31 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 0 | 14 | 14 | 9 | 6 | 0 |
Figure S73. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S80. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| nPatients | T0+T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 53 | 126 | 281 | 124 |
| subtype1 | 7 | 28 | 57 | 28 |
| subtype2 | 17 | 28 | 40 | 15 |
| subtype3 | 22 | 36 | 106 | 51 |
| subtype4 | 7 | 24 | 48 | 5 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 10 | 30 | 25 |
Figure S74. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
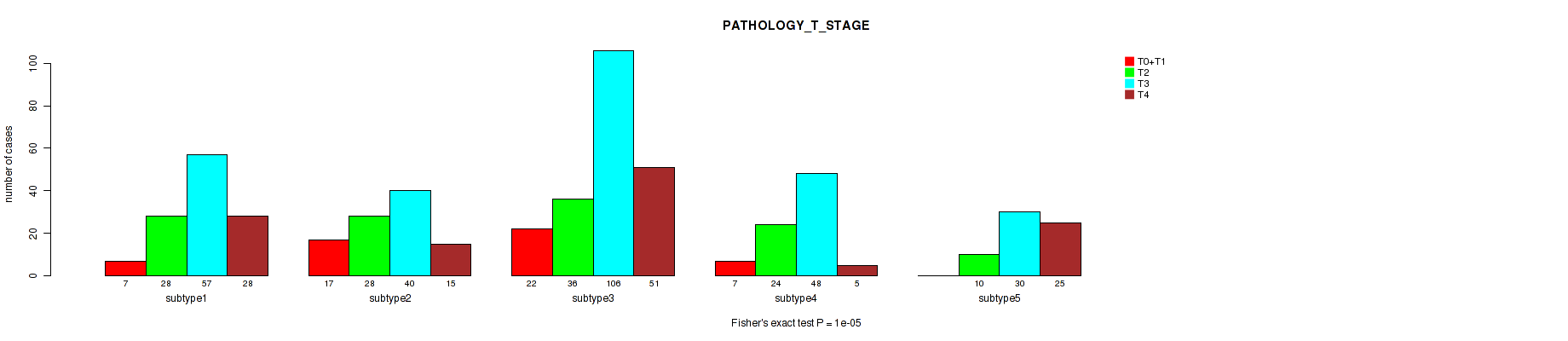
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S81. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| nPatients | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 201 | 183 | 96 | 96 |
| subtype1 | 30 | 41 | 25 | 21 |
| subtype2 | 42 | 28 | 12 | 15 |
| subtype3 | 65 | 68 | 45 | 38 |
| subtype4 | 47 | 27 | 6 | 3 |
| subtype5 | 17 | 19 | 8 | 19 |
Figure S75. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
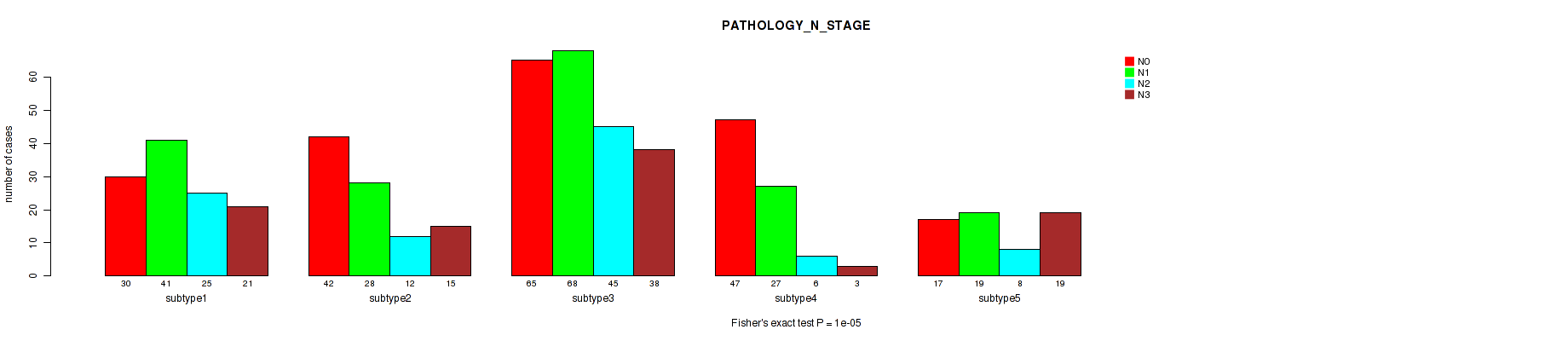
P value = 0.533 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.65
Table S82. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 514 | 39 |
| subtype1 | 100 | 12 |
| subtype2 | 91 | 5 |
| subtype3 | 191 | 15 |
| subtype4 | 74 | 4 |
| subtype5 | 58 | 3 |
Figure S76. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'

P value = 0.0162 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.035
Table S83. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 182 | 428 |
| subtype1 | 36 | 89 |
| subtype2 | 36 | 70 |
| subtype3 | 73 | 154 |
| subtype4 | 13 | 72 |
| subtype5 | 24 | 43 |
Figure S77. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
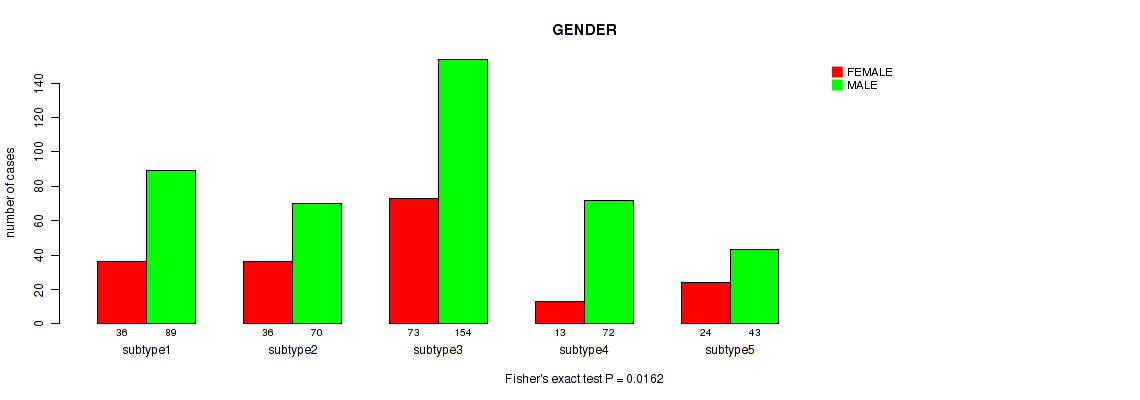
P value = 0.00018 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.00063
Table S84. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA DIFFUSE TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA TUBULAR TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA MUCINOUS TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA PAPILLARY TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA SIGNET RING TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 71 | 163 | 80 | 78 | 22 | 8 | 13 |
| subtype1 | 5 | 34 | 26 | 27 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 12 | 33 | 19 | 14 | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 33 | 70 | 32 | 31 | 8 | 3 | 6 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 21 | 24 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 2 |
Figure S78. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'

P value = 0.544 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.65
Table S85. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 6 | 604 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 123 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 106 |
| subtype3 | 4 | 223 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 85 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 67 |
Figure S79. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'

P value = 0.0124 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.027
Table S86. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 91 | 35.4 (21.9) |
| subtype1 | 8 | 46.5 (18.5) |
| subtype2 | 6 | 18.3 (17.2) |
| subtype3 | 26 | 41.7 (24.7) |
| subtype4 | 50 | 31.5 (18.9) |
| subtype5 | 1 | 80.0 (NA) |
Figure S80. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'

P value = 0.887 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.9
Table S87. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 | RX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 348 | 18 | 18 | 25 |
| subtype1 | 84 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| subtype2 | 62 | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 152 | 9 | 8 | 9 |
| subtype4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 48 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
Figure S81. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
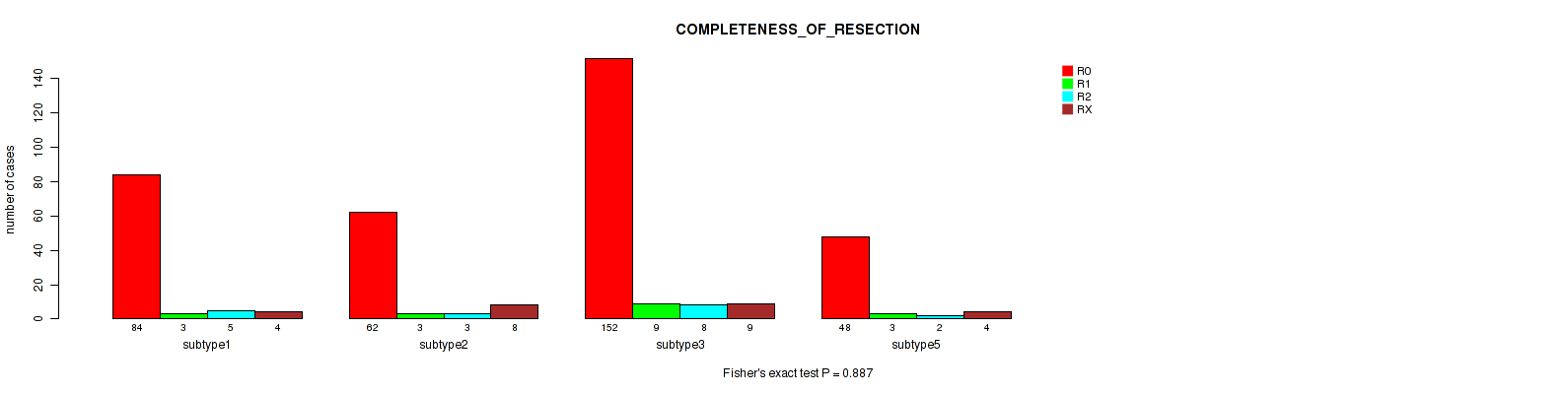
P value = 0.155 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.24
Table S88. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 387 | 5.5 (8.1) |
| subtype1 | 86 | 5.4 (6.2) |
| subtype2 | 71 | 5.3 (9.8) |
| subtype3 | 173 | 5.7 (8.2) |
| subtype4 | 2 | 0.5 (0.7) |
| subtype5 | 55 | 5.7 (8.1) |
Figure S82. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
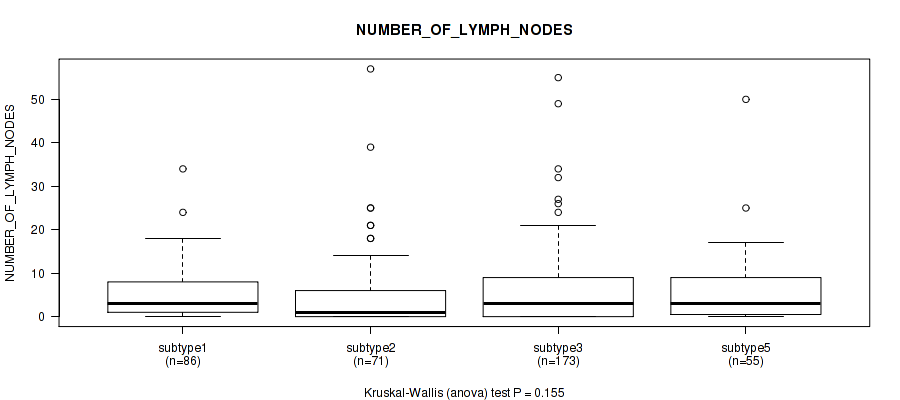
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S89. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 129 | 14 | 385 |
| subtype1 | 23 | 4 | 73 |
| subtype2 | 19 | 4 | 66 |
| subtype3 | 29 | 3 | 159 |
| subtype4 | 40 | 2 | 40 |
| subtype5 | 18 | 1 | 47 |
Figure S83. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'

P value = 0.459 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.57
Table S90. Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 394 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 76 |
| subtype2 | 0 | 64 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 136 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 58 |
| subtype5 | 1 | 60 |
Figure S84. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #6: 'MIRSEQ CHIERARCHICAL' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'

Table S91. Description of clustering approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 133 | 208 | 170 |
P value = 0.00971 (logrank test), Q value = 0.022
Table S92. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 497 | 193 | 0.1 - 122.3 (12.7) |
| subtype1 | 131 | 63 | 0.1 - 79.1 (12.3) |
| subtype2 | 201 | 67 | 0.1 - 122.3 (12.8) |
| subtype3 | 165 | 63 | 0.1 - 83.2 (13.2) |
Figure S85. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
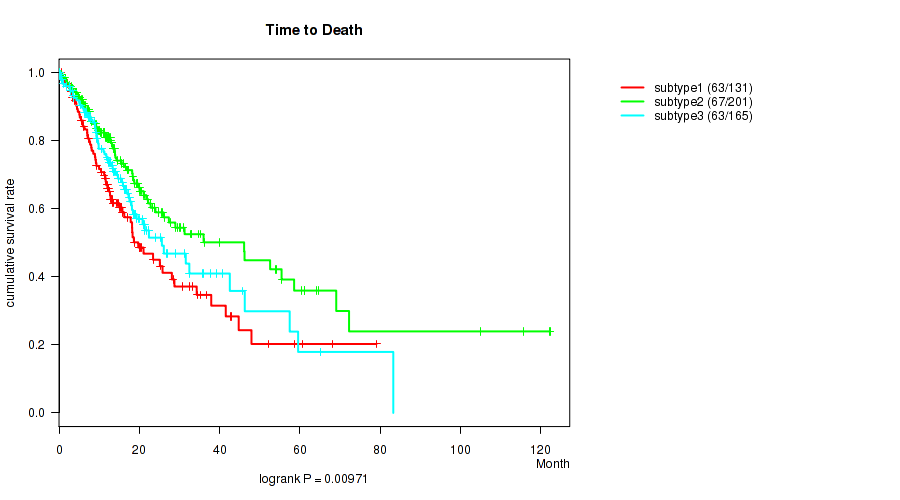
P value = 3.96e-07 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 1.1e-05
Table S93. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 505 | 64.4 (11.3) |
| subtype1 | 132 | 60.5 (11.1) |
| subtype2 | 203 | 67.2 (10.9) |
| subtype3 | 170 | 64.0 (11.1) |
Figure S86. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'

P value = 0.00151 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.004
Table S94. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE II | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 10 | 12 | 37 | 30 | 71 | 75 | 28 | 84 | 62 | 41 | 37 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 28 | 19 | 13 | 17 | 13 | 6 | 10 | 3 |
| subtype2 | 9 | 8 | 18 | 13 | 22 | 30 | 8 | 31 | 31 | 17 | 11 | 1 |
| subtype3 | 0 | 2 | 12 | 14 | 21 | 26 | 7 | 36 | 18 | 18 | 16 | 0 |
Figure S87. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
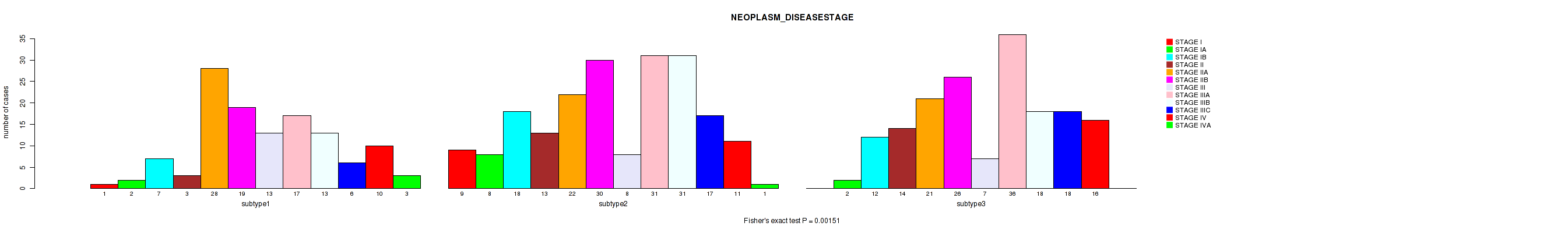
P value = 0.00012 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.00043
Table S95. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| nPatients | T0+T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 44 | 105 | 248 | 99 |
| subtype1 | 9 | 30 | 71 | 13 |
| subtype2 | 29 | 41 | 97 | 36 |
| subtype3 | 6 | 34 | 80 | 50 |
Figure S88. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
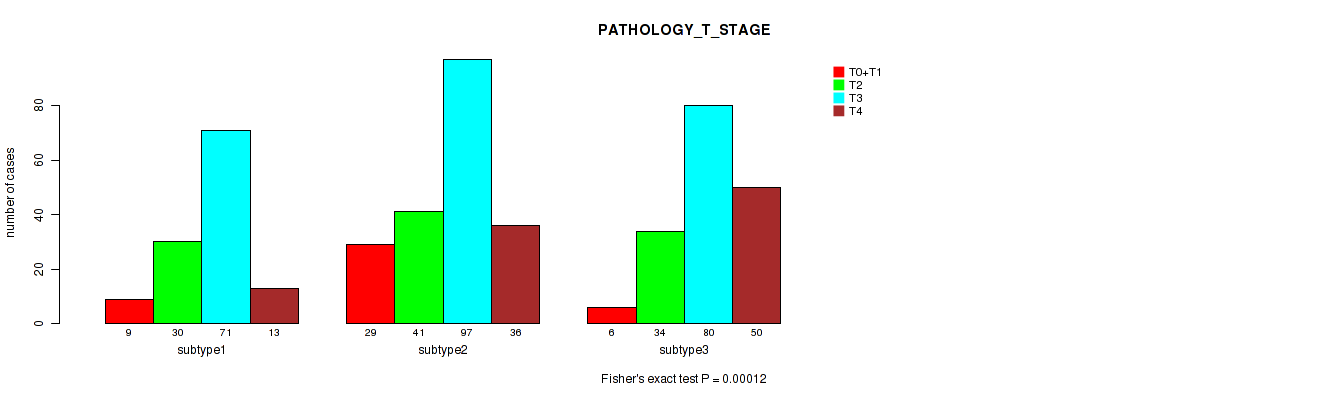
P value = 0.02 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.042
Table S96. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| nPatients | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 172 | 153 | 84 | 80 |
| subtype1 | 45 | 48 | 18 | 11 |
| subtype2 | 72 | 53 | 43 | 33 |
| subtype3 | 55 | 52 | 23 | 36 |
Figure S89. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'

P value = 0.285 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.39
Table S97. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 432 | 31 |
| subtype1 | 105 | 11 |
| subtype2 | 179 | 9 |
| subtype3 | 148 | 11 |
Figure S90. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
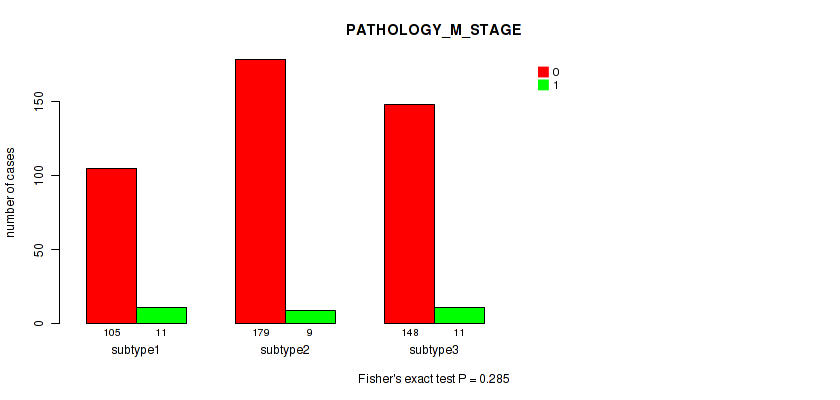
P value = 0.00809 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.018
Table S98. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 142 | 369 |
| subtype1 | 24 | 109 |
| subtype2 | 61 | 147 |
| subtype3 | 57 | 113 |
Figure S91. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'

P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S99. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA DIFFUSE TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA TUBULAR TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA MUCINOUS TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA PAPILLARY TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA SIGNET RING TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 57 | 115 | 68 | 69 | 19 | 6 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 4 | 13 | 11 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 17 | 50 | 39 | 44 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| subtype3 | 36 | 52 | 18 | 13 | 13 | 1 | 5 |
Figure S92. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
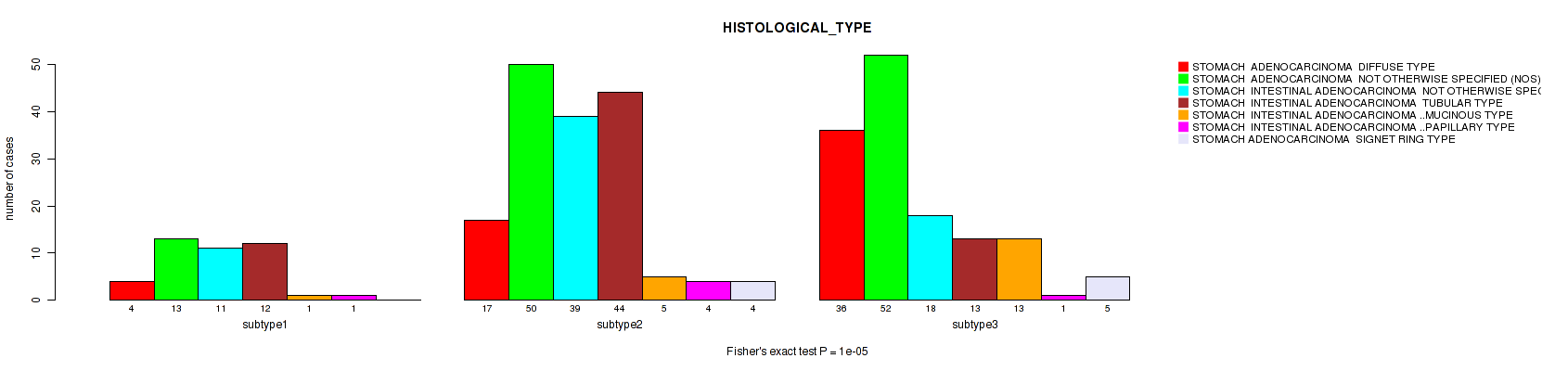
P value = 0.855 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.9
Table S100. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 5 | 506 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 132 |
| subtype2 | 3 | 205 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 169 |
Figure S93. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'

P value = 0.0412 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.076
Table S101. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 88 | 35.8 (22.0) |
| subtype1 | 53 | 30.9 (19.5) |
| subtype2 | 19 | 40.0 (19.4) |
| subtype3 | 16 | 47.2 (28.1) |
Figure S94. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'

P value = 0.701 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.77
Table S102. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 294 | 14 | 10 |
| subtype1 | 34 | 2 | 2 |
| subtype2 | 144 | 5 | 4 |
| subtype3 | 116 | 7 | 4 |
Figure S95. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'

P value = 0.445 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.56
Table S103. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 309 | 5.5 (7.9) |
| subtype1 | 38 | 5.2 (6.7) |
| subtype2 | 149 | 5.5 (8.8) |
| subtype3 | 122 | 5.6 (7.2) |
Figure S96. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'

P value = 0.00142 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.0039
Table S104. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 107 | 12 | 335 |
| subtype1 | 42 | 3 | 69 |
| subtype2 | 31 | 7 | 138 |
| subtype3 | 34 | 2 | 128 |
Figure S97. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
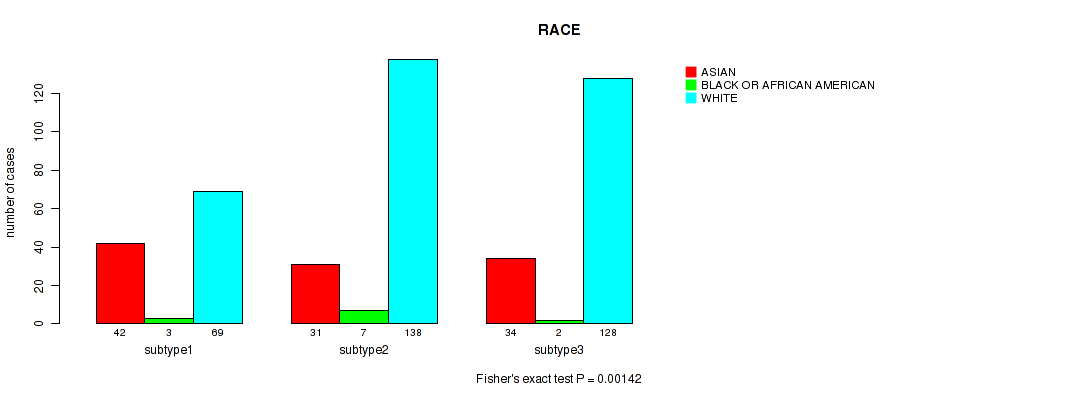
P value = 0.795 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.85
Table S105. Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 324 |
| subtype1 | 2 | 74 |
| subtype2 | 3 | 119 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 131 |
Figure S98. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #7: 'MIRseq Mature CNMF subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
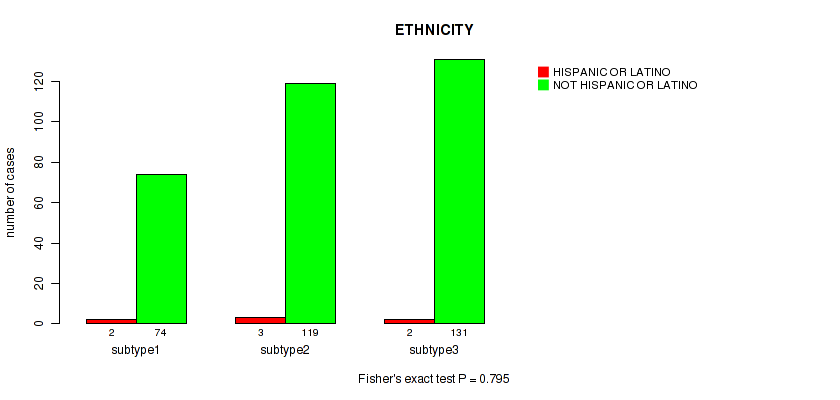
Table S106. Description of clustering approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes'
| Cluster Labels | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 47 | 120 | 162 | 100 | 82 |
P value = 0.0462 (logrank test), Q value = 0.083
Table S107. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
| nPatients | nDeath | Duration Range (Median), Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 497 | 193 | 0.1 - 122.3 (12.7) |
| subtype1 | 45 | 22 | 0.1 - 60.6 (9.3) |
| subtype2 | 117 | 53 | 0.4 - 122.1 (14.3) |
| subtype3 | 158 | 48 | 0.1 - 122.3 (13.3) |
| subtype4 | 97 | 42 | 0.1 - 83.2 (12.6) |
| subtype5 | 80 | 28 | 0.1 - 68.0 (12.5) |
Figure S99. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #1: 'Time to Death'
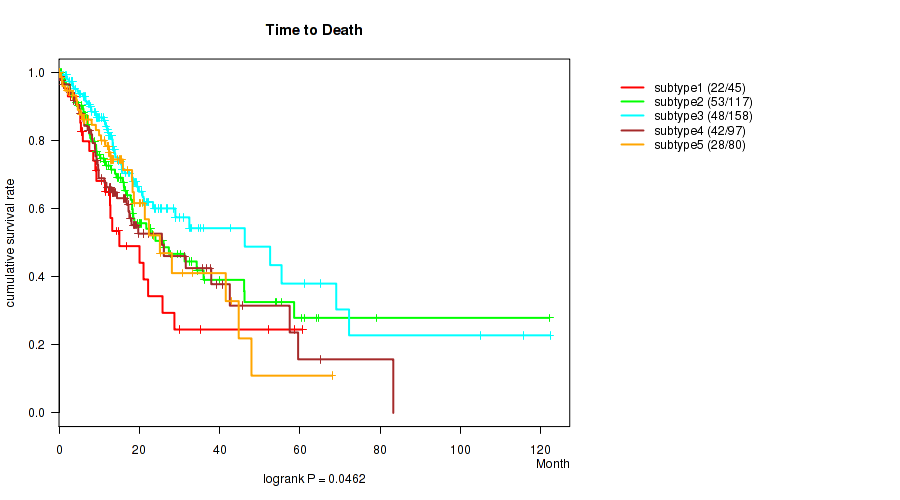
P value = 2.08e-06 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 3.9e-05
Table S108. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 505 | 64.4 (11.3) |
| subtype1 | 46 | 65.2 (10.8) |
| subtype2 | 118 | 65.9 (10.7) |
| subtype3 | 159 | 66.5 (11.1) |
| subtype4 | 100 | 63.5 (11.6) |
| subtype5 | 82 | 58.7 (10.9) |
Figure S100. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #2: 'YEARS_TO_BIRTH'
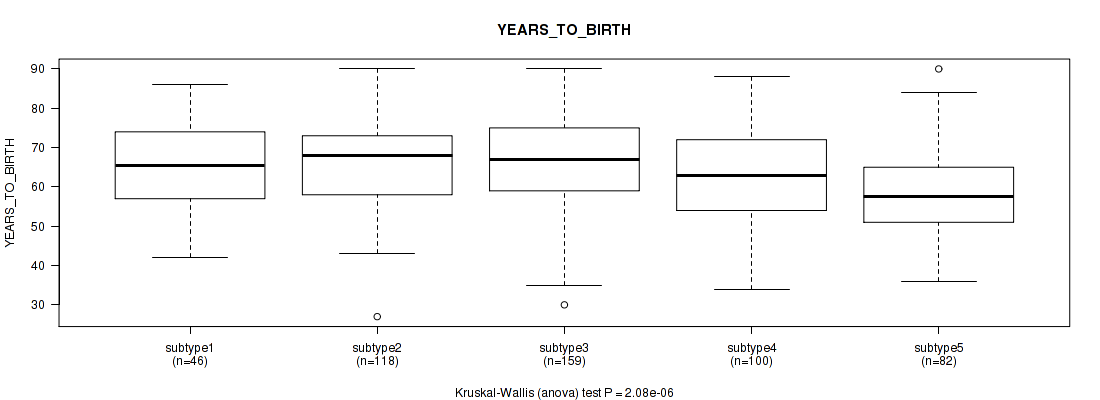
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S109. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
| nPatients | STAGE I | STAGE IA | STAGE IB | STAGE II | STAGE IIA | STAGE IIB | STAGE III | STAGE IIIA | STAGE IIIB | STAGE IIIC | STAGE IV | STAGE IVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 10 | 12 | 37 | 30 | 71 | 75 | 28 | 84 | 62 | 41 | 37 | 4 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 12 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 9 | 5 | 13 | 4 | 10 | 18 | 8 | 11 | 14 | 9 | 5 | 3 |
| subtype3 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 15 | 16 | 27 | 4 | 33 | 22 | 14 | 15 | 0 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 8 | 11 | 13 | 2 | 19 | 15 | 13 | 12 | 0 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 32 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
Figure S101. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #3: 'NEOPLASM_DISEASESTAGE'
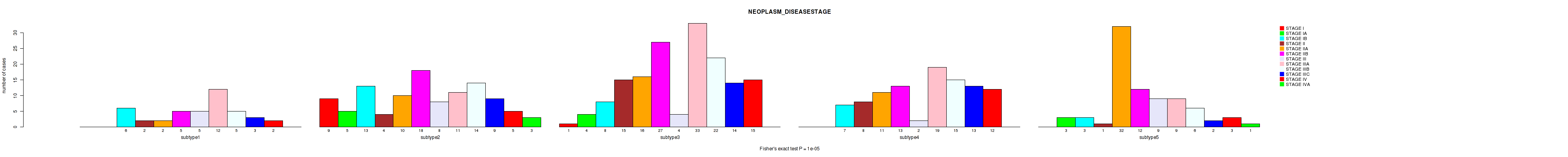
P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S110. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
| nPatients | T0+T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 44 | 105 | 248 | 99 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 10 | 22 | 9 |
| subtype2 | 24 | 20 | 46 | 20 |
| subtype3 | 9 | 33 | 85 | 34 |
| subtype4 | 1 | 18 | 50 | 31 |
| subtype5 | 7 | 24 | 45 | 5 |
Figure S102. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #4: 'PATHOLOGY_T_STAGE'
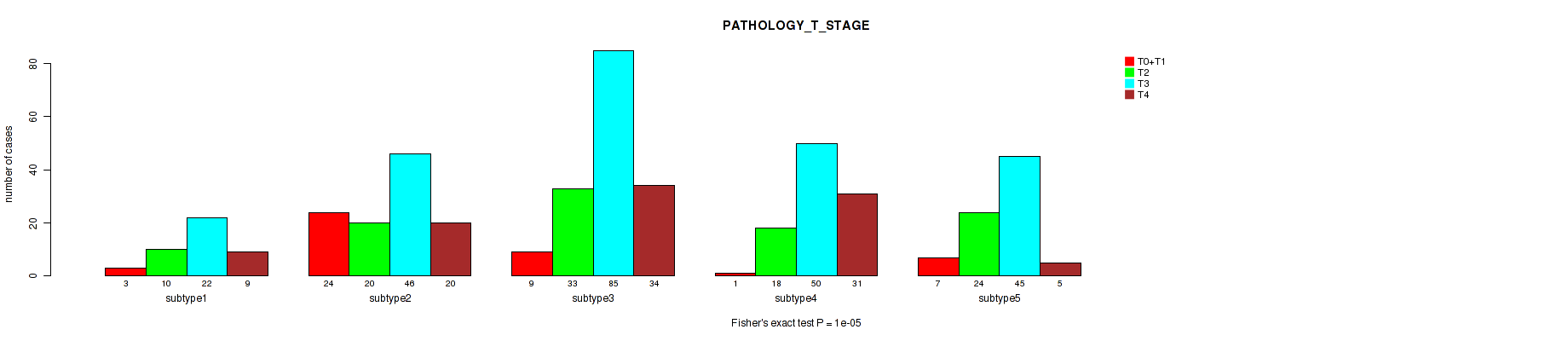
P value = 5e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 2e-04
Table S111. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'
| nPatients | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 172 | 153 | 84 | 80 |
| subtype1 | 10 | 18 | 8 | 8 |
| subtype2 | 43 | 35 | 19 | 12 |
| subtype3 | 47 | 46 | 33 | 32 |
| subtype4 | 26 | 29 | 18 | 25 |
| subtype5 | 46 | 25 | 6 | 3 |
Figure S103. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #5: 'PATHOLOGY_N_STAGE'

P value = 0.588 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.66
Table S112. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'
| nPatients | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 432 | 31 |
| subtype1 | 40 | 1 |
| subtype2 | 90 | 8 |
| subtype3 | 144 | 9 |
| subtype4 | 86 | 9 |
| subtype5 | 72 | 4 |
Figure S104. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #6: 'PATHOLOGY_M_STAGE'

P value = 0.00503 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.012
Table S113. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
| nPatients | FEMALE | MALE |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 142 | 369 |
| subtype1 | 12 | 35 |
| subtype2 | 34 | 86 |
| subtype3 | 44 | 118 |
| subtype4 | 40 | 60 |
| subtype5 | 12 | 70 |
Figure S105. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #7: 'GENDER'
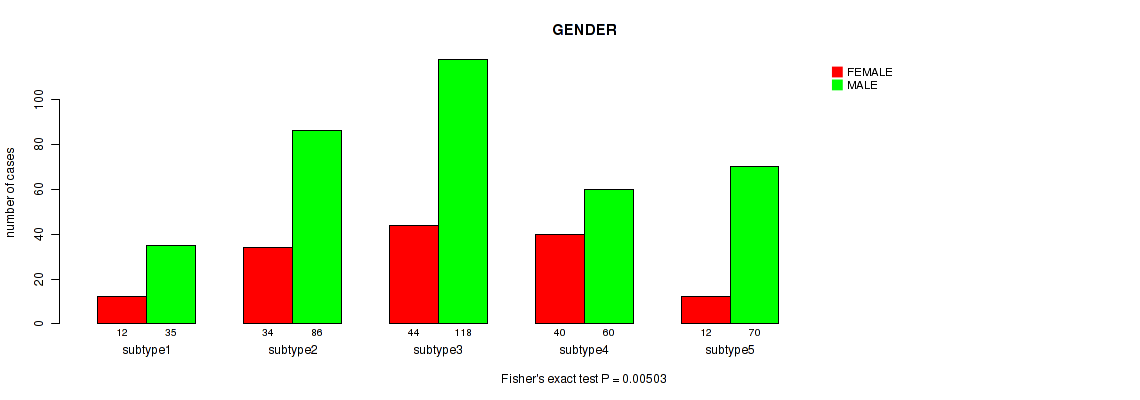
P value = 2e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 8.6e-05
Table S114. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
| nPatients | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA DIFFUSE TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA NOT OTHERWISE SPECIFIED (NOS) | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA TUBULAR TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA MUCINOUS TYPE | STOMACH INTESTINAL ADENOCARCINOMA PAPILLARY TYPE | STOMACH ADENOCARCINOMA SIGNET RING TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 57 | 115 | 68 | 69 | 19 | 6 | 9 |
| subtype1 | 0 | 16 | 7 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 7 | 14 | 19 | 27 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 23 | 53 | 27 | 23 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
| subtype4 | 27 | 30 | 15 | 9 | 11 | 1 | 2 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Figure S106. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #8: 'HISTOLOGICAL_TYPE'
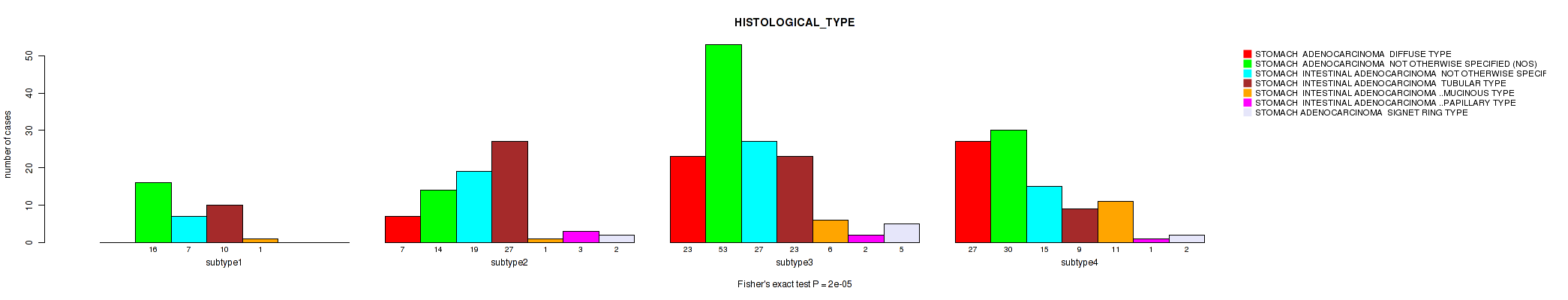
P value = 0.448 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.56
Table S115. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
| nPatients | NO | YES |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 5 | 506 |
| subtype1 | 1 | 46 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 119 |
| subtype3 | 3 | 159 |
| subtype4 | 0 | 100 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 82 |
Figure S107. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #9: 'RADIATIONS_RADIATION_REGIMENINDICATION'
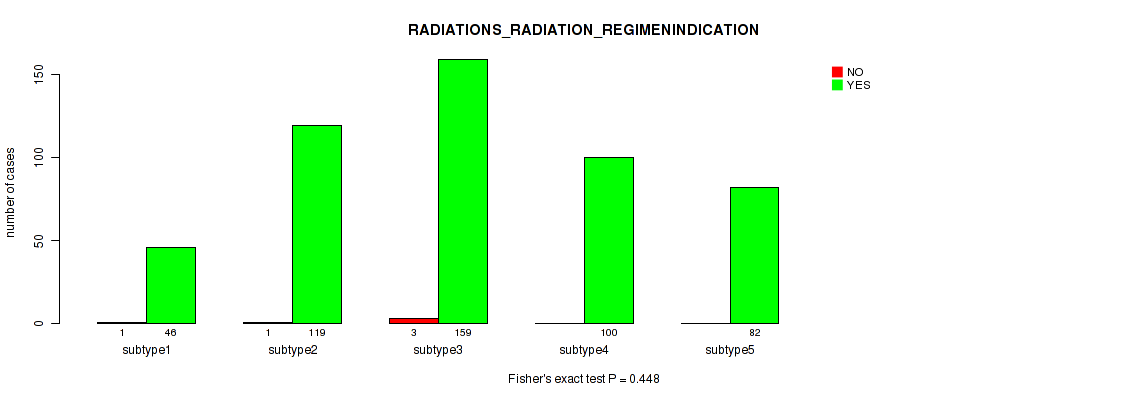
P value = 0.246 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.35
Table S116. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 88 | 35.8 (22.0) |
| subtype1 | 4 | 40.0 (22.7) |
| subtype2 | 21 | 36.1 (20.3) |
| subtype3 | 15 | 47.5 (29.0) |
| subtype4 | 1 | 40.0 (NA) |
| subtype5 | 47 | 31.5 (19.5) |
Figure S108. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #10: 'NUMBER_PACK_YEARS_SMOKED'

P value = 0.341 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.45
Table S117. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
| nPatients | R0 | R1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 294 | 14 | 10 |
| subtype1 | 29 | 2 | 0 |
| subtype2 | 66 | 0 | 2 |
| subtype3 | 118 | 6 | 5 |
| subtype4 | 79 | 6 | 3 |
| subtype5 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
Figure S109. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #11: 'COMPLETENESS_OF_RESECTION'
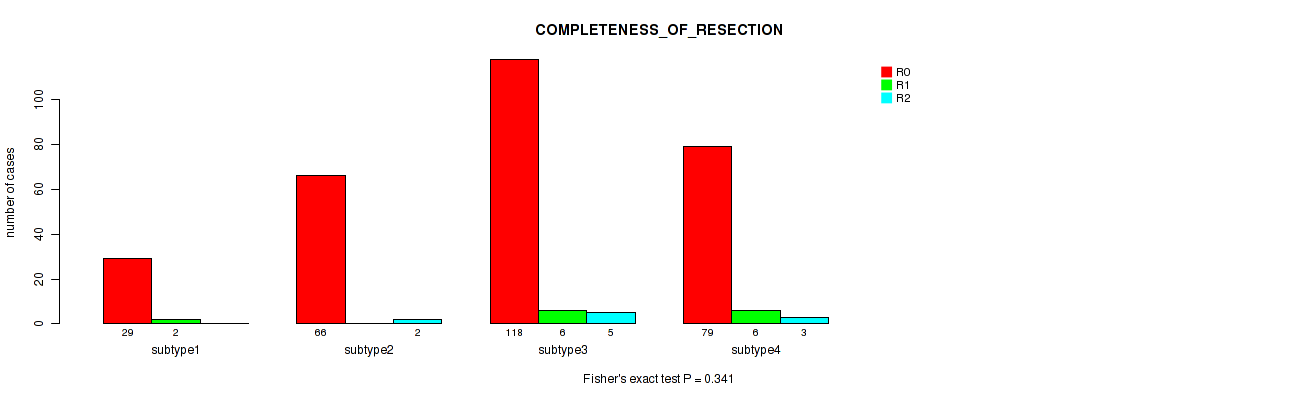
P value = 0.0274 (Kruskal-Wallis (anova)), Q value = 0.055
Table S118. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'
| nPatients | Mean (Std.Dev) | |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 309 | 5.5 (7.9) |
| subtype1 | 30 | 5.2 (5.8) |
| subtype2 | 70 | 4.4 (8.8) |
| subtype3 | 124 | 6.2 (8.3) |
| subtype4 | 83 | 5.6 (7.4) |
| subtype5 | 2 | 0.5 (0.7) |
Figure S110. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #12: 'NUMBER_OF_LYMPH_NODES'

P value = 1e-05 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 5.3e-05
Table S119. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'
| nPatients | ASIAN | BLACK OR AFRICAN AMERICAN | WHITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 107 | 12 | 335 |
| subtype1 | 7 | 2 | 28 |
| subtype2 | 14 | 5 | 81 |
| subtype3 | 21 | 4 | 115 |
| subtype4 | 26 | 0 | 72 |
| subtype5 | 39 | 1 | 39 |
Figure S111. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #13: 'RACE'

P value = 0.0342 (Fisher's exact test), Q value = 0.066
Table S120. Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'
| nPatients | HISPANIC OR LATINO | NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | 7 | 324 |
| subtype1 | 3 | 22 |
| subtype2 | 1 | 54 |
| subtype3 | 2 | 104 |
| subtype4 | 1 | 88 |
| subtype5 | 0 | 56 |
Figure S112. Get High-res Image Clustering Approach #8: 'MIRseq Mature cHierClus subtypes' versus Clinical Feature #14: 'ETHNICITY'

-
Cluster data file = /xchip/cga/gdac-prod/tcga-gdac/jobResults/GDAC_mergedClustering/STES-TP/15125163/STES-TP.mergedcluster.txt
-
Clinical data file = /xchip/cga/gdac-prod/tcga-gdac/jobResults/Append_Data/STES-TP/15090071/STES-TP.merged_data.txt
-
Number of patients = 612
-
Number of clustering approaches = 8
-
Number of selected clinical features = 14
-
Exclude small clusters that include fewer than K patients, K = 3
consensus non-negative matrix factorization clustering approach (Brunet et al. 2004)
Resampling-based clustering method (Monti et al. 2003)
For survival clinical features, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of tumors with and without gene mutations were plotted and the statistical significance P values were estimated by logrank test (Bland and Altman 2004) using the 'survdiff' function in R
For binary clinical features, two-tailed Fisher's exact tests (Fisher 1922) were used to estimate the P values using the 'fisher.test' function in R
For multiple hypothesis correction, Q value is the False Discovery Rate (FDR) analogue of the P value (Benjamini and Hochberg 1995), defined as the minimum FDR at which the test may be called significant. We used the 'Benjamini and Hochberg' method of 'p.adjust' function in R to convert P values into Q values.
In addition to the links below, the full results of the analysis summarized in this report can also be downloaded programmatically using firehose_get, or interactively from either the Broad GDAC website or TCGA Data Coordination Center Portal.